Google has become synonymous with the internet. “Just Google it” has become a verb we use daily.
It is no longer just another search engine but a tool to make our everyday lives better and more accessible. Over the years, Google has expanded the utility of its tools, giving us more than just a means to explore the World Wide Web. Being the most popular and visited global web-based search engine, Google has become omnipresent, almost a living being that we all require in our daily lives.

From learning new recipes, leveraging the powerful domain name through Google Ads, taking up DIY skills or exploring the deep, dark corners of the web, Google has enriched our lives more than we can count. That being said, have you ever wondered about the history of Google search and how it all began?
Let us answer some of your most pertinent questions about Google and its beginnings.

Founding Fathers Of Google Search Engine History
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of the first Google search’s details, let us find out about the founding fathers of Google — Larry Page And Sergey Brin. Google has fast grown into the world’s largest internet search engine, all thanks to the brilliance of these fascinating gentlemen.
Both Page and Brin were PhD students at California’s Stanford University. During his years as a Computer Science graduate, Larry Page dedicated effort to an intriguing research project dealing with search algorithms. In 1996, this search algorithm was given the curious name of “BackRub”.

While the invention of search engines is not a new one, Google, despite being a latecomer, would soon become one of the most popular platforms, marking when Google became popular for finding almost anything on the internet, even though it Repositioned several times in its infancy to optimise its internet search services before it finally settled in Mountain View, California.
The 2000 Google version expanded rapidly. By 2004, Google had made its first initial public offering and became one of the most prominent media companies globally.
The Journey Of Page And Brin
The Journey since the Google search engine started is a fascinating one. They met at University and began their journey together, keeping in touch even after graduating from their Computer Science programmes. Brin, known for his expertise in mathematics, and Page, with his ever-growing interest in learning more about the behaviour of linking on the internet, created an algorithm called PageRank.

This algorithm was named after Larry Page and explored the world of ranking search results. They ranked results based primarily on linking behaviour. These technologies fused, setting the stage for the Google search engine launch date on September 4, 1998, which was launched on Stanford’s private network in August 1996.
Their research paper, circulating around Silicon Valley, became immensely popular and was published under “ The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine.”
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
How Larry Page And Sergey Brin Conceived The Name Google
Page and Brin were known for their creative brainwaves, and so, inspired by the multitude of links between web pages, they renamed their company to Google. So, why was it called googol? You may be wondering. Googol refers to a mathematical term (the number 1 followed by 100 zeros.)
The wordplay on the mathematical term googol (the number 1 followed by 100 zeros) was superbly apt for the company as it aligned perfectly with the vision of Page and Brin. Their newfound company represented this vision, then renamed Google, which would rewrite history by expertly assimilating information from the world and making it readily accessible on the web.
Google Decides To Take Another Leap Forward
As Google expanded as a company, it started to catch the attention of investors and the academic community. Google was incorporated in September, the year that co-founder Andy Bechtolsheim made the massive decision to invest $100,000 in the company. Long story short, that was the inception of Google Inc.
Through the initial years of Google, the duo Brin and Page had almost no financial support to bring their company to a well-known standing worldwide. The Sun Microsystems CEO’s investment greatly assisted the subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., enabling them to move out of their dorms and into their first office.

It may be surprising (or not) to know that Google’s first office was a garage in the Palo Alto area, Menlo Park, California, owned by Susan Wojcicki. What may be more surprising is that Wojcicki became Google’s employee number 16 and is now the CEO of YouTube.
With not much else but some old, outdated computers, a ping pong table for entertainment, a plethora of Google services, and a bright, blue carpet as their only prized possession, Google began their business.
Hiring Eric Schmidt To “Supervise” Google
Although the company grew exponentially, Larry and Sergey concluded that the company needed “adult supervision” to reach its full potential. So, in 2001, Page and Brin hired Eric Schmidt, the former CEO of Novell, to guide Google. With his experience and immense talent, Schmidt soon joined the board of directors and became the company’s Chairman in March 2001.

In 2004, it introduced some of our now-favourite Google products like Gmail, Google Docs, and Google Drive. Schmidt stayed in his position as CEO of the company for ten years, after which he cheekily announced that the company “no longer required adult supervision.”
Of course, this wasn’t before Schmidt became vice president and the company’s executive chairman, leaving the CEO spot wide open for Page. Honestly, there could be no person more befitting for the role of the company’s CEO than Page.
The (Failed) Relationship Between Yahoo And Google
Before Google became synonymous with the web and became the world’s most popular search engine, Yahoo was the number 1 search engine on the internet. However, by 2000, Google’s popularity grew immensely, and soon, it became the default search engine for Yahoo.
In early 2002, Yahoo made an ambitious bid to buy Google for $3 billion. Google confidently declined, asserting its worth was a cool $5 billion at least.
In the same year, Google would develop and release something that would change how we distribute and publish digital media on the web. Google released Google News, a popular content aggregation service that became a viral platform for browsing digital content online.
Learning About Google’s Parent Company — Alphabet
Not many people are aware that Google’s parent company is called Alphabet. The holding company, Alphabet, permitted Google’s expansion of its domain from a regular search engine to becoming a technology conglomerate. Alphabet, the parent company of Google Inc., has its headquarters in Mountain View, California.
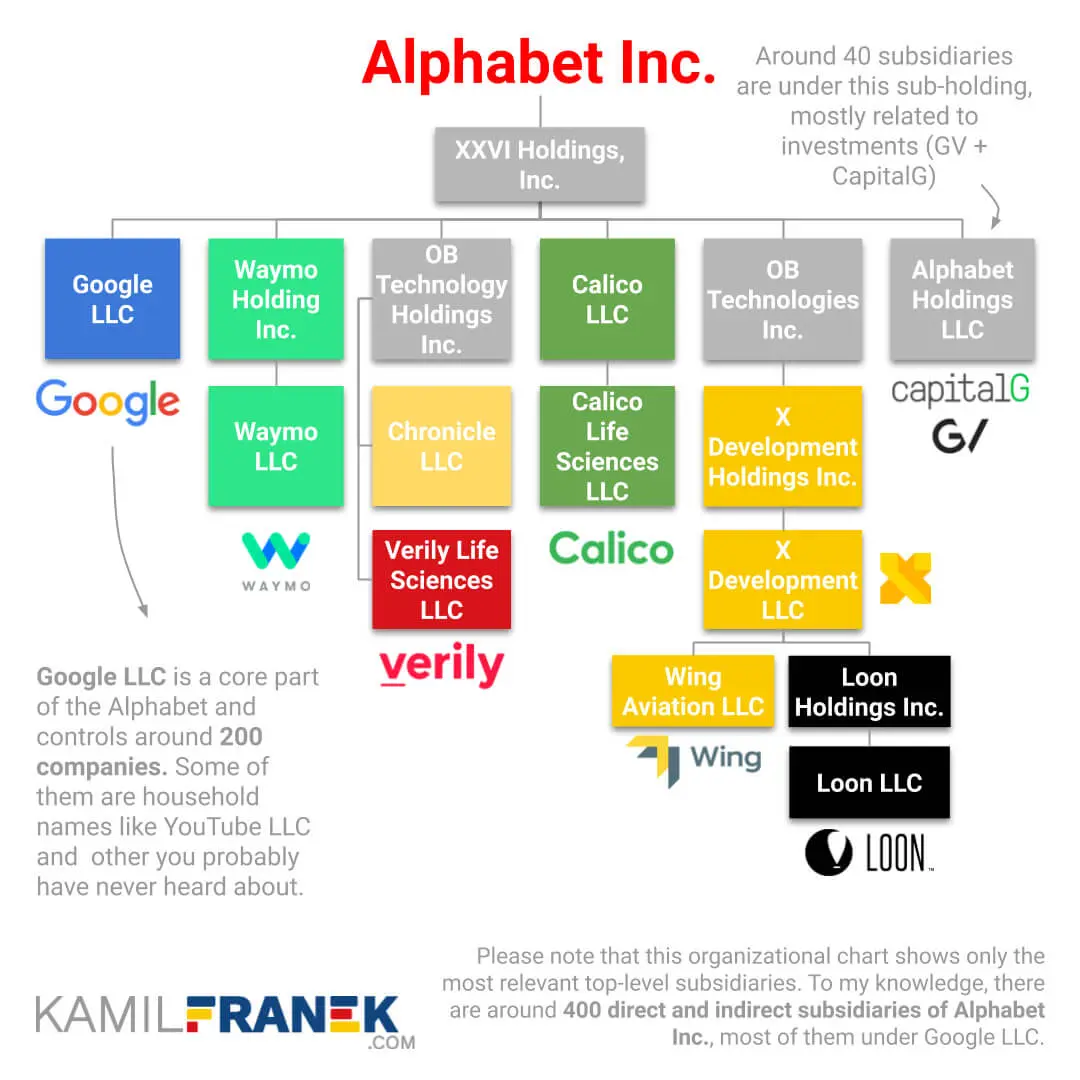
It is heavily involved in several other business types, such as advertising services, software, hardware, cloud computing, phone, desktop, and mobile applications. It also provides business to several industries, which we will mention below -
- Calico — developed to fight age-related diseases.
- Google Ventures — provides funding to new companies with big ideas (like Google itself had)
- Google X — working on groundbreaking ideas and breakthroughs
- Nest — provides users with fascinating, intelligent home products
- Google Capital — investing in long-term technology trends
- Google — Ads, Google Maps, YouTube, Android, Google Search, Apps
Page released a memo where Google announced that the new design structure of Alphabet would essentially help the company be “cleaner and more accountable.” Furthermore, Page states that this structure will allow each business that Google owns to have more independence and freedom to grow, which everyone was looking forward to.
With luck, its investors accepted Alphabet’s new design structure well. How do we know this? The company saw its shares shoot up to 6% after the announcement.
Google’s Move Into Googleplex
By July, synonymous with 2003 Google, the company had begun to grow exponentially. The company hired engineers, had its sales and ads team, and introduced Google’s first company dog — Yoshka. But we’ll talk more about the adorable mutt in just a bit.
As Google’s workforce and business expanded, it began looking for a larger workspace to accommodate its 1,000+ employees. It soon shifted and moved to its new office, known as Googleplex. Now, Googleplex is the company’s largest campus. Moreover, it continues to expand and acquire additional buildings and spaces.
What About Yoshka?
Google has everything — even a dog! Yoshka is Google’s first company dog and its Top Dog. When the company relocated to its new office space — Googleplex- Yoshka was happy to join them. Moreover, Yoshka even had an official job at Google, interviewing new applicants (but unfortunately, no dogs) and later moving on to part-time consultation.

Unfortunately, Yoshka suffered a leg injury, which meant no more work and running around the Googleplex office.
Since Yoshka’s introduction into the company’s office, there has been a massive change in the atmosphere and vibe inside. Google thought to make its offices dog-friendly, encouraging workers to bring their dogs to work more often.
After Yoshka died in 2011, the company built a café in honour of its Top Dog. Yoshka’s Café, which the café was called, even had a small museum dedicated to the beautiful Leonberger. This museum proudly displays Yoshka’s official Google badge, fluffy ball, collar, and favourite toy.
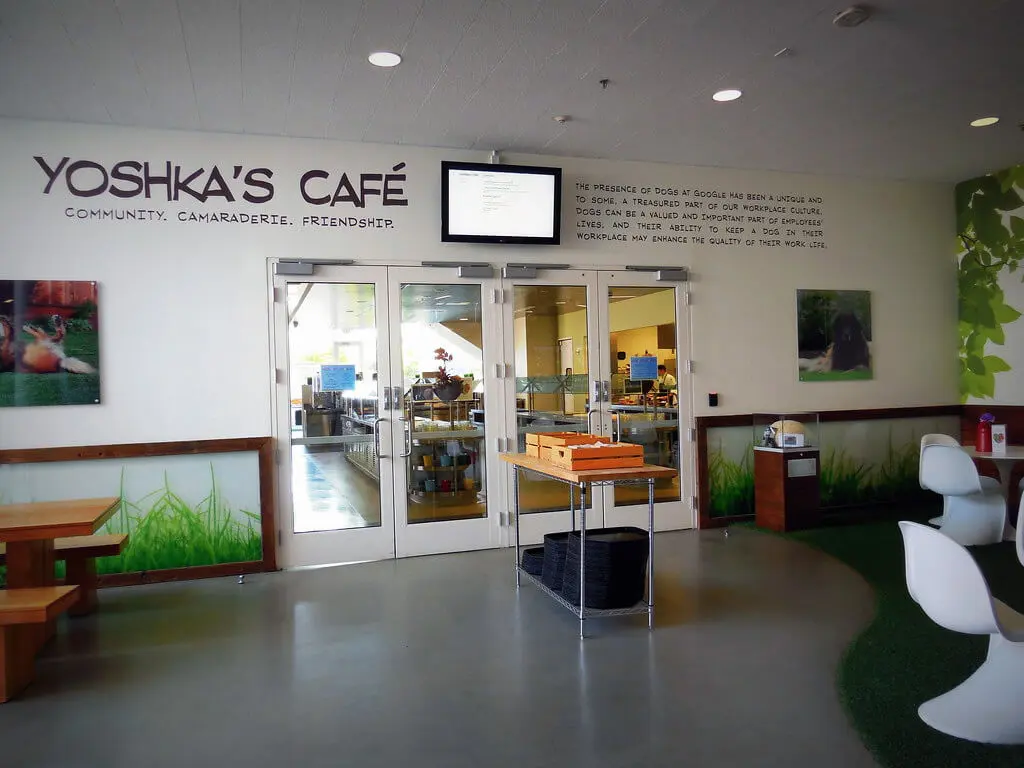

Several dog parks on Mountain View’s campus are designed especially for Google’s workers’ beloved pets. One of its most popular dog parks is called The Googleplex. Furthermore, the company has a Google employee group and a message board called Doogler, which was created for its employees and their pets.
Google 2004 -Officially Launched Gmail Services
Paul Buchheit, a Google employee, decided to address a significant concern of the company — increased storage requirements and extensive internal communication. Buchheit had prior experience working with web-based email services and was confident in his skills to design a faster and more responsive email service using Ajax.
Finally, Gmail was launched to the public on April 1 2004. This email service featured advanced search, 1 GB of storage, and several other fantastic features that most competitor web services lacked at the time. While most other companies offered a couple of mere megabytes as storage space, Google successfully captivated its billion audiences by offering a massive 1 GB of storage — which was unheard of at the time.
One Of The Most Important Steps In Google’s Journey — Going Public
After Google received its initial investment of $100,000 from Bechtolsheim, it subsided on many angel investments from several firms on the market, one of the significant ones being Jeff Bezos, founder and CEO of Amazon.
Other venture capital firms like Sequoia Capital and Kleiner Perkins invested in the company, which amounted to around 25 million dollars. What made Google’s IPO even more successful was the substantial advertising revenue generated by its web advertising products. This led to the company’s initial public offering being completed in 2009.
Although Google initially priced each stock at just $85 for a share, it eventually raised $1.7 billion, significantly increasing the company’s market capitalisation and giving the company a total valuation reaching over 1 million times the initial investment.
The Next Big Move — Google Launched Google Maps
In 2005, with millions of searches per day, Google introduced Google Maps; Google said in a statement that “Maps can be useful and fun.” However, it wasn’t until 2009 that Google rolled out one of its most significant updates — GPS navigation for mobile phones. Users soon realised the importance of this feature on their mobile phones as they could easily navigate uncharted territories without distinct fear.
Google Buys YouTube
Several other giants on the market, like Yahoo and Viacom, attempted to acquire YouTube; however, Google’s efforts ( and its offer of $1.65 billion) finally enabled Google bought YouTube successfully in 2006.
Fortunately, Google acquired a YouTube deal, and the ensuing integration with a Google account benefited both parties. While Google could redirect most of the video-sharing site traffic towards itself, the latter successfully had access to Google’s tremendous resources — which it desperately required as a new company.
Acquisition Of DoubleClick
Google established the foundation of its advertising platform by introducing Google Ads in 2000, later rebranding to Google Ads, making it known as one of the most vital forces in web advertising. However, it wasn’t until April 2007 that Google finally built a solid foundation in the advertising market by acquiring DoubleClick for $3.1 billion. This enabled Google to display ads, which helped expand its reach even further across the internet.
Its acquisition of DoubleClick in April became its number one most expensive acquisition — till it acquired Motorola Mobility for $12.5 billion in 2001.
Google And Chrome
In September 2008, Google hired Mozilla Firefox developers to help them bring a specific vision to life — developing a fast and stable web browsing software, leveraging open source technologies for a reliable search engine. This saw the inception of the Google Chrome browser, which became the most popular web browser for mobile and computer systems globally in just four years.
It has been ten years since Chrome was developed. Now, it has successfully become the most prominent driving force of the company, making Google Search what it is today — the most relevant and popular software.
In September 2005, Google made a wise and strategic decision to purchase Android for around $50 million. However, it wasn’t until September 2008 that it made another major announcement — the launch of the T-Mobile G1 or HTC Dream, The first mobile operating system-driven Android phone.
Several features of Google’s first Android smartphone have become the fundamental pillars of most mobile operating systems today. These include notification features, integration with Google’s services, open software technology, etc.
Welcoming Nexus One
Motorola, Samsung, and HTC conducted several experiments that were not entirely aesthetic or functional as Android devices began gaining popularity. Although these brands ran Google’s Android software, it was buried under unsightly and sometimes confusing hardware akin to navigating without a search bar.
Well, all that changed with the introduction of the Nexus One. Although HTC built it, it used Google’s technology and was a near-perfect example of what Google envisioned for its Android devices.
2010 — The Good And The Bad For Google
The beginning of 2010 wasn’t the best of times for Google, as it was shocked to discover an extremely sophisticated phishing attack on the internal infrastructure of its Chinese website. This led to the company being forced to rapidly switch its gears, even though it knew it would be a risky move. However, it wasn’t long before Alphabet’s subsidiary encountered these issues, leading to Google being banned from China.
A few months down the line, Oracle decided to file a lawsuit over Android, which, eight years later, is still in progress as Google attempts to appeal to the SC.
That said, by the end of 2010, Google rolled out seven Toyota Priuses, packed with sensational features that would amaze audiences worldwide. These hybrid cars, a part of the company’s search history, were designed to be the company’s first self-driving cars, loaded with sensors and artificial intelligence to assist them.
Since then, Google has continued its research into self-driving technology with enterprises like Cisco Systems and IBM.
Launching Google’s Operating System
The next couple of years were significant for Google as it began rolling out all types of new software, systems, and products that would eventually blow the minds of its audiences. One of the significant launches in 2011 was an open-source system developed by Google that would host web apps — the Chrome OS.
Soon enough, Google launched Chromebooks, which are still prevalent and a significant driver in the education industry.
Google And Its Failures
1. Google+
Inspired by Facebook and its growing popularity amongst consumers, Google decided to launch Google+. The only issue was — that it created an invite-only network for sharing and viewing links and pictures and chatting with a close group of friends on Hangouts.
Unfortunately, audiences did not welcome Google+ with the same enthusiasm as they did for Facebook. After years of attempted redesigns and restructuring, Google finally decided to let go of the idea. So, although Google+ remains an entity on the internet, its user profiles are primarily inactive.
2. Google Buzz
A similar situation occurred when Google tried to launch Google Buzz, which lasted 22 months. The company attempted to clone Twitter; unfortunately, it added no significant features to draw audiences away from Twitter and towards Google Buzz.
Although these are not the most relevant of Google’s failures, there are a few others that audiences remember (and some that they don’t). These include -
- Google Labs — from 2006 to 2011
- Google Now — 2012 to 2016
- Orkut — 2004 to 2014
- Google Allo — 2016 to 2019
- Picasa — 2002 to 2016
- Google Goggles — 2010 to 2018
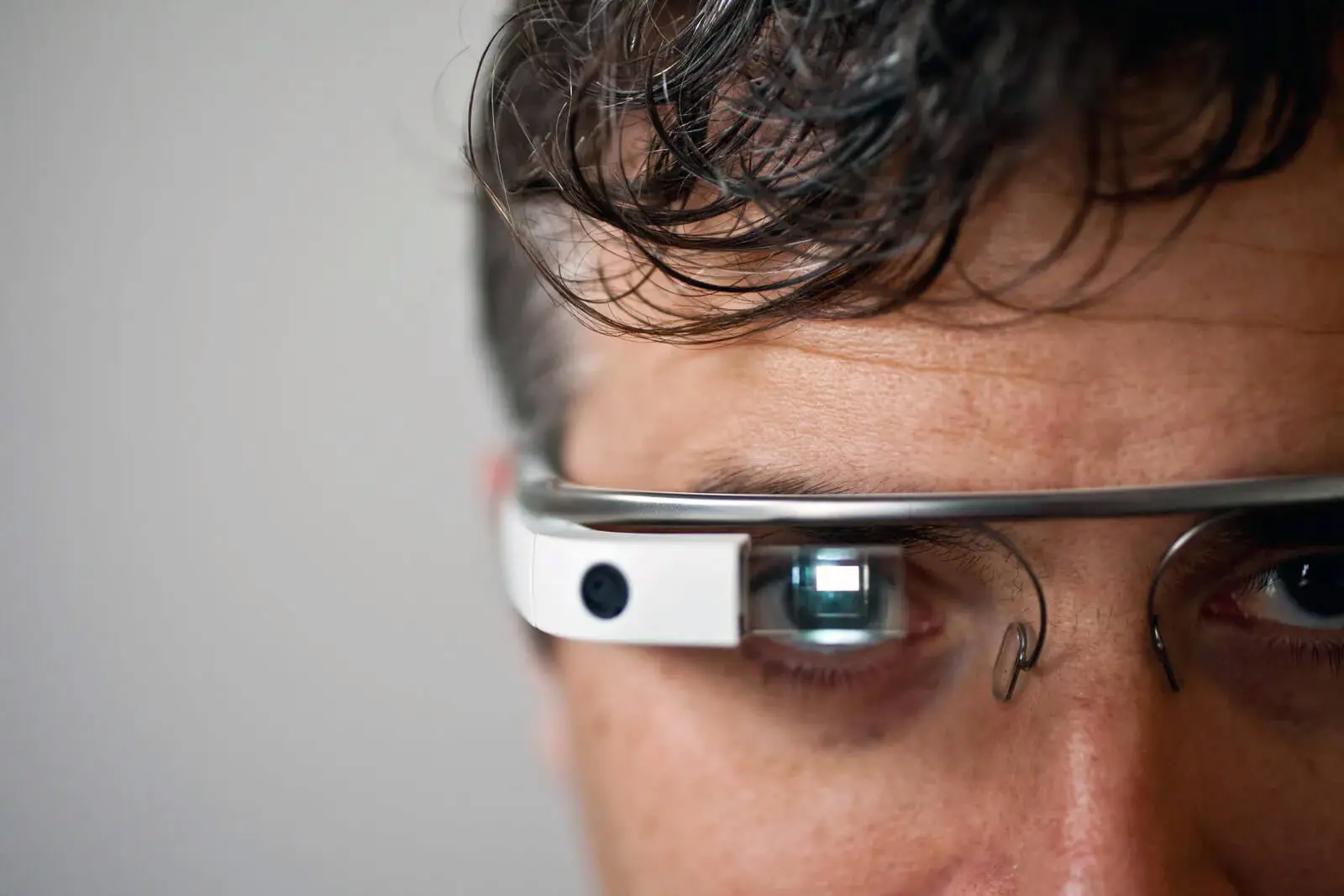
Google X — Its Most Interesting Project
Google X is by far one of the fascinating divisions of Alphabet. They have designed and developed several experimental hardware like Google Glass, one of Google’s most famous products. Even though Brin was stoked to show off the wonders of Project Glass, it was quickly shut down due to privacy and safety risks.

2013 — The Beginning And End Of Certain Google Products
2013 elicits mixed feelings from audiences — while this year saw the shutting down of the beloved Google Reader, it also saw the announcement of Google Chromecast. That said, Google has barely added any updates to Chromecast since its launch, and audiences often wonder why that is. However, it remains one of the stream’s most straightforward and affordable ways.
Stepping Into The AI Territory
By 2014, Google LLC had acquired DeepMind — an AI firm based in London. This was a brilliant move, as it slowly but surely made Google a leader in Artificial Intelligence technology.
Summing Up Google from 2015 To Now
2015 saw the reorganisation of Google’s structure known as Alphabet Inc. Hiring the now-CEO of the company, Sundar Pichai, has been an immensely beneficial and brilliant move. Google unveiled Google’s new brand logo soon after this shift.
The year also saw the launch of Google’s Assistant - Google Assistant — Amazon Alexa. And although Google was slightly late in releasing its assistant, it has been a massive success — and will hopefully continue to be one. It has also launched several Smart Home products, Android handsets, computers, mobiles, etc.
Google also continues to build new and improved software into its search engine to improve users’ performance. All said and done, Google is a much bigger and more prominent entity on the market now. It has taken giant leaps since it started a Stanford research project two decades ago.






