Keyword optimisation is one of digital marketers’ most effective SEO techniques. It involves researching and selecting keywords for your web content that are most likely to drive traffic and improve website ranking in Google’s Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
However, in many cases, using the same keywords on different pages can cause the pages to compete for the same rank. This is referred to as keyword cannibalisation, the process of multiple pages targeting similar keywords, negatively affecting the website’s organic performance.
There are several causes for keyword cannibalisation. You might publish similar blog posts over time, or create new web pages without redirecting the old ones. Sometimes, multiple paths lead to a product category, or similar keywords are optimised across different pages. Additionally, subcategory pages might not be optimised properly.
Keyword cannibalisation can be highly detrimental to SEO, as it causes your pages to compete for ranking in SERPs. The reason for that is when multiple pages target the same keyword. It becomes difficult for Google to determine which one to rank higher.
Additionally, the click-through rate and backlinks are spread across multiple pages rather than concentrated on one, potentially lowering their rank. Keyword cannibalisation can also lead to a poor user experience, as users might find it confusing when they see multiple results from the same site for a single query.
Moreover, it causes search engines to crawl unnecessary URLs, eating up the crawl budget. This might not be a big deal for smaller blogs, but for larger sites, it can be quite problematic due to their sheer number of pages.
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
The Impact of Keyword Cannibalisation on SEO
Keyword cannibalisation is a pervasive cannibalisation issue and can affect all types of websites, including e-commerce ones, news websites, corporate blogs, etc. While using the same keyword on different pages does not cause Google to penalise those pages, it lowers the authority and quality of the pages.
Since multiple pages compete for the same keyword or keywords, the strength of the URLs is reduced or divided, and their organic visibility is negatively affected. Instead of having one piece of content that offers good value to users and has a high CTR, several irrelevant URLs may need to provide complete information.
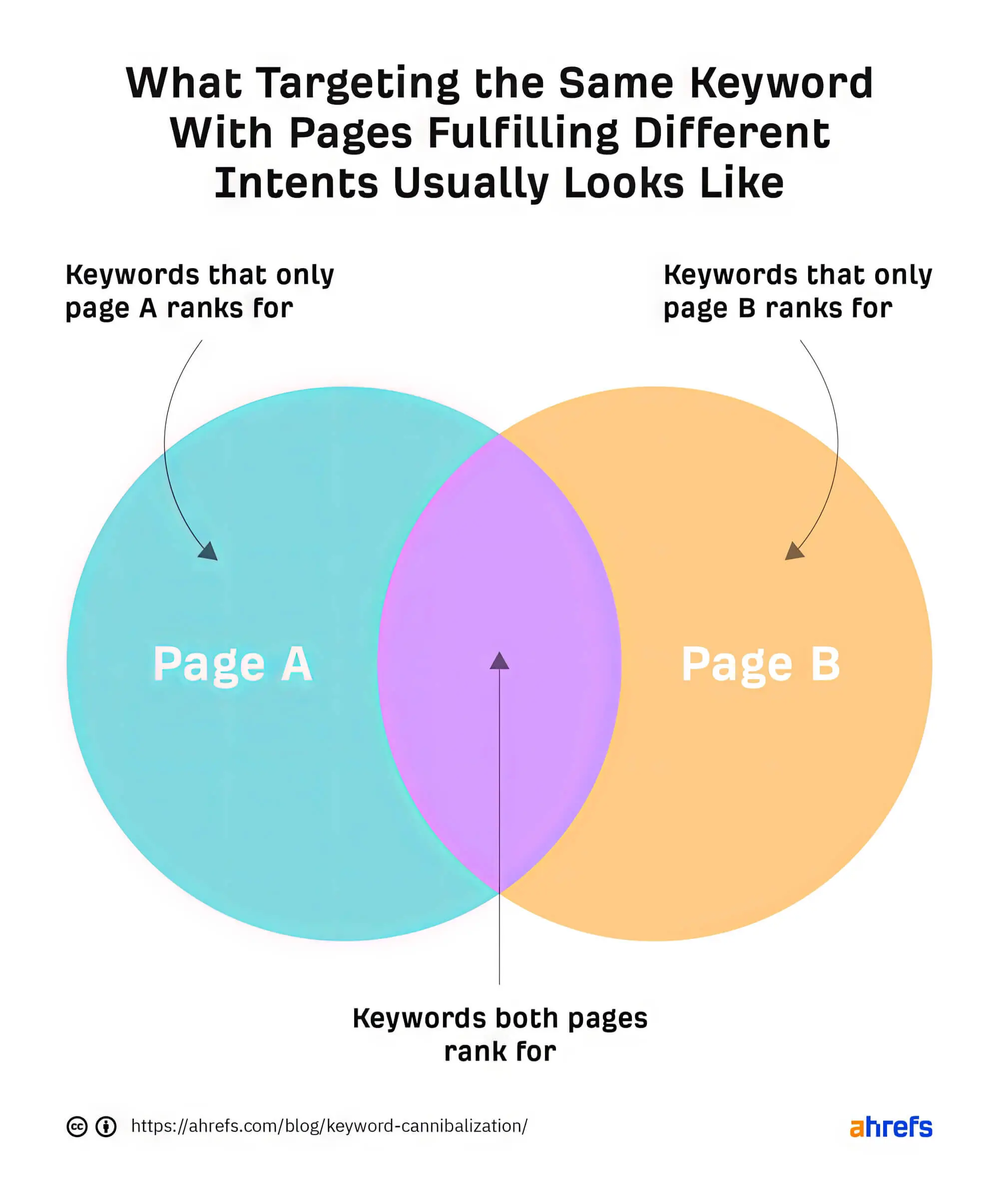
This can result in a rebound that can also impact your SEO negatively, as it may seem to search engines that the content of those two posts is unrelated. Similarly, users might find the content less useful, and user experience is one of the most important factors Google considers when ranking pages.
Aside from that, when the authority between competing pages is divided, search engines cannot understand which page provides more value to users and better answers the query. Competing pages appear for the same search intent, but the algorithms must ensure the content is relevant and correct as per the query.
In these cases, search engines often favour competitor pages deemed more reliable. As a result, your pages might show up in SERPs but not at the top.
Signs and Symptoms of Keyword Cannibalisation
There are several indicators that assist in identifying keyword cannibalisation, such as:
1. Fluctuating Rankings
As explained above, when multiple pages rank for the same keyword, search engines can have difficulty determining which page to rank higher. This can cause the rankings of these pages to fluctuate frequently, resulting in inconsistent visibility in the search results.
2. Reduced Click-Through-Rates often wherein keyword cannibalisation occurs
Like search engines, users can get confused when presented with multiple web pages from the same website for the same query. This can lead to reduced CTR as users may need help choosing between the different pages or perceive that the website may need more comprehensive information.
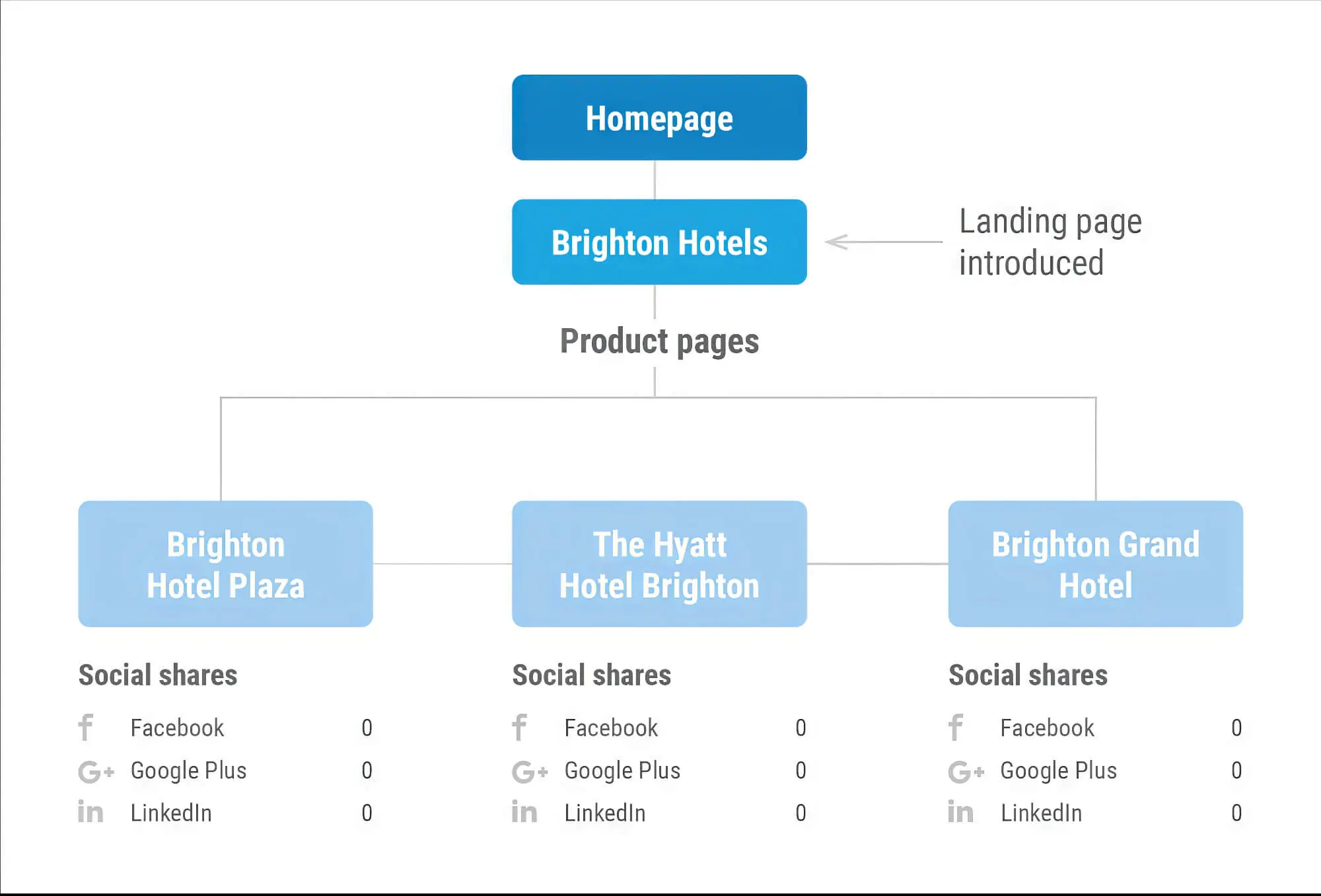
3. Duplicate Content Issues
Multiple URLs with the same target keyword can lead to similar or duplicate content. Since search engines like Google prioritise unique and high-value content, duplicate content can negatively impact the rankings of those pages since they may not provide value to users.
4. Internal Linking Challenges
Internal linking is an essential SEO strategy for distributing links across different web pages and highlighting the importance of specific pages to search engines. Keyword cannibalisation can confuse which pages to link to, leading to inefficient link distribution.
5. Lack Of Clear Focus For Individual Pages
Keyword cannibalisation can reduce the relevance of each page. When multiple pages compete for the same keyword, it can become challenging to establish a clear focus for each page, reducing their effectiveness in ranking for specific search rankings.
Strategies for Fixing Keyword Cannibalization
Addressing keyword cannibalisation needs a strategic plan to optimise your website content. Here are some effective solutions to tackle the issue.
1. Conducting Keyword Research
Undertake comprehensive keyword research to identify the most valuable and relevant keywords for each website page. Ensure each page targets unique and specific keywords that align with its content and purpose. Various tools, like SEMrush, Ahrefs and Google Keyword Planner, can be used to identify the most relevant keywords.
2. Creating A Content Hierarchy
Consider organising the content of your website into a clear and logical hierarchy. This involves defining broader topics for high-level pages and more specific subtopics for individual ones. Doing so can help you avoid overlapping content and ensure each page has a distinct focus. Such hierarchy also helps search engines understand the relationships between web pages and search queries.
3. Implementing Proper Internal Linking
Review your internal links and ensure each page links to other relevant pages with complementary or similar content. Anchor text can be used to accurately describe the content of the linked page and the target keyword.
4. Updating Or Consolidating Content
If you have multiple pages that rank for the same keyword and cover similar topics, consider updating the content on those pages to make them more distinct and valuable. Alternatively, if the content is extremely similar, you can consolidate the pages into a single comprehensive page that covers all aspects of the topic.
5. Monitoring Website Performance
you must consistently check your website’s performance as part of the effort to fix keyword cannibalisation using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Check the keyword rankings frequently, and pay attention to the organic traffic and CTR for important pages. Performance metrics make it more transparent when pages exhibit keyword cannibalisation issues and take necessary action to fix them.
Resolving Keyword Cannibalisation Issues
1. Conduct A Content Inventory
The first step in solving keyword cannibalisation is conducting a thorough content inventory of your website. This process uncovers target keywords and main topics for every page. Tools like Sitebulb or Screaming Frog can be really helpful here.
2. Undertake Keyword Research
Keyword research tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Google Keyword Planner can help you perform keyword research and identify the most valuable and relevant keywords. Compare the target keywords in your content inventory with the keyword research results to identify instances of keyword cannibalisation.
3. Analyse Keyword Rankings And Organic Traffic
You can use the Google Search Console and SEO software to analyse each page’s keyword rankings and organic traffic. Look for pages utilising the same keywords and observe their fluctuating rankings and traffic patterns. Third-party tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush can also be used to analyse organic traffic and keyword rankings comprehensively.
4. Identify Overlapping Content
Manually review the content of pages that target similar or identical keywords and search for instances of duplicate or nearly identical content across different pages. Identify pages that cover similar topics but have different target keywords.
5. Prioritise Pages And Keywords
Prioritise pages that are more important to your overall SEO strategy have higher traffic potential, or are essential for your business goals. Choose the best-performing page or the most relevant one to be the primary page for each target keyword.

6. Consolidate Content
As mentioned above, if you find similar pages with overlapping content targeting the same keyword, you can consolidate them into a single page. Rewrite and combine content from the redundant pages to make the consolidated page more informative and valuable. Also, implement 301 redirects from these pages to the consolidated page to preserve their SEO value.
7. Optimise Page Titles And Meta Tags
After identifying the primary page for each target keyword, optimise its page title, meta description, and meta tags to accurately reflect the focus of the content and the target keyword. Use unique and descriptive meta titles and meta tags for each page to avoid confusion and improve the CTR.
8. Implement Proper Internal Linking
Check your internal linking structure and ensure that relevant anchor text is used for internal links between different pages. Link from less essential or redundant pages to the primary page for the target keyword. Ensure that the anchor text accurately describes the content of the linked page.
For instance, in the case of e-commerce websites, each product page can be linked back to the category page, which should be optimised for ranking.
9. Monitor And Measure The Website Performance
After refining the strategy, keep an eye on your website and keyword rankings to ensure cannibalisation issues are resolved using Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Track the impact of consolidating content, optimising page content, and optimising page titles and meta tags on organic traffic and search engine rankings.
10. Conduct Periodic Audits
Regularly conduct audits to identify and address new instances of keyword cannibalisation that may arise over time. Continuously optimise your content strategy to ensure each page has a distinct focus and effectively targets relevant keywords. Reviewing your website’s structure and content hierarchy at set intervals makes it possible to identify situations with multiple pages targeting the same or similar keywords.
Periodic audits help businesses maintain a strong SEO foundation, improve page rankings, and provide users with an enjoyable browsing experience.
FAQs
1. How can you detect keyword cannibalisation?
Detecting keyword cannibalisation requires little effort and can be done in several ways. You can use your website search widget to search for keywords competing with one another. Doing so will show the various URLs that appear for a specific keyword query.
Alternatively, you can use the Google-specific SITE command, which can help detect indexed pages and even show the content within a domain. Or use Search Analytics in the Google Search Console to view the URLs for which a specific keyword ranks. Using the pages tab, one could see a list of pages that highlight instances of keyword cannibalisation.
Finally, some external tools, such as Ubersuggest, can provide comprehensive data for detecting cannibalisation.
2. What is the difference between keyword cannibalisation and keyword stuffing?
While keyword cannibalisation occurs when web pages rank for the same keywords, keyword stuffing refers to overusing or excessively repeating specific keywords in the content or meta tags, etc. The latter is considered a black hat SEO technique and may result in search engines penalising web pages that utilise it. This is because it degrades the content’s quality and negatively affects user experience.
People resort to keyword stuffing to artificially boost web page rankings or meet keyword density requirements without considering its impact on the quality and relevance of the content. It can be rectified by creating high-quality content using keywords naturally while ensuring it offers value to users.
3. How often should you perform keyword cannibalisation checks on your website?
It is highly recommended to perform periodic audits to identify and address instances of keyword cannibalisation. However, how often this should be done will depend on various factors, such as the website size, how frequently new content is published, and update frequency.
Larger websites with extensive content may require more frequent checks since the chances of keyword cannibalisation are much higher. Similarly, audits will be needed more often if the content is updated or new content is published frequently. Other factors that can affect how often checks are needed include major website changes, SEO performance changes, and changes in keyword rankings.
4. What should you generally avoid when fixing keyword cannibalisation issues?
There are specific methods that are generally not advisable when trying to fix keyword cannibalisation issues, such as:
A. Deleting The Page
You should only delete a page with keyword cannibalisation problems if it only ranks for the cannibalising keyword or does not offer any value to the users.
B. Noindexing The Page
When you noindex a page, search engines do not include it in their index, so it does not rank. This is one of the reasons why it is not a recommended method of dealing with keyword cannibalisation.
C. Canonicalising The Page
If there are several duplicate pages or more than one page with similar content, canonicalisation might help improve the page ranking. However, it might not help resolve the problem of keyword cannibalisation in other cases.
D. De-optimising The Page
It is impossible to de-optimise a page’s content for a single keyword. This is because removing internal links with the cannibalising keyword as the anchor will also affect the Google rankings for other keywords.
5. What to do if multiple landing pages or product pages target the same or similar keywords, leading to the wrong page ranking in the search results?
When keyword cannibalisation occurs on a landing page or product page, the first thing to do is to undertake keyword research, focusing on long-tail keywords. This can help discover relevant keyword suggestions for different product and category pages.
Ensure each page offers unique content that aligns with the long-tail and focus keywords. Avoid duplicating content across multiple URLs and group each product and category page under a keyword cluster.
If two pages or more belonging to the same keyword cluster compete for the same keywords, consider directing more traffic to the better-performing page.
Reduce Keyword Conflict and Maximise Traffic
Keyword cannibalisation is a critical issue in digital marketing that can lead to the wrong page ranking in the search results, resulting in confusion and a poor user experience. When similar pages target the same keyword, the authority and focus of the landing page get diluted.
However, by following the proper methods, businesses can identify and address the problem, ensuring their pages are tactically tuned with long tail keyword optimisation to solve keyword cannibalisation. Doing so can help improve their ranking in the search results and provide users with a better experience.
Conducting regular content audits, mapping keywords strategically, and implementing proper internal linking can go a long way in preventing keyword cannibalisation.






