Summary / TL;DR
Psychological purchasing triggers, also called emotional or mental triggers, are marketing tools that influence buyer behaviour by appealing to emotions rather than logic. The article explains how emotions like fear, guilt, trust, urgency, and belonging can increase conversions when used ethically in advertising. Marketers also harness cognitive biases such as loss aversion, the bandwagon effect, and the compromise effect to guide consumer decisions subtly. Techniques include limited-time offers, free trials, and social proof like testimonials. While effective, misuse of these triggers can damage brand trust, so marketers are advised to apply them with transparency, moderation, and respect for consumer autonomy.
The primary goal of all businesses is to sell their products and services to customers.
After all, the revenues generated from these sales are used to expand the business further. That is the reason why many businesses strive to maximise their sales numbers by any means necessary.
However, in their quest to increase sales, business owners need to remember one thing—properly motivating the buyers. Most will become annoyed if a brand tries to force its products on people by any means necessary. And many will even shun the brand entirely due to its aggressiveness.
This is where psychological purchasing triggers come in handy. These tools enable a brand to effectively persuade someone to become a customer, all without using aggressive or cheap tactics.
So, what are these psychological purchasing triggers exactly? That’s what we’re here to explore. Let’s dive in and discover more!
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
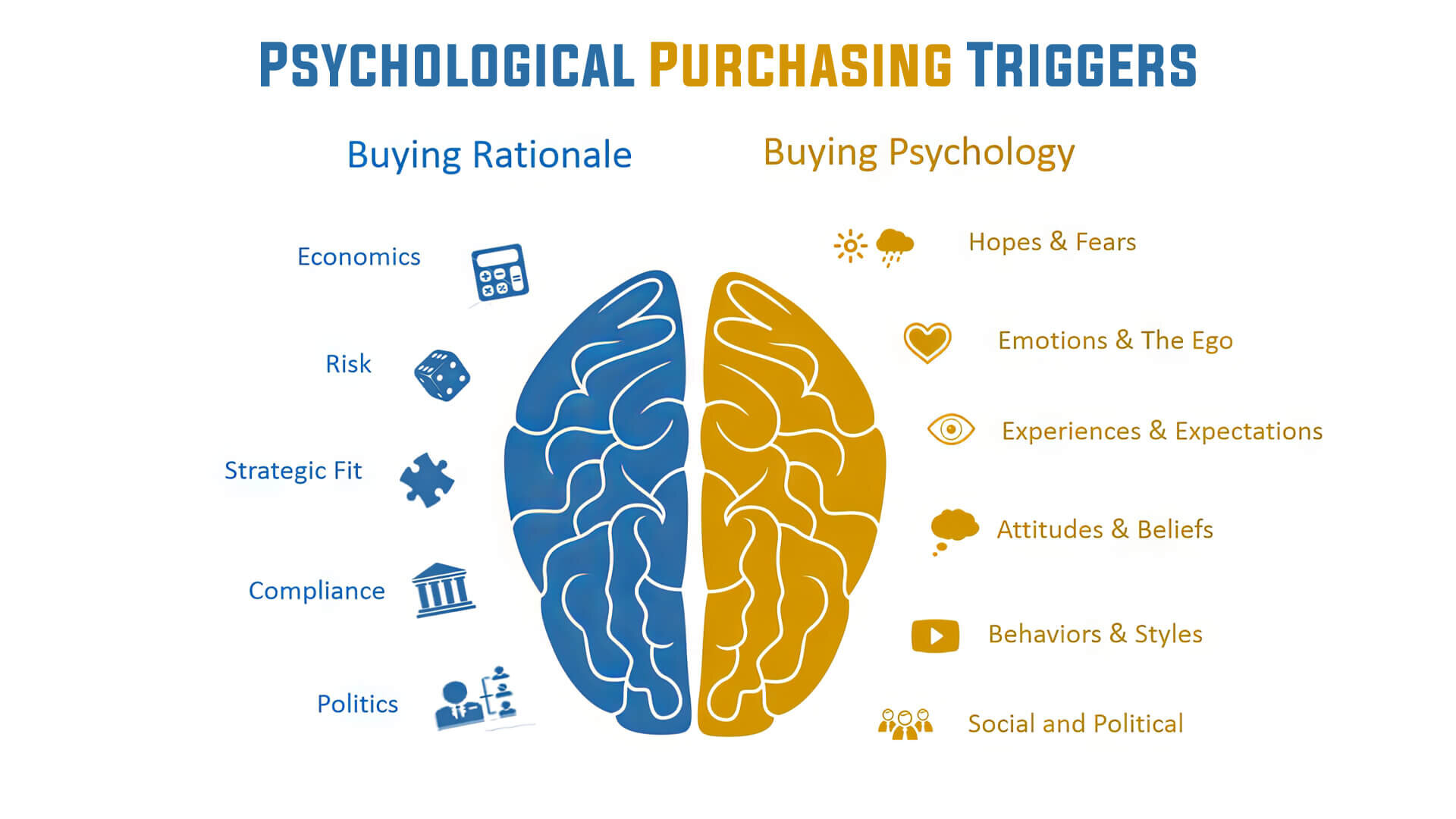
Understanding Psychological Purchasing Triggers
First and foremost, let’s delve into consumer psychology to understand what psychological triggers actually are. Also known as mental triggers or emotional triggers, these are things that affect our mental state. From a purely psychological point of view, these triggers are usually events that evoke negative emotions.
That is because a mental or emotional trigger is often associated with a traumatic event that occurred in the past. Whenever the person encounters a trigger, they exhibit intense emotions.
However, in the domain of marketing, psychological triggers are not always associated with negative emotions. Instead, these triggers are used to create a strong but indirect need in customers’ minds. That, in turn, helps to influence their purchasing behaviour to benefit the seller or the marketer.

To grasp how these psychological triggers affect consumer behaviour, it’s vital to understand how our minds operate. While we often think of ourselves as logical beings, much of our thinking is actually driven by emotions and feelings. This shows that our thought processes are more emotional than logical.
Psychological triggers try to exploit this emotional aspect of the mind. Marketing strategies and ads that use psychological triggers resonate with our feelings and emotions so that we may feel connected to the brand. Businesses can inspire their customers to buy products and services by doing that.
Power Of Emotional Triggers
As we have suggested before, emotions can greatly influence our decisions. If emotions fuel the entire thought process, it can lead to impulse buying behaviour.
Interestingly, certain emotions have a stronger impact on our decision-making than others. Below, we delve into some of these powerful emotional triggers.
1. Fear
Fear is a highly dominant emotion in decision-making. It can completely override logic and rationality and force us to act subconsciously. Because of this, it is one of the most leveraged emotional triggers in marketing. Specifically, businesses subtly use the fear of missing out (FOMO) to influence consumer decisions.
2. Guilt
Guilt is another strong emotion that influences thought processes and buying decisions. Marketers may try to provoke you into feeling guilty about your decisions. This is usually done by highlighting the positive impact of buying the marketed product or service. Naturally, the emotional trigger influences you to purchase to reduce your guilt.
3. Trust
Unlike the previous two emotions, trust aims to affect the mind positively. Brands use this emotional trigger to create a loyal consumer base. By promoting transparency and improving communications, the brand creates a positive reputation that eventually increases customer trust. However, gaining trust can be time-consuming, making managing this emotional trigger more challenging.

4. Time
Time is an emotional trigger that persuades users to take quick action. By imposing a time limit on a certain product or service, brands can create a sense of urgency, significantly influencing consumer buying behaviour. Naturally, limited time to purchase anything triggers another emotion - FOMO - which eventually forces them to buy the product.
5. Value
There is little doubt about the fact that consumers want to get the best value from their purchases. So, if a brand can convince customers that its products and services have great value, it can successfully influence their decision-making process. Besides, if used correctly, this emotional trigger can be used to build trust among users, further reinforcing the customer’s buying decision.
6. Belonging
We humans are inherently social, always seeking a sense of belonging wherever we are. This sense of belonging offers us validation and a feeling of importance. It’s a potent emotional trigger, so if a brand’s product or service can provide it, you might be drawn to give it a try.
7. Competition
Almost every human has a competitive side, so we strive to be better than the next person. A good marketing strategy seeks to utilise this aspect to drive sales. If it can pit people against each other in healthy competition, people will take that opportunity and buy the product or service that will make them stand out.
Cognitive Biases And Decision-Making
This is another form of psychological trigger that affects our thought processes. Most people are exposed to a large volume of information on a daily basis. Cognitive biases simplify the decision-making process, allowing people to navigate complex information using systematic filters. These filters are crucial in individual decision-making and are based on preferences and opinions, meaning the final thought process deviates from being rational or objective and becomes subjective.
In simple words, cognitive biases allow us to believe what we want to believe. Marketers tend to use this subjectivity present in cognitive biases to drive sales. In that context, brands use different types of cognitive biases to influence the consumer’s decision-making process. We have discussed some of the most prominent ones below.
1. Loss Aversion Bias
The bias for loss aversion highlights how people fear losing something precious. They value this fear more than getting something new with almost the same worth. For example, if you have $100 in your wallet, your fear of losing that money will be much greater than the happiness of getting another $100.
A skilled marketer can use this bias to influence their target audience to buy a product or service. They can offer a free coupon or a free trial to use a product, which allows the consumer to try out the particular product without spending any money.
After using it for a while, they will start to feel they own the product. So, when the trial or coupon expires, they must purchase it to keep using it. One great example of this strategy is antivirus software, which often comes with free trials. Once the trial period ends, many people end up purchasing the software.
2. Mere Exposure Effect
The mere exposure effect is another cognitive bias that determines the purchasing behaviour of consumers. It demonstrates that people tend to develop a preference for things that they are familiar with.
This means that if a person chooses between a familiar item and a new item, they will always choose the former, even if the latter item is objectively better. Because of this reason, it is known as the familiarity principle.
Big and renowned brands often use this bias to sell their products. This doesn’t mean smaller brands cannot use this strategy, though. More people will learn about them if they can expand their reach and improve visibility. And with time, they can build up familiarity among potential customers to a level where the mere exposure effect becomes useful.
3. Bandwagon Effect
The bandwagon effect is another powerful cognitive bias influencing users’ conscious thought processes. It illustrates the tendency of an individual to engage in certain activities just because other people are doing them. In other words, their behaviour and thoughts are shaped by public opinion instead of their own.
Apple’s marketing strategy is one good example of the bandwagon effect. Since the brand and its products are popular among the majority, individuals may be tempted to buy an Apple product, even if they do not need it.
Even a smaller brand can use this bias to its advantage if it is fashionable enough. If it is marketed as flashy and glamorous, it will definitely attract the general public’s interest. The bandwagon effect can drive sales once it becomes popular and everybody starts talking about the brand.
4. Compromise Effect
The compromise effect is another cognitive bias marketing strategists use to drive sales. This effect highlights the tendency of people to go for a middle ground or “compromise” when presented with multiple extreme choices.
For example, let’s assume that there are three different products. The first product has a very low price, the second one has a moderate price, and the third has a high price. If you present these products to a consumer, they will likely choose the second product since it offers a good deal over the other two.
This means that if a brand can keep the prices and features of its products moderately balanced, then people will choose their products over other extreme options.
Social Influence And Social Proof
Social influence is a phenomenon where individual choices are shaped by what society thinks as a whole. If you have read through the discussion presented so far, you can easily explain why social skills and influence are regarded as potent psychological triggers.
However, not everyone is influenced by the mere opinions of others. Such individuals require a much more powerful trigger, or else their thought processes cannot be swayed. This is where social proof comes into the picture.
Providing sufficient proof that your product or service is helpful and not just hyped up might raise their curiosity. This proof can be in the form of feedback from other users, certifications received by the product, and other similar acknowledgements.
For example, if you run an online store that sells a particular product, you can display testimonials, reviews and other user-generated content on the landing page. Furthermore, if the product has received any awards in the past, you can display that, too. All these things can be used as marketing materials, as strong social proof highlighting the usefulness of the item you offer.
Ethical Considerations In Using Psychological Triggers
Many consumers and marketing experts have expressed scepticism to the idea of using psychological triggers in marketing, and with good reasons. After all, these triggers aim to manipulate users’ emotional thought processes. Because of that, there’s always an element of risk to them, and if used carelessly, there can be negative consequences.
That is why brands must follow all the relevant ethical considerations while using psychological triggers to avoid bad incidents. Below, we have discussed a few of the most important ethical considerations.
1. Practise Constraint
Businesses should always practise moral constraints when utilising psychological triggers. In other words, they should try to avoid using too many triggers simultaneously. Conversely, their triggers should not seem extreme or insensitive as that can be counterproductive.
2. Prioritise Ethical Behaviour As A Key Part Of The Marketing Process
Brands should prioritise ethical behaviours instead of focusing solely on performance metrics like conversion rates, sales and profits. They should avoid condoning immoral behaviour to make people buy their products.

3. Maintain Transparency
Most businesses collect consumer data to identify market trends and implement suitable triggers catering to those trends. In this regard, brands should be transparent about the data they are collecting to build up consumer awareness. They should also prioritise data safety and privacy to avoid third-party manipulation.
Exploring the Psychology Behind Your Purchasing Decisions
If implemented correctly, psychological triggers can be highly useful, especially when building up brand image and boosting profit margins. When combined with other marketing strategies, such as digital marketing, they can work wonders for a company.
Of course, unethical implementation may have the opposite effect in the long run. If a brand is found to be immorally manipulating consumers for its own gain, it can also have serious legal repercussions.
That is why it is a good idea for business owners to seek advice from qualified marketing professionals before implementing such triggers. These individuals can provide effective guidance so the company can achieve its financial goals.





