Summary / TL;DR
Website speed is a confirmed ranking factor that significantly affects SEO and user experience. Since Google’s 2018 Speed Update, load time impacts mobile rankings more heavily, with slow sites increasing bounce rates by up to 90%. Page speed measures such as Fully Loaded Page, Time To First Byte, and First Contentful Paint are key indicators of performance. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights diagnose technical issues, but connection speed can skew mobile test results. Improving server response times, compressing images, cleaning up code, enabling browser caching, and using a CDN can boost load speed. Faster pages lead to better user engagement, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates.
Is your website traffic suffering because your pages take too much time to load? Are visitors leaving your site because of slow loading speed?
Many website owners are unaware of how their website load times affect their search engine rankings. If you want a straight answer — yes, your page load time is a ranking factor and will impact the SEO significantly.

No matter how stunning your website looks or how engaging your content is, if it takes forever to load, visitors will simply leave. That’s just the way it is!
Your site speed is influenced by various factors, including the size of the page files, the efficiency of your server, how well images are compressed, and even your URL structure.
But with tools like PageSpeed Insights, you can easily monitor and conduct a speed test to improve your site speed. Today, we’ll discuss website speed and how it can impact your page experience and website ranking.
To start, let’s take a look at some interesting page speed facts:
- eCommerce sites that load in 1–2 seconds have 3x higher conversion rates
- A 1-second delay in page load time reduces page views by 11%
- According to 83% of online users, websites should load within three seconds or less
- Approximately $18 billion is lost annually as a result of abandoned shopping carts
- Page load time has the greatest impact on conversion rates during the first five seconds.
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
What Is Page Speed?
In layperson’s terms, page speed is the time it takes for a web page to open or load once users visit it. The speed of different web pages can vary because of their content, like scripts and images. However, page speed is relative because it doesn’t always depend on your site’s server or performance.
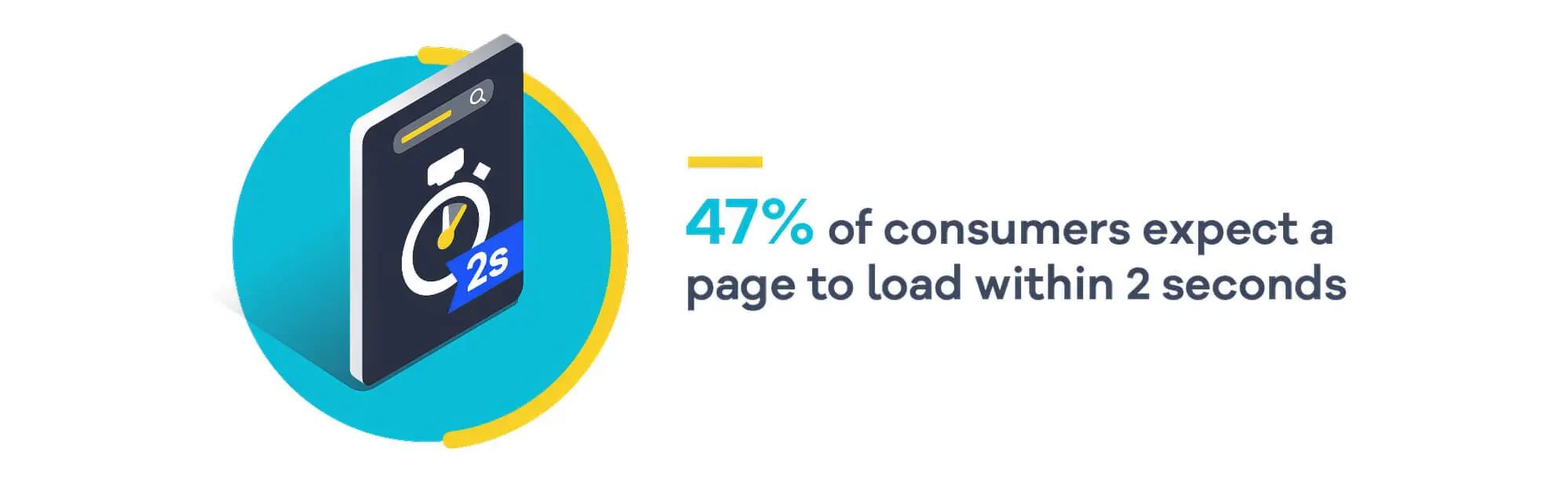
It also depends on many factors in the real world, like the user’s internet speed, the processing power of the user’s device, their browser, the number of background apps running, etc. You can only focus on improving your end of the business, such as the site’s server and performance, because you have no control over the other factors.
To begin with, you must know the different methods of measuring your page speed. We’ve discussed the three common ways below.
1. Fully Loaded Page
It shows the time Google takes to fully load 100% of a web page’s content or resources after a visitor opens the page. This is the most straightforward way to measure how fast an entire page can load, showing all its resources once your visitors click on the page link.
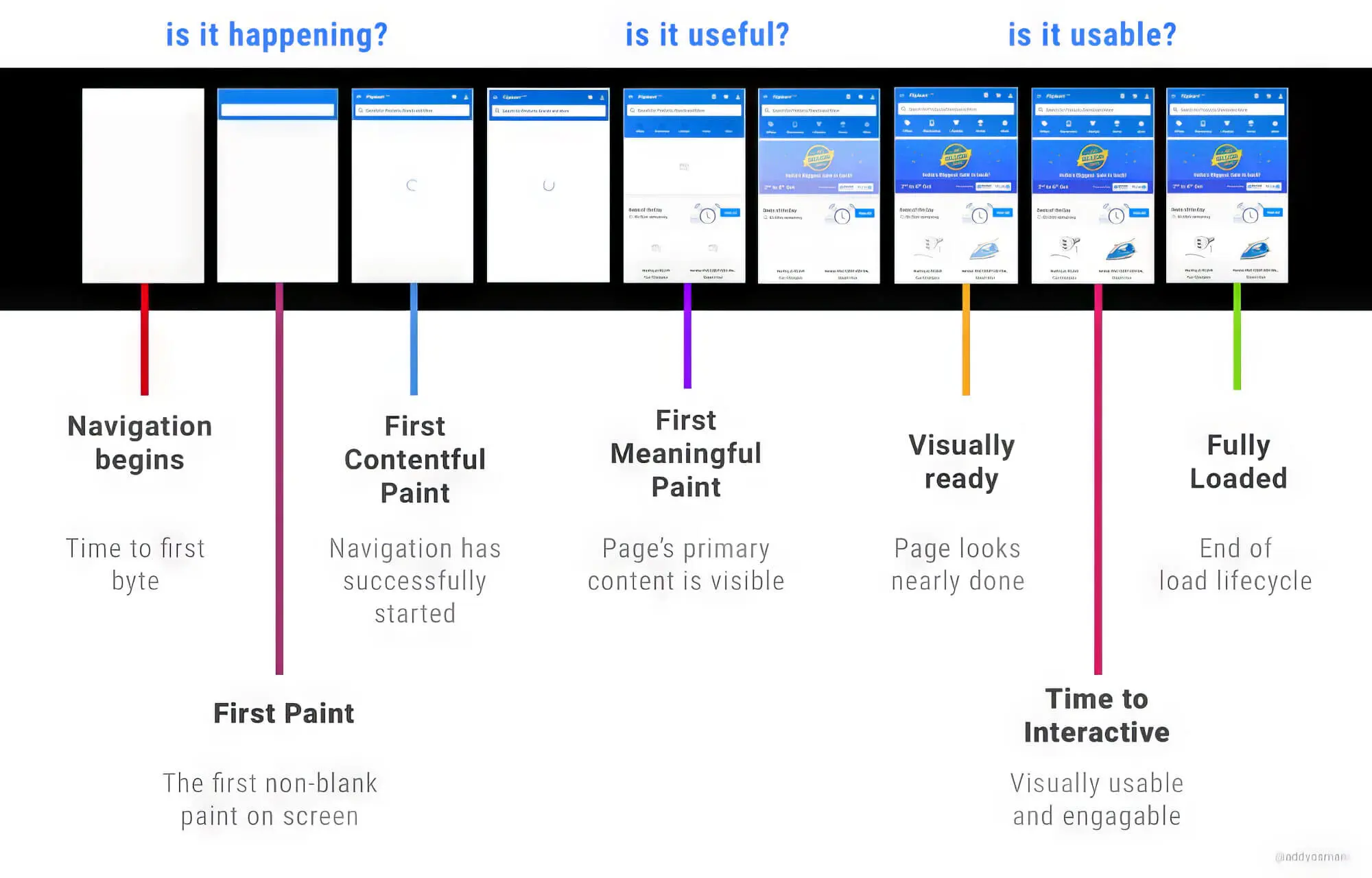
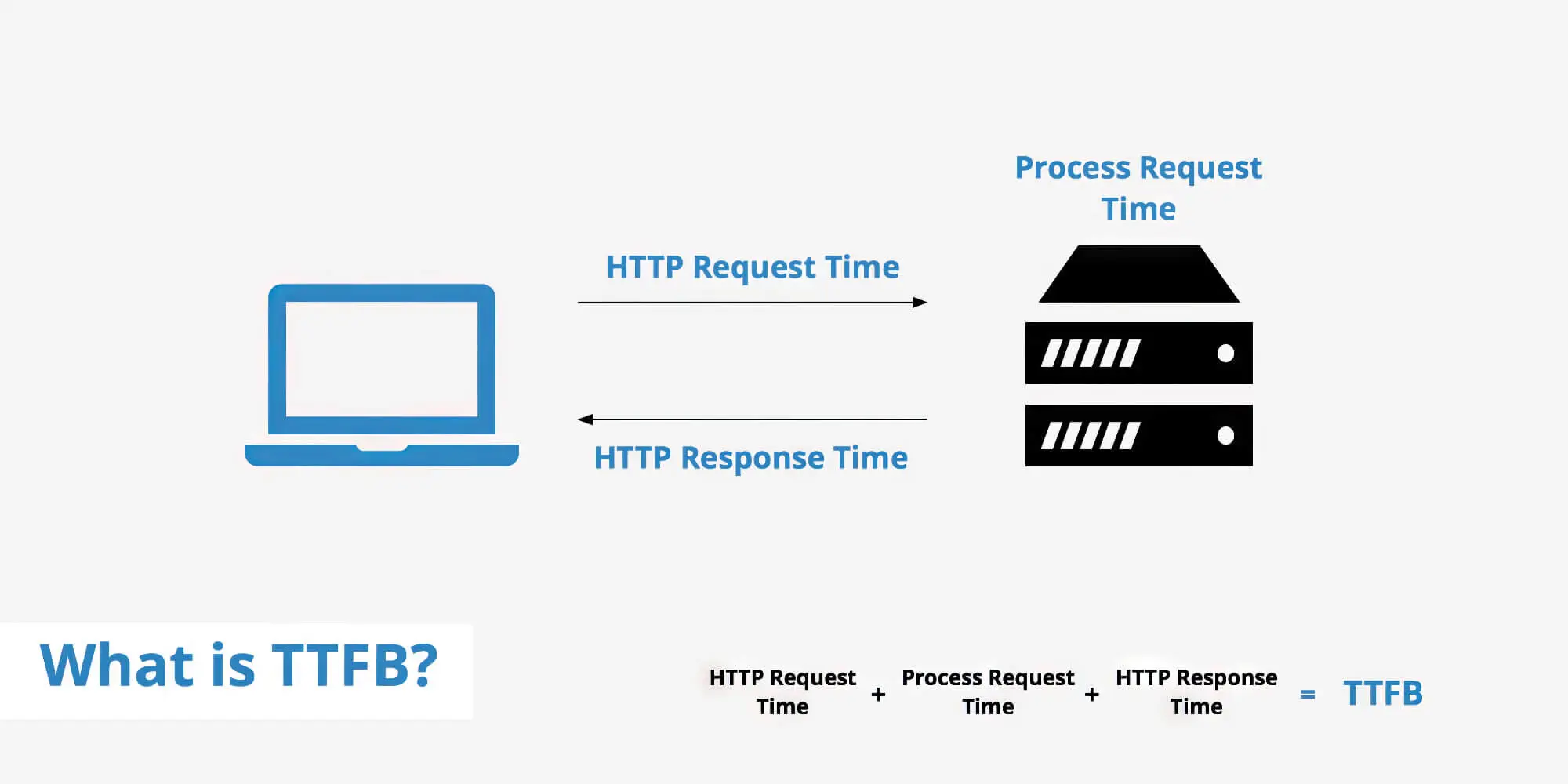
2. Time To First Byte (TTFB)
TTFB measures the time a web page takes to start its loading process. If your visitors ever open a landing page and have to stare at a white page on the screen, it means that the TTFB is at work.
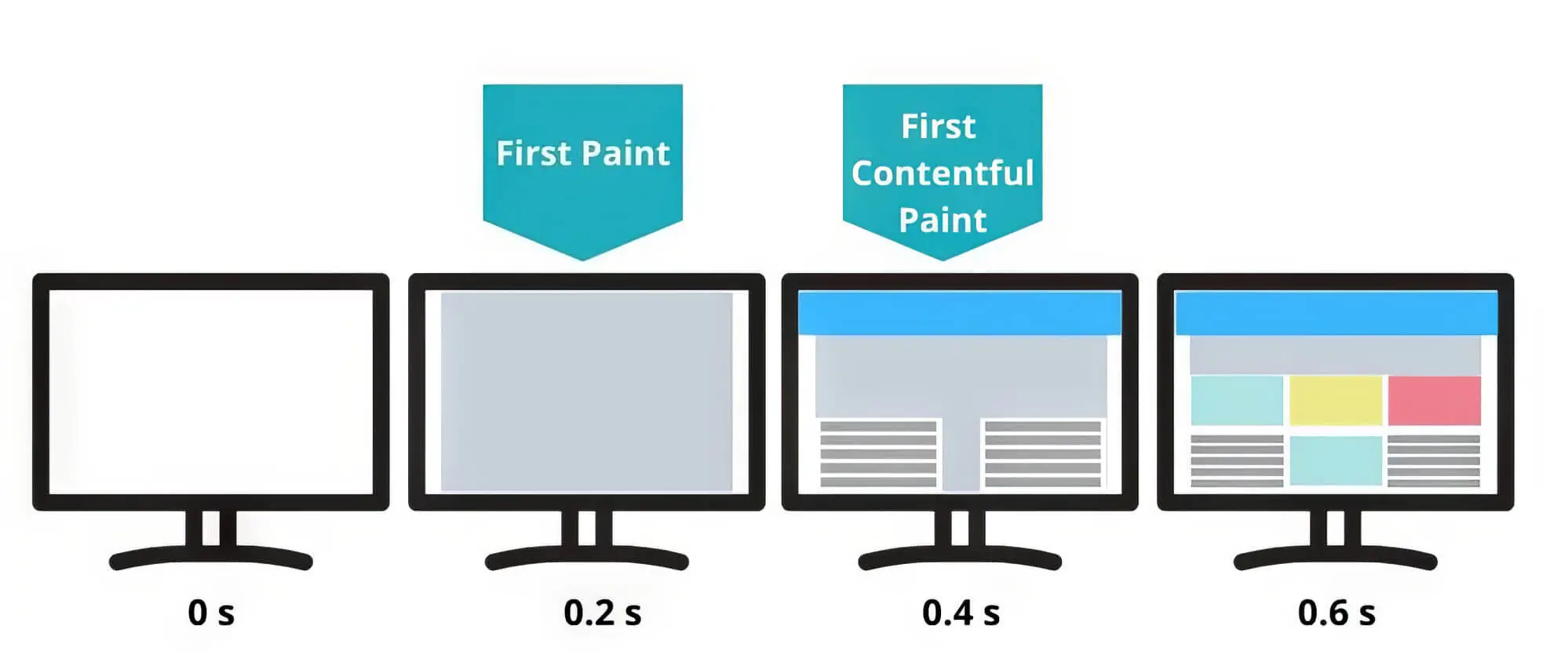
3. First Contextual Paint
In most cases, your visitors might come across a web page that takes time to load fully but shows some of its content. First, Contentful Paint measures how fast a page can load to show substantial content the user can read after visiting the page.
Say one of your online blogs takes ten seconds to load, which can be too long if you only consider the loading speed on the entire page. In contrast, considering the First Contextual Paint might be a better way to determine how your users interact with the blog post while the page loads.
For instance, even though it might take ten seconds for the entire page to load, users might come across the First Meaningful Paint within 1.5 seconds of landing on the page. They can instantly start interacting with your web page without waiting for the rest of the page to load. So, to your users, your web page is fast enough to reduce bounce rates.
Page Speed As A Ranking Factor
Google has regarded page speed as crucial since 2010, stressing its importance. However, until 2017, it acted more as a performance indicator than a direct ranking factor. This meant that even pages with average load speeds could achieve respectable Google rankings.
However, the importance of site speed as a ranking factor increased significantly in July 2018 with Google’s Algorithm Speed Update. This new page speed update prioritises site speed as a ranking factor for mobile searches when users browse web pages on their mobile devices. Before this 2018 Google update, the impact of page speed on a website’s search rankings was restricted to desktop users.
Additionally, recent studies from Google reveal that bounce rates can rise by 32% when page load times increase from one second to three seconds. Should your pages take more than five seconds to load, you risk losing substantial organic traffic, with bounce rates soaring to as much as 90%.
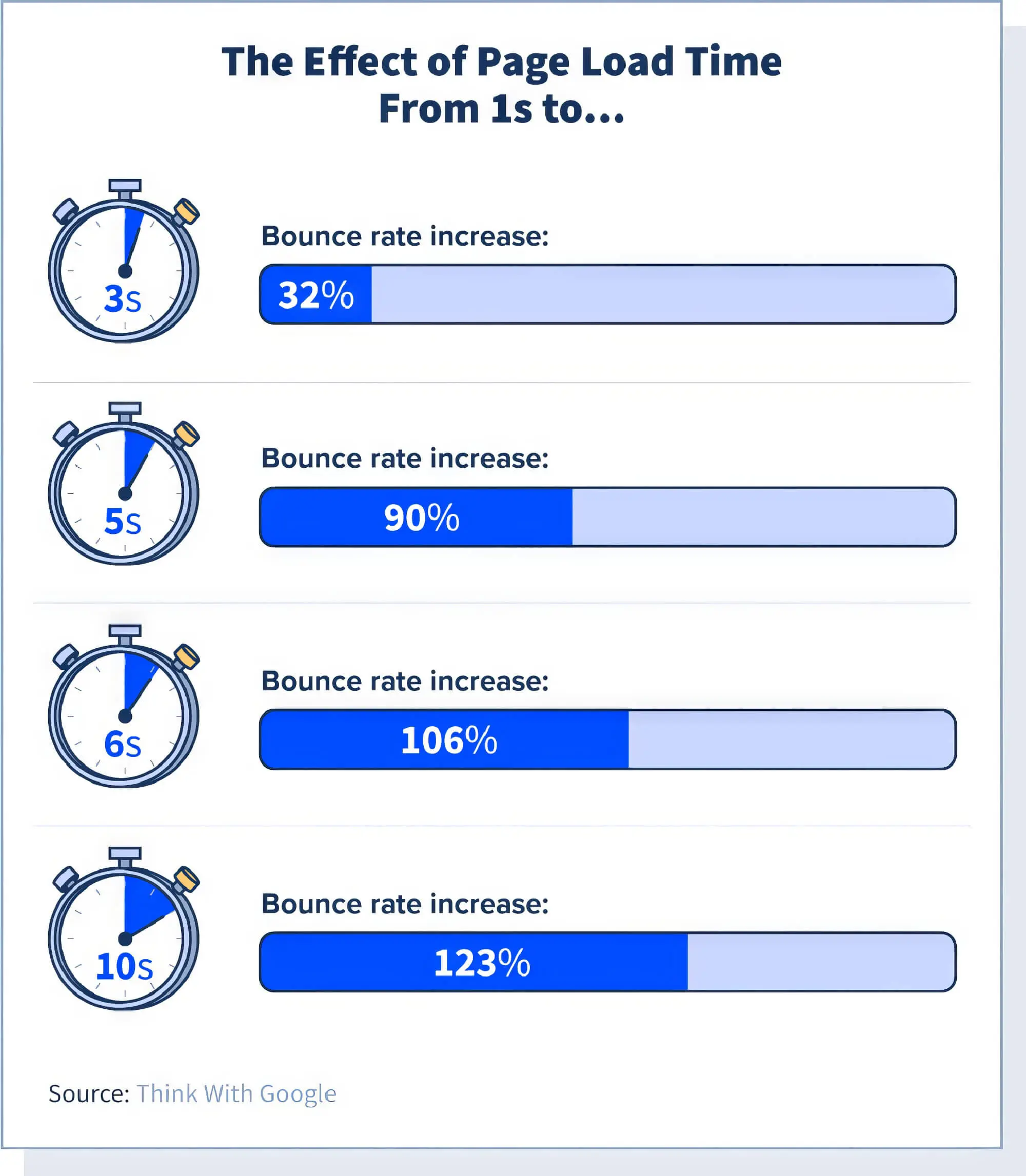
Additionally, if the website takes more than ten seconds to load, you can experience a bounce rate of 123%. Your conversion rate will automatically suffer if the bounce rate increases consistently due to your slow site speed.
Your website’s performance and search ranking are heavily tied to page speed, as search engines reward sites that deliver better results. With Google’s mobile-first index, optimizing your page speed is now more essential than ever to boost your rankings.
Google PageSpeed Insights
Now that you know how page speed works as a ranking factor, you might ask — What metrics does Google use to measure a website’s loading speed? This is where Google PageSpeed Insights comes in because the online tool uses a combination of page metrics to determine your website loading time. It identifies website performance and technical SEO problems and analyses your site’s user experience (UX).
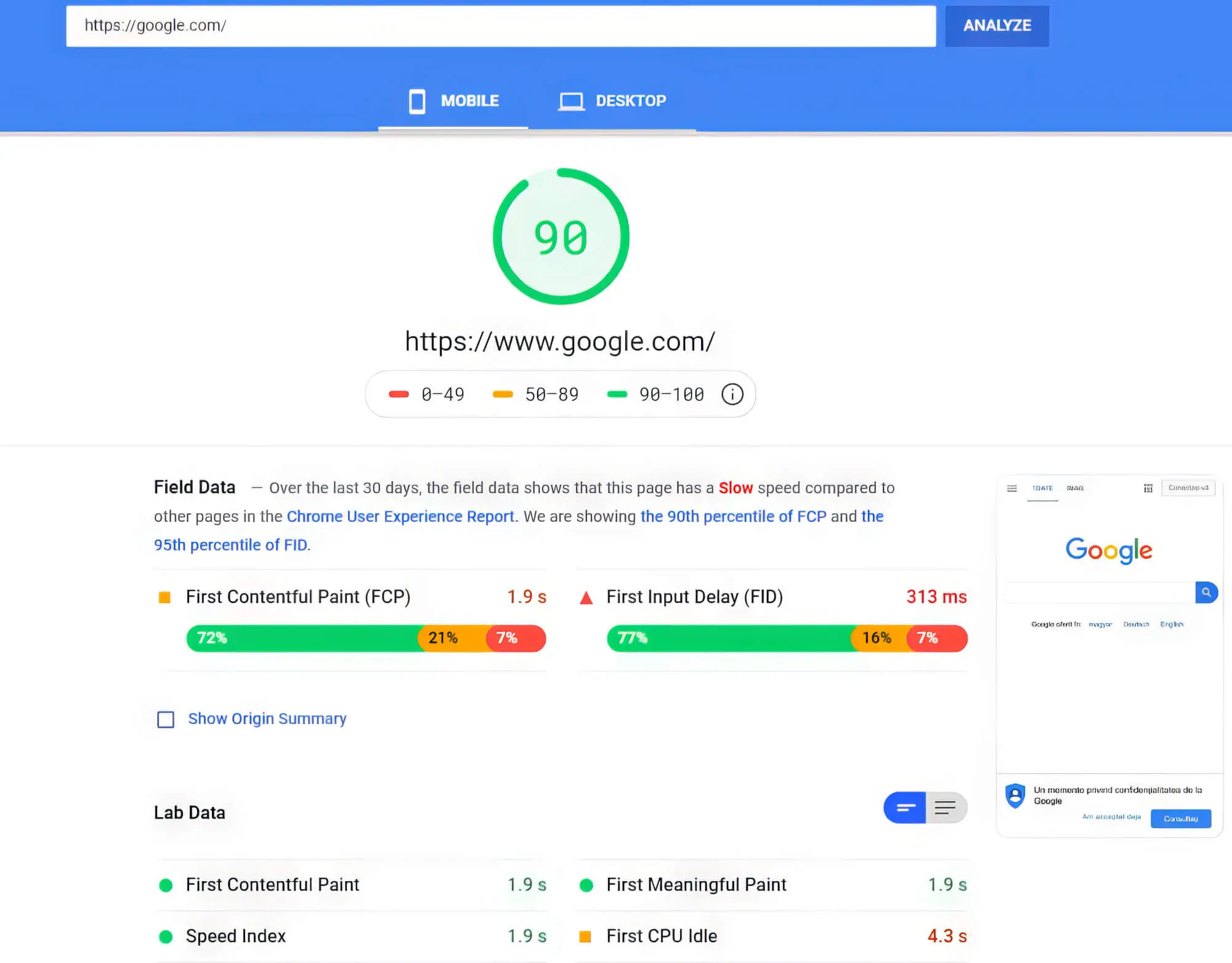
Once you enter your site URL, the tool will automatically run a diagnosis and show results regarding the site’s performance. You can view detailed information about the various factors impacting your page speed. Although there are other online tools, most SEO experts prefer using PageSpeed Insights to check website speed and performance.
Desktop Vs. Mobile
While testing the site speed, PageSpeed Insights offers two scores — a mobile version and a desktop version. Initially, only the desktop version was available, but since mobile searches have become more popular over the past few years, Google prioritises page speed for mobile versions. As of 2012, over 50% of online users are mobile users, prompting Google to launch its mobile-first index.
The first result on PageSpeed Insights is the mobile version of your website speed. In this case, your site is tested on a mobile device using a mobile connection, usually a 4G connection. However, many real users have a 3G connection, which can affect your site speed.
The problem with the mobile version score is that it’s not always about your site’s performance or speed and depends more on the mobile connection speed. So, based on the result, it might seem like your mobile site is slow, but it’s a slow connection speed.
In contrast, the desktop version speed score is always higher, thanks to light and fibre optics having a faster connection than 4G. Even though the site goes through the same testing, the scores differ because of the connection speeds.
The mobile version scores are more significant because mobile devices mostly work with slower connections. Thus, if you want to improve your page speed, focus on increasing its mobile version speed because the desktop version usually shows decent results.
How Does Page Speed Affect SEO?
As mentioned earlier, with Google’s Algorithm Speed Update in 2018, page or site speed is a direct ranking factor and can impact your website’s SEO. However, page speed can indirectly impact your site’s SEO performance by decreasing dwell time and increasing bounce rates.

Google prioritises a good user experience when ranking a website, and it has been seen that users usually leave a site after three seconds. So, if your page has a loading time of three seconds or more, it’s less likely to rank higher on a Google search because of the bad user experience.
Even while checking the PageSpeed Insights score, always prioritise your loading time (measured in seconds) over the score (measured on a scale of 0 to 100). Also, consider your server’s and hosting provider’s performance while measuring the site speed because the page speed loading score will vary based on the server’s different locations.
Imagine your server is based in Australia. If Google tests your site using a 3G connection in the US, your PageSpeed Insights score might suffer. While these scores are helpful, don’t rely solely on them — focus more on actual page load times.
You can also use other online tools to measure and enhance your page speed, which we will discuss in the following sections.
How To Improve Your Website’s Speed?
1. Server Response Time
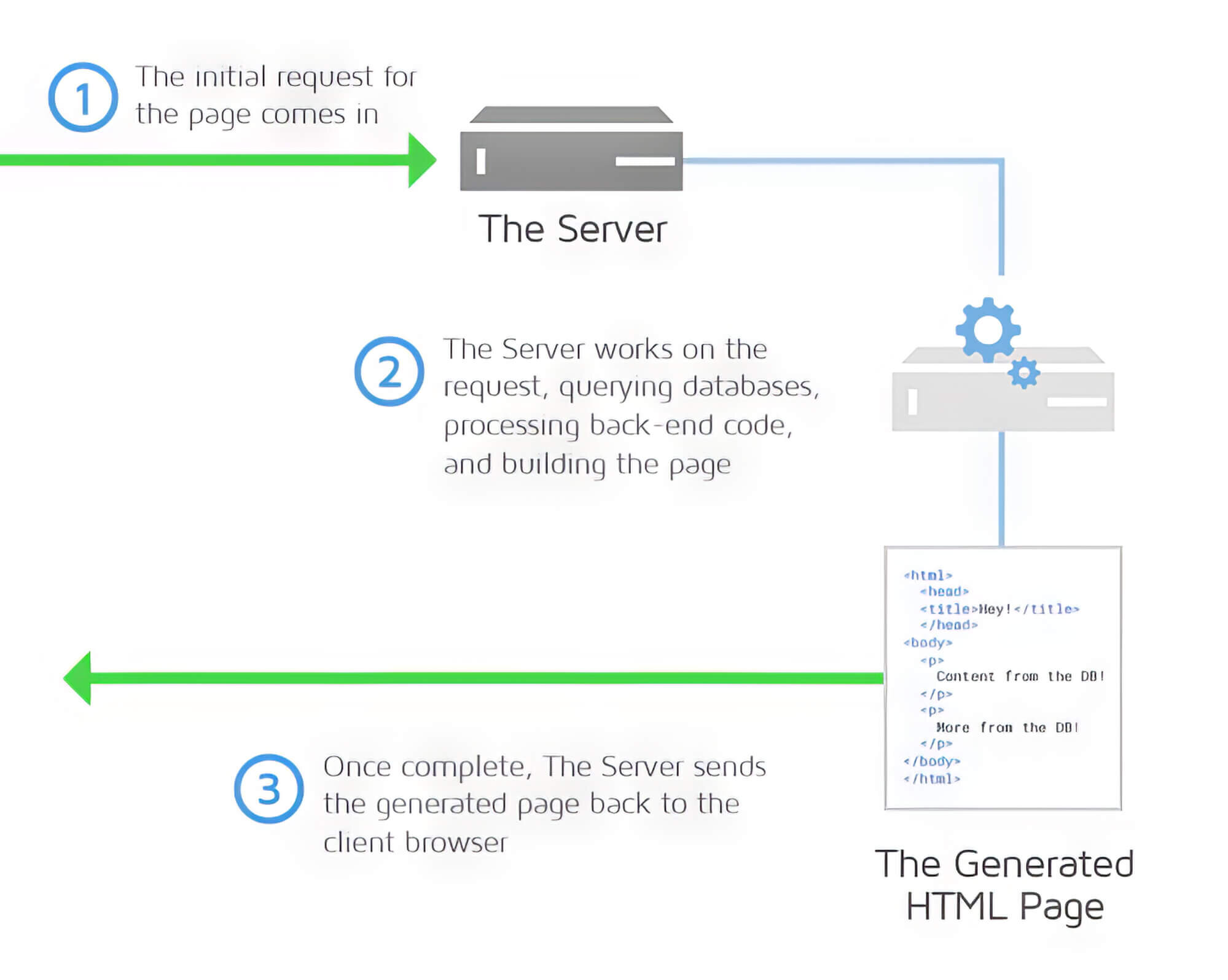
You don’t have direct control over server performance. Enhancing server response time usually means reducing the load or upgrading hardware, but these options are out of your hands if you don’t own the server.
The only thing you can do here is to select a good server, to begin with, to avoid the issue of slow server response time. A hosting company with a decent Google rank is supposed to offer a quality online service. However, if you’re sharing a server with several other websites, it’ll receive too many requests at a time, which will undoubtedly slow down your site loading time.
Since there are many web hosts, choosing a suitable hosting company can be confusing. But it’s always best to choose a web host based on your website requirements. For instance, if you want to emphasise local SEO, select a local server to get the best results while targeting the local audience.
In contrast, if you choose a foreign server, the online data must travel long distances before reaching your target audience. Under such circumstances, your site speed will automatically go down, affecting the website rankings. You can also consider upgrading to a dedicated server or a premium host to improve your website loading speed.
2. Image Compression
Images often pose the biggest challenge for maintaining site speed, as they can account for 50-90% of a page’s size. Website owners typically encounter two main issues with images:
- Actual image size vs. their screen size (in pixels)
- Disk size (in bytes)
Disk size refers to an image’s physical space on an SSD or a hard disk. The higher the disk size of an image, the more time it’ll take to download. For instance, a 100 KB image will download much faster than a 1000 KB or 1 MB image. So, if you have ten 1MB images on your web page, it’ll load very slowly.
To avoid this problem, you need to optimise the images. With programs like the WP Smush plugin, you can compress the disk size of your images without compromising their quality. You can compress a 1000x1000-pixel image to 150 KB from 200 KB. Although there won’t be any noticeable difference in the image quality, your site will load 25% faster because of the compressed disk size.
On the other hand, screen size signifies the display size of an image. If you use an image bigger than the size at which it’ll be displayed on the site, it’ll take more time to load.
For instance, if you upload a 1000x1000-pixel image for a designated display size of 300x300 pixels, you’ll lose loading time for the extra 700x700 pixels. The browser has to download the actual 1000x1000-pixel and then compress it to 300x300 pixels. It naturally takes more to download and compress the image.
But you can easily avoid this problem by uploading an image with the same height and width as the display size. Many content management systems (CMSs), like WordPress, automatically adjust the actual image size with its display size by creating multiple variants of the image once you upload it.
3. CSS And HTML Structure
The loading speed of your web page greatly depends on its HTML structure. Browsers always read the page from top to bottom and load all its elements similarly. If you want any component on your web page to load faster, place it higher on the page.
Usually, the problems with a web page’s loading speed lie with the CSS files, not its HTML structure. If your CSS is chaotic and unorganised, it’ll automatically slow down the page’s loading speed and result in a bad user experience.

Most web pages follow a basic HTML structure order of head, body, and footer. But if your CSS file designs the footer first, the footer will load before the body and header. Basic CSS training can help you understand this hierarchy better, and you can quickly identify such problems with the code.
Similarly, add non-vital scripts to the page footer so they are loaded last. In contrast, essential scripts, like Analytics, must be run immediately. That’s why add such scripts to the page header and ensure they run correctly.
4. Minification And Script Compression
Minification helps to compress a file size by removing unnecessary characters and information. For instance, while writing CSS and JavaScript, amateur coders often use spaces to make their code neat and tidy.
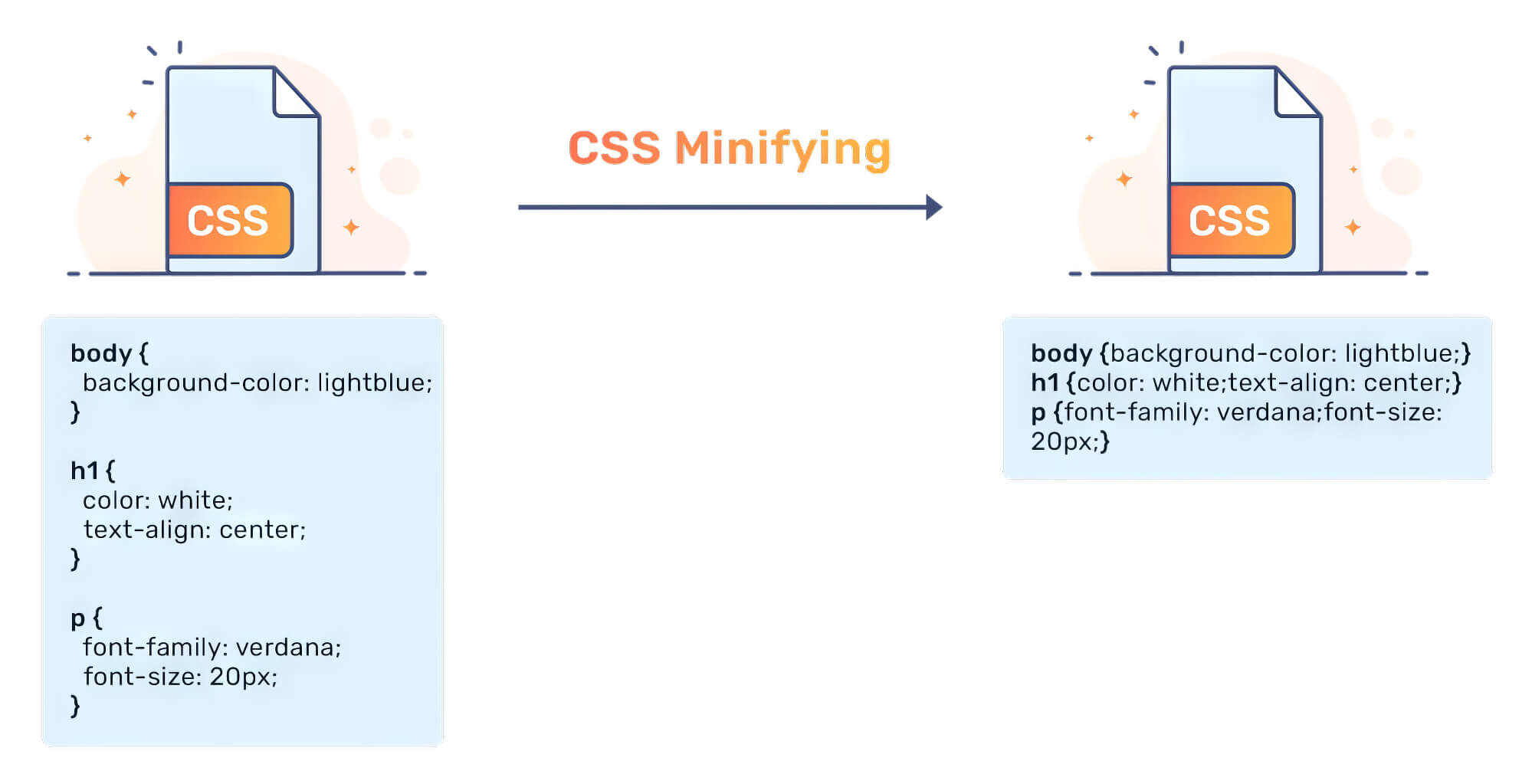
However, these extra spaces can slow the code, affecting the website loading time. So, cleaning up your code is essential to make your site load faster. You can also minify code by combining identical components, like the header and footer.
Further, you shrink files by removing recurring information sequences and replacing them with only one particular sequence through compression. GZip compression is the most common example in this context. You can combine the scripts using free plugins and have one file instead of two to improve your site and page speed.
5. Activate Browser Caching
Browser caching allows regular visitors to store some parts of your web page on the browser cache, so the next time they visit your page, it’ll load much faster. You can use a short cache policy to allow the storage of dynamic elements and a long cache policy for storing static resources.
Cache plugins on WordPress, such as W3 Total Cache or WP Rocket, can help you properly handle cache protocols. You can also set up a .htaccess file cache for the site’s cache control if you don’t use a CMS like WordPress. However, browser caching won’t work for first-time visitors.
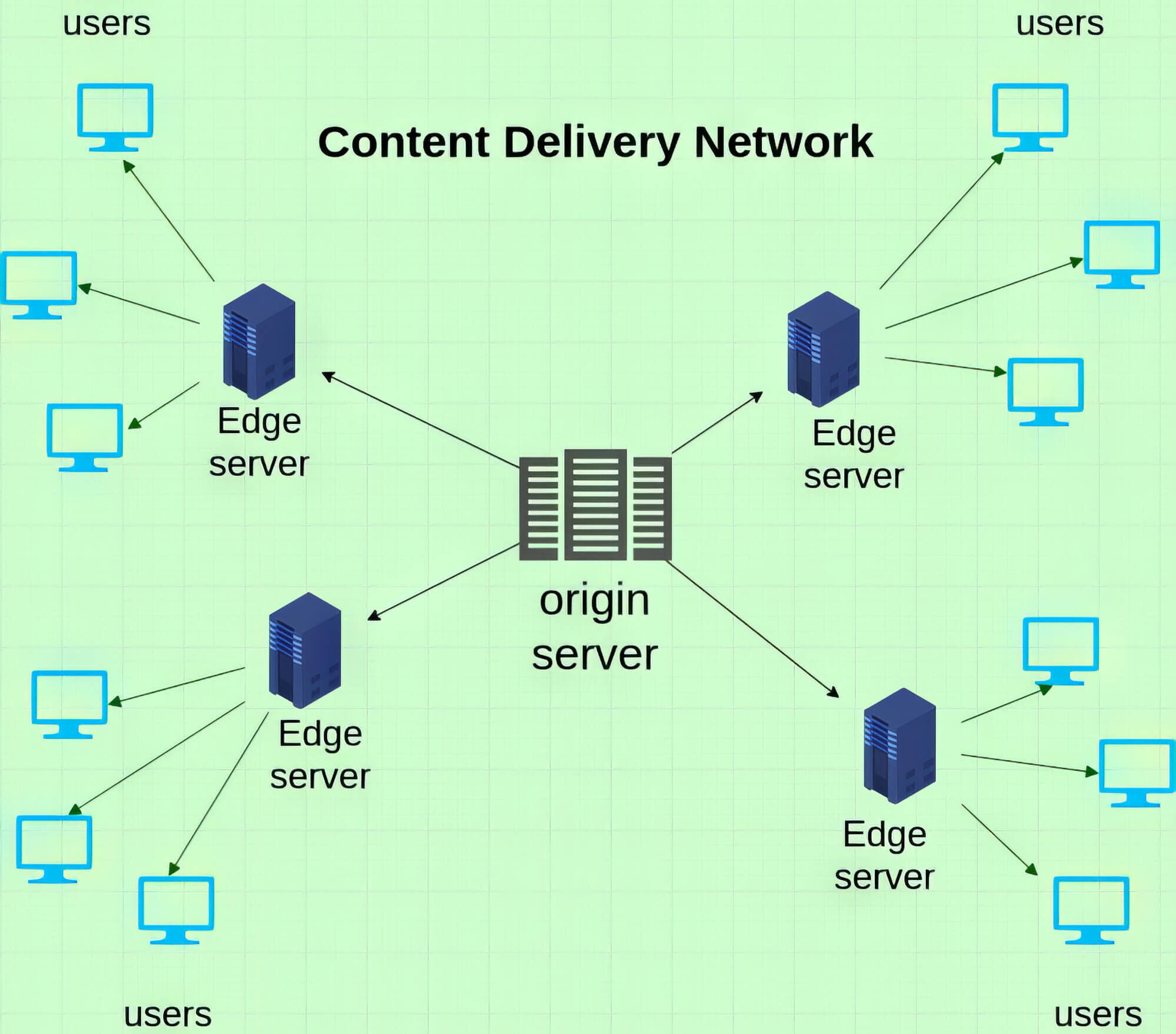
6. Implement A CDN
Implementing a content delivery network (CDN) is an excellent way to boost your site’s loading time. It detects your visitors’ physical location and provides them with your site’s content from a server near them. This way, your site resources don’t have to travel long distances before reaching the visitors, and your website will load much faster.
Other SEO Tools To Improve And Measure Site Speed
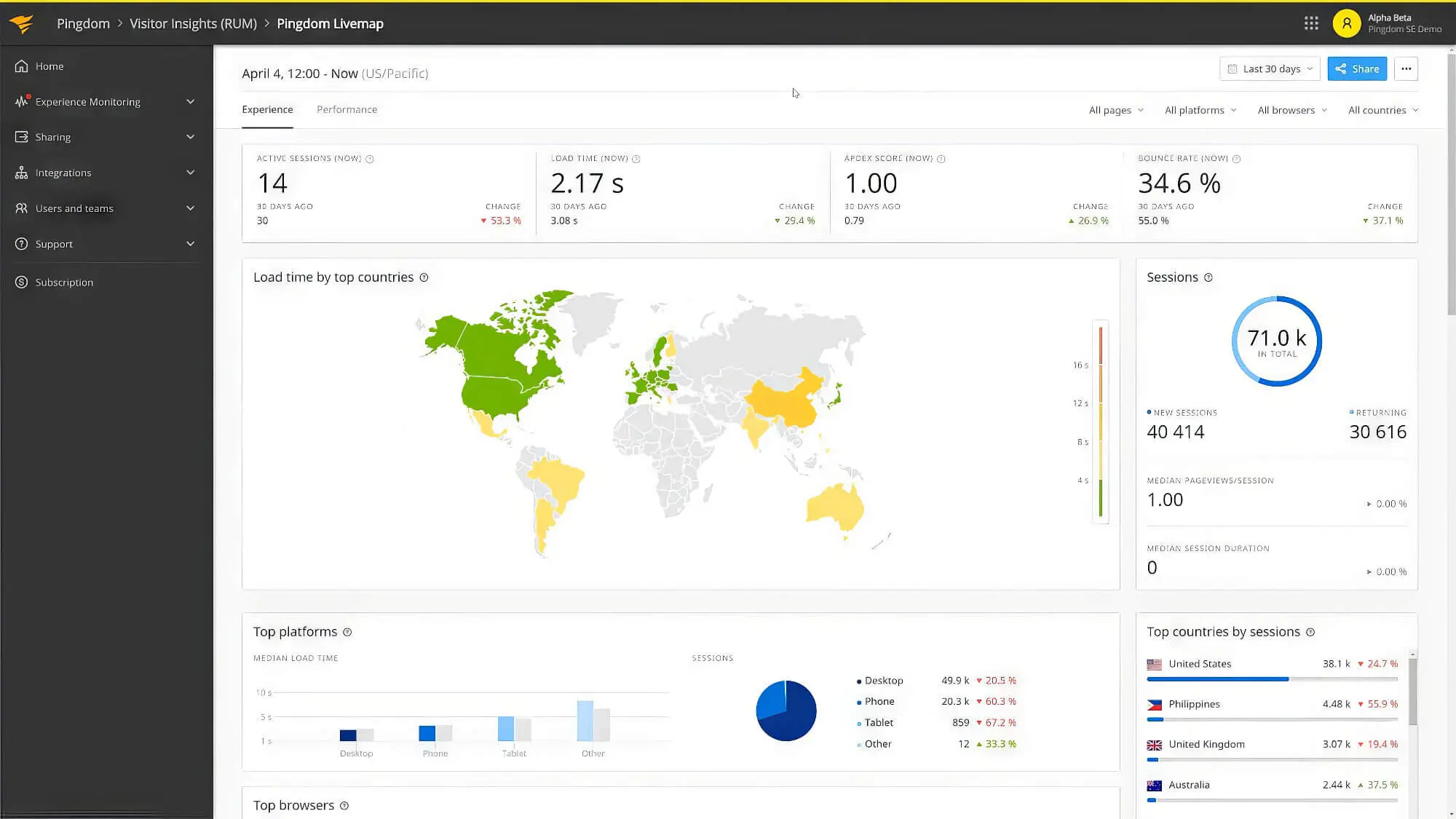
1. Pingdom
Pingdom allows you to choose the location of the test and offers results regarding your web page loading speed based on the location. For instance, if you’re focusing on local SEO and using a local server, choose a location closest to your server to get more accurate results. You can also run multiple tests from different locations to check the site speed if you have a global customer pool.
2. Mod_pagespeed
It’s a Google server add-on that directly fixes site and page speed problems on the server’s end. Even if you have unoptimised images on your page, mod_pagespeed optimises, compresses, and converts them into next-generation image formats. However, it can increase server load every time you upload an unoptimised image, and the tool has to use the server’s processing power to convert the image.
3. Google AMP
Google Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a Google Chrome plugin that helps to improve your site loading speed on mobile searches. It strips down your web page of heavier and slower-loading elements. So, every time users open the Chrome browser on their mobile devices to view their search results and click on your web page, it loads instantly.

With A Fast Website, You Can Rank High!
So, how does site speed affect SEO? We hope you’ve learned how site and page speed impact website rankings from our guide. Although several online tools offer scores on your page speed, always prioritise the page loading time instead of these scores to improve your page speed.
Additionally, image compression, finding a decent server, minifying your code, and having a clean HTML and CSS structure can largely benefit you in designing a fast site. You can choose a shared server if you have a small site, but it’s best to select a premium web host to maintain a large website’s loading speed.
If you don’t have an in-house SEO team, the best way to get the job done is by hiring experienced professionals, such as sitecentre® in Perth, who can apply their extensive knowledge to get the job done quickly and successfully. We can work with you to optimise your website and page speed to ensure you meet your business objectives and goals. Please find out how we can help you by contacting us today!
Thank you for taking the time to read our guide on why page load time is a critical factor that can affect SEO. See you in the next article!




