Summary / TL;DR
Robots.txt is a plain text file used in SEO to control how search engine crawlers access and index a website’s content. By specifying directives like User-agent, Disallow, Allow, Crawl-delay, and Sitemap, site owners can manage crawler behaviour to prevent indexing of duplicate or sensitive content, reduce server load, and guide bots to important pages. The file must be stored in the website’s root directory, written in a simple text editor, and named in lowercase to be recognised. While helpful for SEO, not all crawlers respect the robots.txt file, especially malicious bots, so additional protective measures may be necessary.
It’s no secret that digital marketing is booming. At the heart of this thriving domain is search engine optimisation (SEO), a key component for success.
It is a crucial strategy that helps improve your website’s optimisation to reach the maximum number of people on the internet. Keywords and search engines play an important role in SEO, but one aspect that website owners sometimes overlook is the robots.txt file.

So, what makes this tiny text file so important? Surprisingly, it plays a key role in boosting your site’s performance on search engine results pages (SERPs).
But how does it accomplish this task? Well, that is what we are here to find out. So, read on if you are curious!
What Is Robots.txt For SEO?
Robots.txt is a plain text file created and used by webmasters (the people who are responsible for maintaining a website). It contains instructions for the search engine crawler robots that access your site for indexing purposes. To be more precise, it instructs what portions of your website should be crawled by these robots and what portions are to be left out.
The robots.txt file belongs to a group of web standards known as the robots exclusion protocol (REP). These standards control the crawling behaviour of search engine robots.
In other words, they regulate how search engine crawlers access and index website content. They also control the information these crawlers serve users in search results.
How Does Robots.txt Work For SEO?
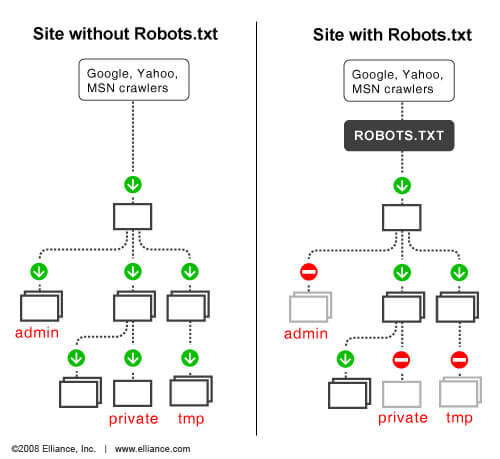
Understanding the robots.txt file involves digging into search engine operations. Primarily, search engines perform two core functions: crawling the internet for content and indexing that content for users.
Search engines typically crawl through the web via links and pages. Given the billions of websites, this task would be time-consuming without effective tools. Enter, search engine bots like web crawlers. They swiftly navigate and sift through the immense number of websites and pages available.
The crawler bot can accomplish this task with the help of the robots.txt file. Once it lands on a website, it seeks out this text file before proceeding. After locating this file, it reads through the crawling instructions to decide on the next course of action.
If the robots.txt file disallows the search engine bot from crawling the site, it will skip it and move on to the next one. But if no directives in the file prohibit the bot, it will crawl the entire site for the necessary information.
How To Use Robots.txt For SEO?
To optimise the robots.txt file for search engines, understanding its technicalities is crucial. You can easily create this file using simple text editors like Notepad or TextEdit.
Here, you should use the correct commands to create the file, or else it might cause unnecessary problems for the crawler bot. In that context, the common commands used in the robots.txt syntax are discussed below.
1. User Agent
The user agent command is used to indicate the web crawler. It does not refer to the search engine itself but to the specific crawler bot that the search engine uses. For instance, Google’s crawler bot is known as “Googlebot.” So, if you want to control Google’s search behaviour on your website, the user agent on your robots.txt file will be Googlebot.
2. Disallow
Disallow directives instruct the user agents not to crawl a specific URL or website directory. These directives should be followed by the pathway that should not be accessed. The crawler will only notice this directive if you mention the pathway. On that note, you can use only a single disallow directive for a particular URL.
3. Allow
The allow directive is the opposite of the disallow directive, for it tells the crawler what parts of the site can be accessed. It is mostly used to allow access to certain pages and folders in an otherwise disallowed directory.
For this purpose, you must mention the path you want the crawler to access after the allow directive. This command is used only for a few major search engines like Google or Bing.
4. Crawl-Delay
The crawl-delay directive specifies how long the crawler should wait before accessing the site’s contents. This unofficial command prevents the server from overloading too many requests.
Googlebot generally doesn’t acknowledge this directive, so you must set the crawl rate via the Google Search Console instead.
5. Sitemap
The sitemap directive is an optional command that points the crawler to the XML sitemap. You can reference multiple XML sitemaps and even sitemaps that are not located on the same host site as the robots.txt file. Google, Bing, and Yahoo recognise this directive and Ask.
Robots.txt Example
Based on the above discussion, we have provided some examples that use the above commands. This will give you an idea about how to structure and format your site’s robots.txt file.
For the sake of convenience, let’s assume that your website URL is www.example.com. Then, the robots.txt file for your site will look like the following:
Example 1
User-agent: GooglebotDisallow: /root-directory/Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap-1.xmlSitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap-1.xmlSitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap-3.xmlThe above example prohibits Googlebot from crawling pages within the “root-directory” folder. It then references three different XML sitemaps using their URLs.
Example 2
Let us give you another advanced example.
User-agent: GooglebotDisallow: /duplicate-content/Disallow: /main-directory/User Agent: *Disallow: /duplicate-content/Disallow: /main-directory/Allow: /main-directory/sample.htmlCrawl-delay: 5In the above example, the robots.txt file has prohibited Googlebot from accessing the “main-directory” and “duplicate-content” folders. Subsequently, it has prohibited all the other search engines from doing the same but has allowed them access to the /main-directory/sample.html web page. Likewise, it has set a crawl-delay interval of five seconds, which means that these other crawlers can make a new request after every five seconds.
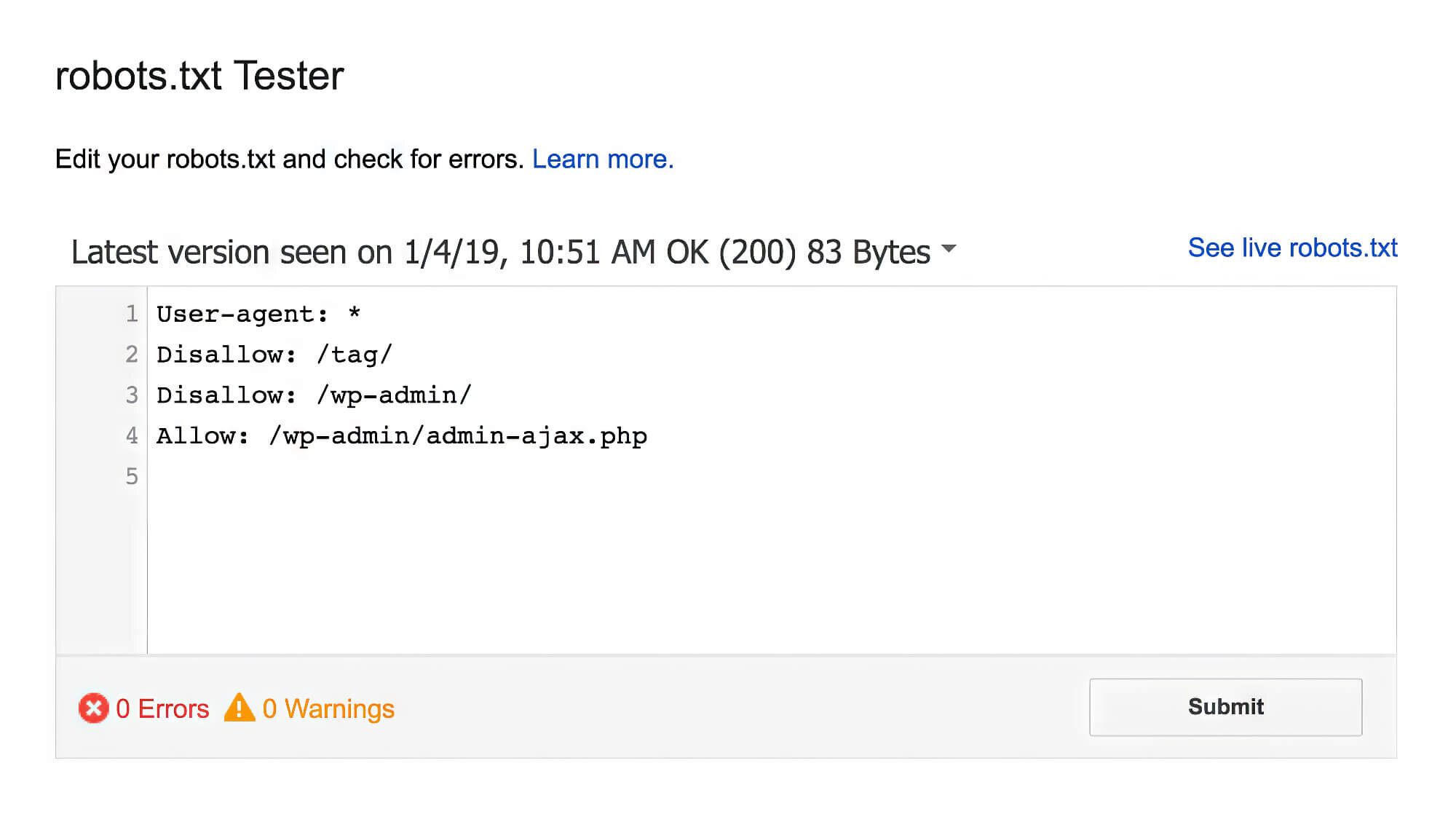
In addition, you’ll notice that you can use more than one disallow directive for the same user agent, albeit in multiple lines. Similarly, the segments for multiple user agents are separated by a single line space. Also, the “*” is a wildcard modifier used to denote any sequence of characters.
How To Optimise Robots.txt For SEO?
In this section, we have discussed some robots.txt and SEO tips you should follow. These may help enhance the overall effectiveness of the robots.txt file, improving your SEO success rate.
First, you should always create the robots.txt file using a text editor. Try to avoid using word processors, as they have different file extensions. In addition, they can introduce unnecessary characters not recognised by crawlers, eventually leading to indexing problems.
You should always keep the robots.txt in the site’s top-level directory. That will make it easier for the crawler bot to access it. Likewise, the filename is case-sensitive, meaning you cannot capitalise any letters in the filename. For instance, you cannot name it “Robots.txt,” as the search engine bot will not recognise that.
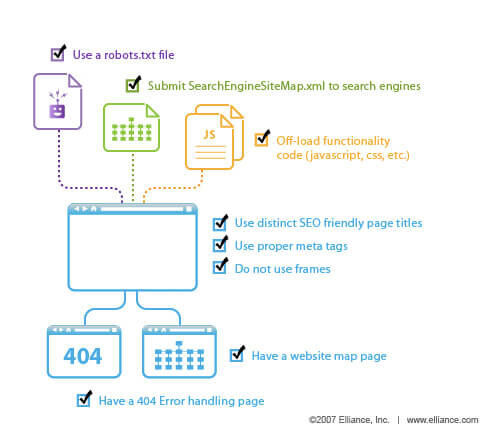
Additionally, you should include a sitemap in the file. Including the sitemap complies with robots.txt and SEO best practices and can help your site perform better in search results.
If you have multiple subdomains within the root domain, you should include a separate robots.txt file for each. So, if your main site is www.example.com, and you have a subdomain with the URL forum.example.com, you should consist of a separate robots.txt file for each.
Why Is Robots.txt Important For SEO?
There are several reasons why robots.txt is essential for your site, as we have listed below.
- Prevent search engines from indexing internal search results pages
- Keep sections and files of your website private
- Preventing search engines from showing duplicate content on SERPs
- Minimising the risks of server overloads by specifying crawl delays
- Referencing the location of your website’s sitemap
In this regard, if you follow the robots.txt guidelines for SEO correctly, you can get sufficient control over what pages and content are indexed in search results. Although, if you wish to keep your entire site fully accessible, you will not need a robots.txt file.
Using Robot.txt for Your Website
If you want better control over your site, it is always advisable to use a robots.txt file in addition to dedicated systems like Google webmaster tools. This file can prevent sensitive areas of your site (such as the admin folders) from appearing in public search results.
That said, specific user agents can completely ignore this file. This is more common for malicious crawlers like email address scapers and malware bots. In that case, you might need extra security measures to protect your site.
However, if you are not as tech-savvy in these matters, there’s no need to worry—we have your back. At sitecentre®, we have qualified SEO experts who can handle such tasks efficiently and affordably. So, if you need any help, you can contact us.






