When it comes to managing content effectively, scalability and flexibility are key. This is precisely why headless CMSes have become so popular.
Over the years, digital marketing platforms have undergone significant transformations, especially in their content frameworks. With headless technology booming in the last decade, it’s now vital for businesses to develop content that’s accessible and adaptive across various digital platforms.

Digital marketing’s rapid evolution has left traditional content management systems behind, paving the way for headless CMS. This advancement marks a new chapter in digital content management.
But if you are new to the digital marketing scene, you might ask — how does a headless CMS work? We’re here to answer the “What is headless content management” systems and how they are better than traditional CMSes. So, let’s dig in!
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
Headless CMS Explained
A headless content management system (CMS) is a back-end content management system where the content “body” or content repository is decoupled or separated from the “head” or presentation layer. You can distribute content in a headless CMS to any digital platform via devices like smartphones, tablets, AI-enabled voice assistant systems, virtual reality headsets, and more.
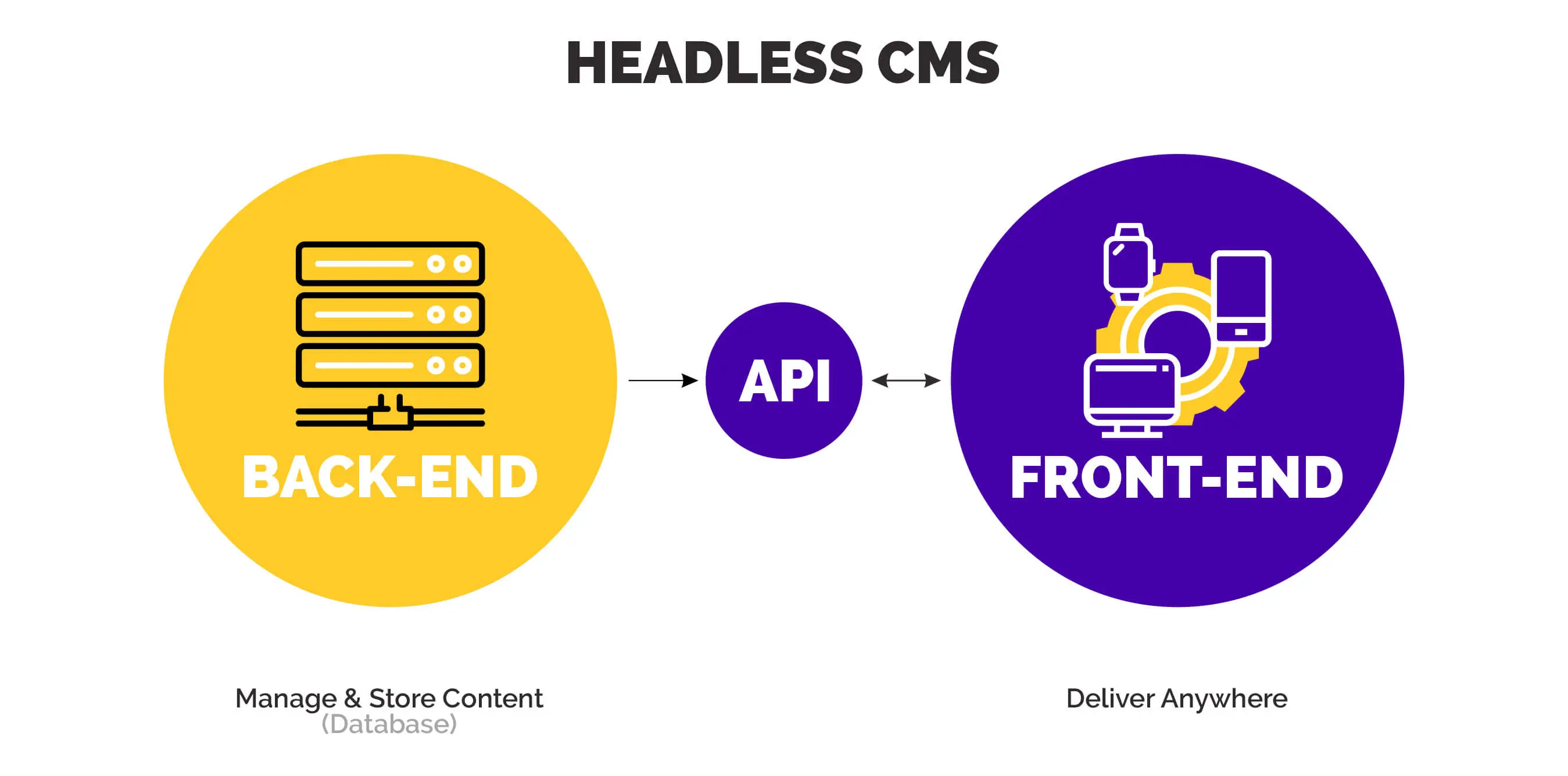
Developers use Application Programming Interfaces (API), such as the GraphQL API or the RESTful API, to deliver content to various digital devices. Thus, with a headless CMS, managing content is much easier as it’s not restricted to a website or a web page. Instead, it can be distributed anywhere and everywhere, such as on mobile sites or your email.
Removing the presentation layer in traditional CMS allows headless CMS to provide smoother access to the same content across various online platforms. By adopting a headless structure, it’s possible to craft omnichannel content for diverse devices and platforms.
The primary focus of a headless CMS is storing and delivering well-structured content, disregarding the specifics of the frontend presentation layer. This approach empowers editors to collaborate on diverse content projects. Digital content management’s future is to create engaging and relevant content that can reach millions of audiences through multiple platform.
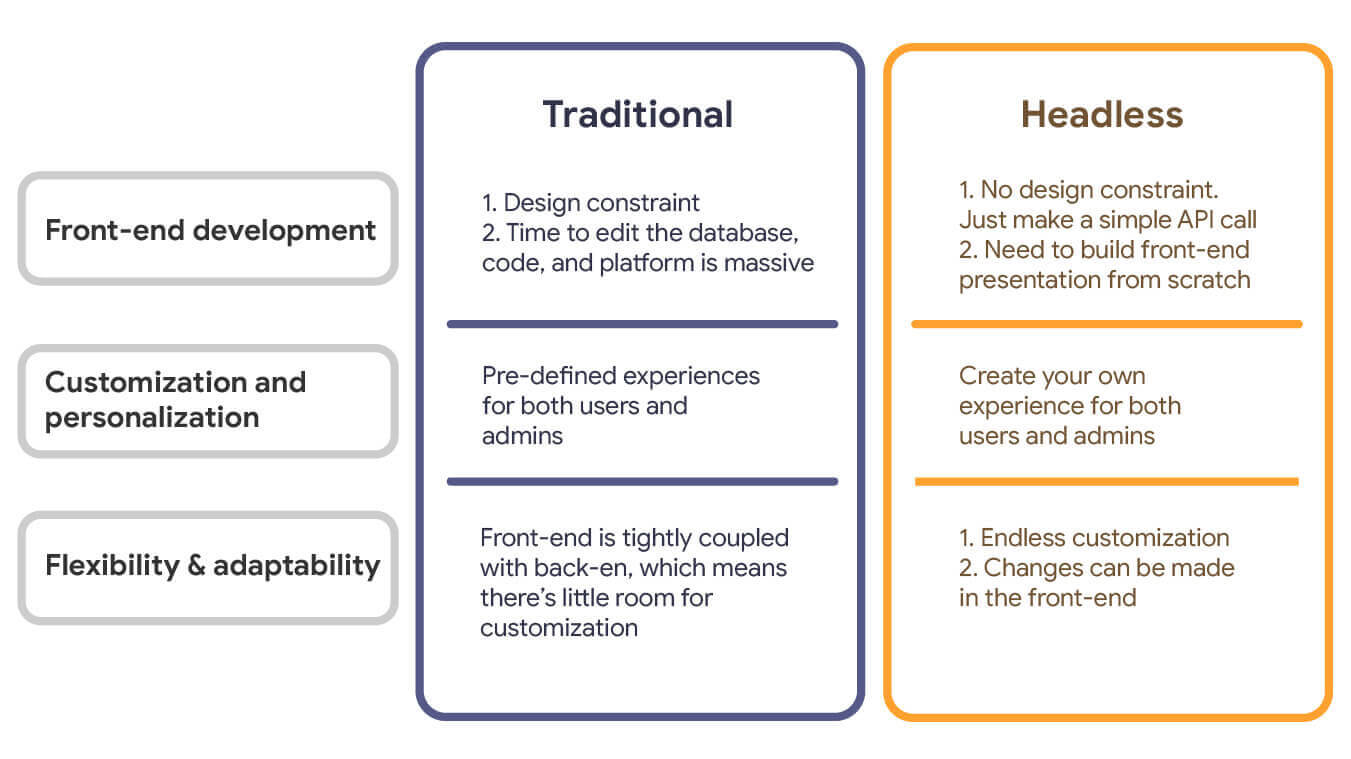
Traditional CMS Vs. Headless CMS
In traditional content management systems, the presentation layer is tightly coupled with the system, distinguishing it from headless CMS. Traditional CMSes rely on the integration of back-end and frontend tools, which are inseparable. Everything is put in one bucket in a conventional or monolithic CMS, so templates and website design tools are inseparable here.
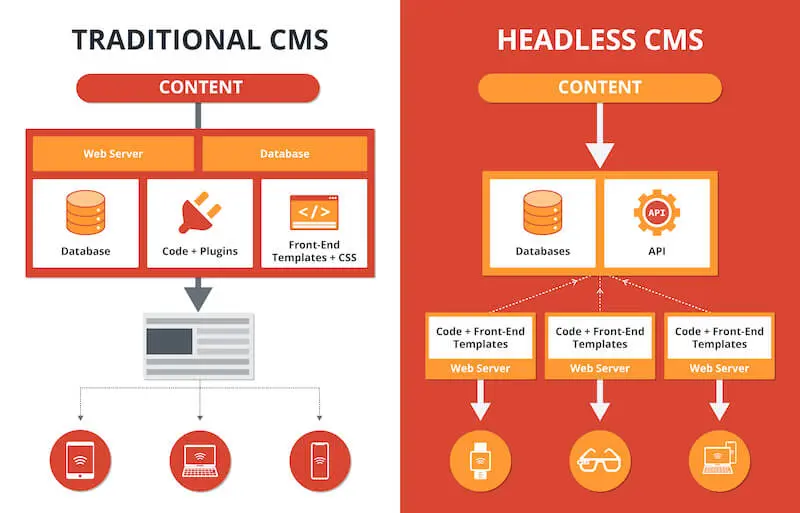
Since content, images, and HTML codes are piled up in a traditional CMS, reusing the content for a new project becomes almost impossible. When you think about monolithic CMSes like WordPress, content delivery applications (CDA) and content management applications (CMA) are coupled, limiting digital content’s availability.
Moreover, traditional CMS relies on webpage-focused frameworks, tailoring content to a single page. Typically, such content is accessible only through specific browsers, making distribution to shared devices challenging.
But the API-first approach of headless CMSes allows easy online content distribution through different channels. You can access the content embedded in a headless CMS using a smartphone or any AI-enabled voice system. Hence, managing content across several digital platforms becomes much easier.
The headless CMS architecture differs distinctly from the content structure because it doesn’t have a presentation layer. Because the template and content are separate in a headless CMS, it is easier for content editors to edit or reuse the content however they see fit.
To sum it up, a headless CMS works for multiple digital platforms, unlike the traditional CMS architecture. Thanks to the decoupled content structures of the headless approach, content creation and editing have become much more effortless.
Content Infrastructure Of A Headless CMS
Content infrastructure is a headless CMS that doesn’t follow the traditional approach of creating and organising content hubs around specific pages. Instead, it follows a content model framework for managing online content types and defining how they relate.
Each organisation custom builds its content models in this headless CMS, so the content creators don’t get stuck within the pre-programmed models of a monolithic CMS. This custom-built content model can break down any content into individual elements, like a blog post headline or similar features.
Content infrastructure enables content creators to establish relationships between various elements and create a flexible model for distributing website content across multiple channels.
What Is A Decoupled CMS?
In traditional CMSes, the front end and back end are tightly interlinked and inseparable. Creating, managing, publishing, and storing content within a single interface is possible. A monolithic CMS offers a seamless setup for non-technical users to publish straightforward content, such as a blog.
But with the rapid digitisation of content, web developers have been working to create sophisticated and personalised content that can be delivered to a broader audience using various digital devices. And that’s how decoupled CMS came into existence to offer an improved digital experience while creating and managing content.
Decoupled CMSes separate back-end and front-end tasks to allow developers to design and code front-end tasks however they want without being restricted by the back-end technologies. But in a decoupled CMS, developers use APIs to seamlessly connect the back-end task, like content management and storage, to any front-end content delivery application.
What Is An API-First CMS?
Even though decoupled CMSes are mostly successful in separating frontend and back-end tasks, they can still come with some front-end tools, like module integrations and page templates. To overcome the limitations of a decoupled CMS, API-first CMSes were developed by web designers.
API-first CMSes are functionally similar to headless CMSes because neither has any default frontend tools. Developers have the freedom to create multiple delivery layers using their preferred coding language and distribute stored content to various channels.
These CMSes are excellent if a team of skilled web developers have hands-on experience creating, managing, and storing some content. The API-First CMS effortlessly manages digital content and responds to the API call from a frontend delivery layer designed separately by the developers.
On the other hand, even though decoupled CMSes effectively separate frontend and back-end tasks, they might still require some publishing support for effective content management.
How Can You Convert A Monolithic CMS Into A Headless CMS?
Before converting a traditional CMS to a headless CMS, you must learn everything about traditional CMS architecture. So, in this section, we’ve discussed the critical characteristics of a monolithic CMS.
A monolithic CMS comes with the following set of features:
- A database to read and write the content
- An admin interface to allow content editors to manage the content
- An integration for content reading or writing
- A frontend tool combining data from the main database using HTML
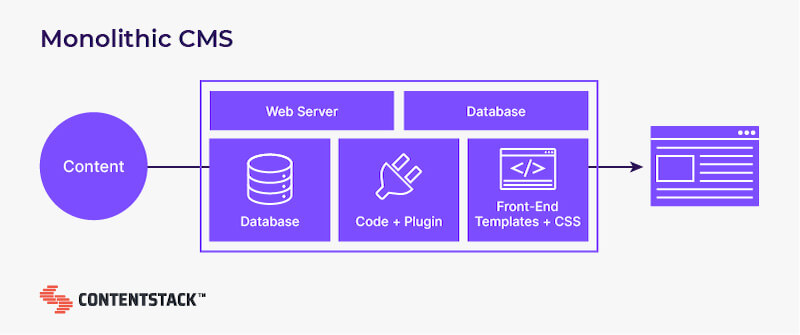
To convert this entire monolithic structure into a headless content management system, remove the frontend templating feature from this stack because that’s the head of a monolithic CMS. Once the template is removed, you can connect the back-end and front-end layers using a RESTful API or a GraphQL API that is easily accessible to other systems.
The APIs will allow users to access published content from any digital platform. Thus, you can successfully convert a monolithic CMS to a headless CMS by modifying its architecture.
Benefits Of Using A Headless CMS
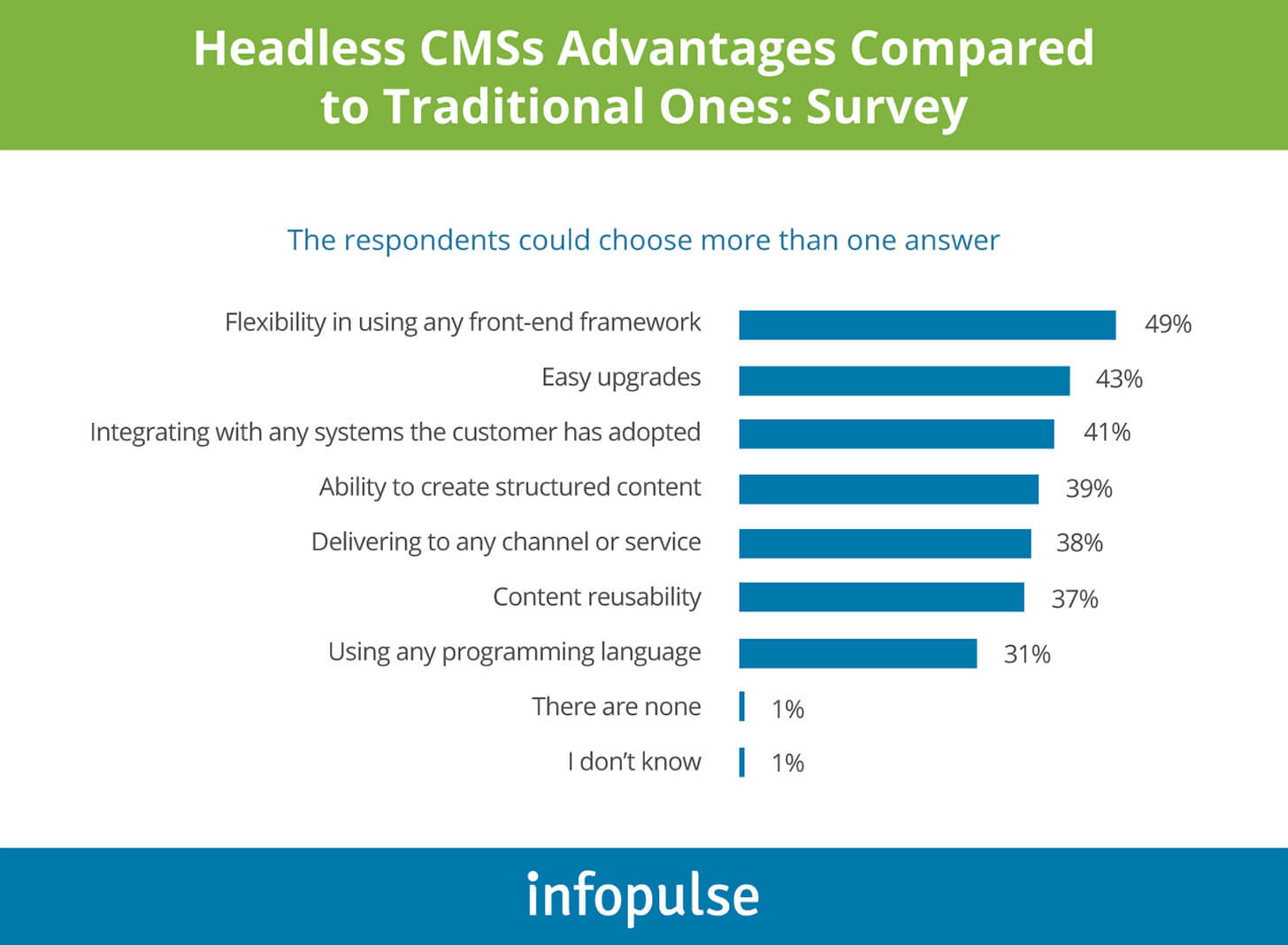
1. Content Delivery Via Multiple Channels
Headless CMS empowers organisations to engage with users across various digital channels, including mobile apps, websites, email marketing, AI-activated voice recognition systems, smartwatches, and more. In a headless CMS, content is stored in a cloud-first content hub, and its distribution is relatively simple because you won’t need to install or manage anything separately.
2. Fast Content Deployment
Headless CMS enables web developers to rapidly create and distribute content across various digital platforms, including static site generators, by utilising an API-first approach. You can apply the Content-as-a-Service (CaaS) architecture to scale and deploy online content to several new channels within minutes.
3. Modular Content
Since the digital content embedded in a headless CMS is not dependent on any front-end tools, it becomes modular. You can easily manage, store, and deploy it across any suitable touchpoint without facing the risk of being reformatted or duplicated.
4. Limitless Integrations
With a headless CMS, content can be showcased on virtually any connected device or software. This means online content isn’t restricted from systems like localisation platforms, personalisation tools, CRM, or AI and Machine Learning.
Why Are Companies Choosing Headless CMS?
With the boom of digital platforms, companies often have to face and handle various CMS instances. Consequently, they must duplicate multiple contents from websites to mobile apps and digital displays. And they are more inclined to choose a headless CMS over a monolithic CMS in recent times, so let’s find out why.
1. Unifies Data
You can forget unnecessary copy and paste with content infrastructure and unify all online content within a single, centralised cloud hub. It makes content editing more manageable, allowing you to change the image or content body in one platform, and the change will automatically appear anywhere the content is available.
Unification enhances compliance and brand consistency, enabling content editors to effortlessly update their content across multiple channels and making brand campaigns a piece of cake.
2. Enables Collaboration
Another advantage of using content infrastructure is allowing simultaneous collaboration. It helps replace the tedious waterfall content development approach and promotes an agile, flexible framework where multiple teams can work simultaneously. This headless CMS offers a competitive advantage to companies that work on rapidly developing new software, microsites, and landing pages.
3. Makes Content Resources Accessible
Reusability of content is an added advantage of content infrastructure. You can easily optimise your resources to create and publish high-quality, engaging online content. When your content is accessible to users via multiple digital platforms, it becomes easier to utilise different features, such as localisation and personalisation, to their maximum potential.
Who Uses Headless CMS?
If we go beyond theory, several industries and organisations have embraced headless CMSes as an integral weapon. To elevate customer digital experiences across diverse platforms and devices, businesses must select the appropriate headless CMS that aligns with their specific needs.
The headless CMS enables companies to connect and interact with their customers at a larger scale and adapt quickly to emerging market opportunities. It helps to streamline all content operations to maintain consistency and flexibility effectively.
Below, we’ve highlighted some industries that use a headless CMS to manage content operations.
1. Sports Teams
Sports teams can build an omnichannel digital platform using a headless CMS to enhance fan engagement. Sports teams can create high-quality personalised content with a headless CMS and help dedicated fans to feel more connected to their idols.
2. Airline Companies
Airline companies have to deal with some of the most complicated content requirements compared to any industry. Their teams must manage critical, real-time communications, international content translation, and localisation.
They also must create a multichannel presence that includes hundreds or even thousands of touchpoints for individual customers. A headless CMS can help airline companies maintain clear, simplified, consistent, accurate and up-to-date communication.
Plus, it’ll enable airline companies to distribute their content across various digital platforms, such as mobile apps, email, official company websites, physical displays, and third-party search sites.
3. Financial Services
Customers depend on real-time information and content for making crucial financial decisions in the financial service industry. They also want to access personalised content that can help them easily navigate through complex financial processes and enable them to make smarter financial decisions.
Financial firms must have the flexibility to nurture innovation while maintaining their reliable foundation to manage content. Hence, a headless CMS can significantly help financial institutions manage the effective personalisation of readily available content to every customer.
4. Online Retailers
The customer is always right in online retail; customer experience triumphs over anything else. When it comes to online shopping, customers quickly criticise brands that cannot meet their needs or offer a poor buying experience.
Thanks to headless CMSes, online retailers can forge individual connections with their customers. They can weave marketing and product information into purchase histories, providing millions a unique, personalised shopping journey.
Possible Disadvantages Of Using A Headless CMS
Even though a headless CMS is quite effective in managing content, it cannot fix every drawback of content management. You might face two significant limitations when creating content using a headless CMS.
Firstly, while a headless CMS offers more flexibility, accessibility can be problematic for non-technical users. As web developers build the frontend presentation layer using JavaScript, non-technical users can’t use the “What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG)” features for writing or editing.
And when you separate the head from the content body in a CMS, you can’t share any real-time customer interaction data between back-end and front-end tools. It means running any content analysis or personalising online content becomes quite troublesome.
Over the years, content personalisation has become a fundamental requirement of content creation. With high-quality personalised content offered by industry leaders like Amazon, Spotify, and Netflix, users are beginning to understand the power of personalised content. Hence, the difficulty of creating personalised content is the greatest letdown of a headless CMS.
Converting To A Headless CMS
We end our informative guide on headless CMSes and how they differ from traditional CMSes in content architecture and operations. After going through our article, we hope you better understand different headless CMS solutions that can help brands create and manage to engage online content.
If you want a detailed understanding of how to design a headless CMS, it’s best to start with the primary content architecture of a traditional CMS. With a headless CMS, it can be possible to distribute your content at a larger scale across any digital platform. However, consider the drawbacks of the headless CMS before applying it to improve your brand’s market presence.
Get in touch with our sitecentre® team if you need assistance with your CMS, content creation, or website design.
On that note, we’ll sign off. Take care and see you next time!