No matter where you look nowadays, SEO is everywhere.
After all, why shouldn’t it be? With search engines becoming an extension of the human brain, it’s more vital than ever before that businesses can get to the top of the SERPs to grab customer attention. And the most sustainable method of doing that is SEO.

These days, it seems like everyone’s talking about different types of SEO: on-page, off-page, and now, technical SEO. But what’s the real difference between them, and why is technical SEO becoming so crucial as search engines keep evolving?
To know all that and much more, stick around until the very end!
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
What Is Technical SEO Anyway?
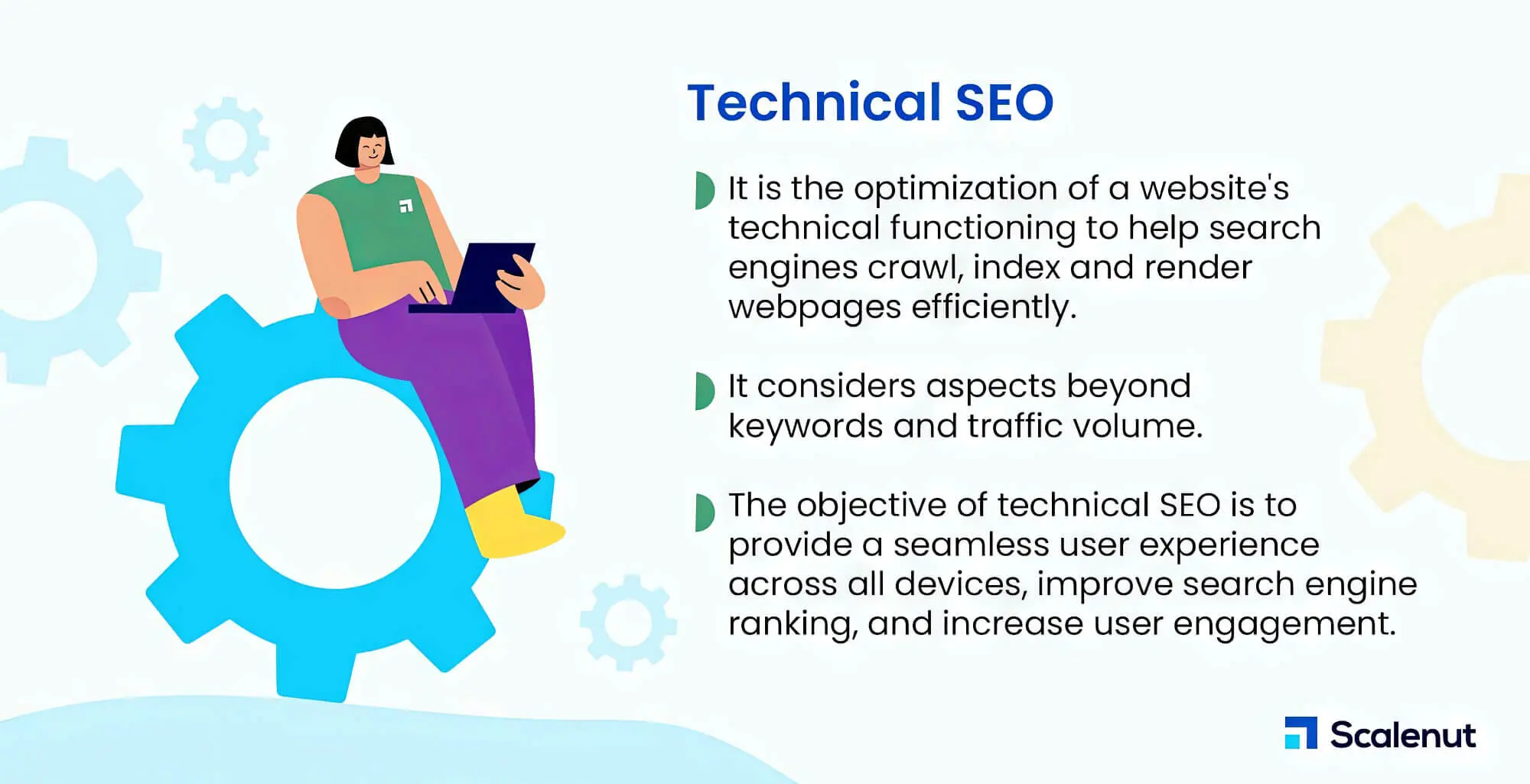
First, address the massive elephant in the room: What’s technical SEO? To put it in as simple terms as possible, technical SEO refers to optimisations in your website and servers that allow search engine bots to crawl and index your website pages better.
Imagine your website as your online storefront. You want to make sure everyone can find it effortlessly. That’s where technical SEO comes in. It’s like providing clear directions, ensuring your site meets the tech needs of search engines so they can find and rank it higher, making it easy for visitors to reach.
Technical SEO optimises essential elements like CSS and JavaScript files on your website yet often overlooked parts, such as proper indexing, content delivery, optimised crawling and site architecture. However, this list is far from exhaustive; modern search engines are evolving at breakneck speeds, and technical SEO needs to evolve to ensure effective website visibility.
How Is It Different From Other SEO Types?
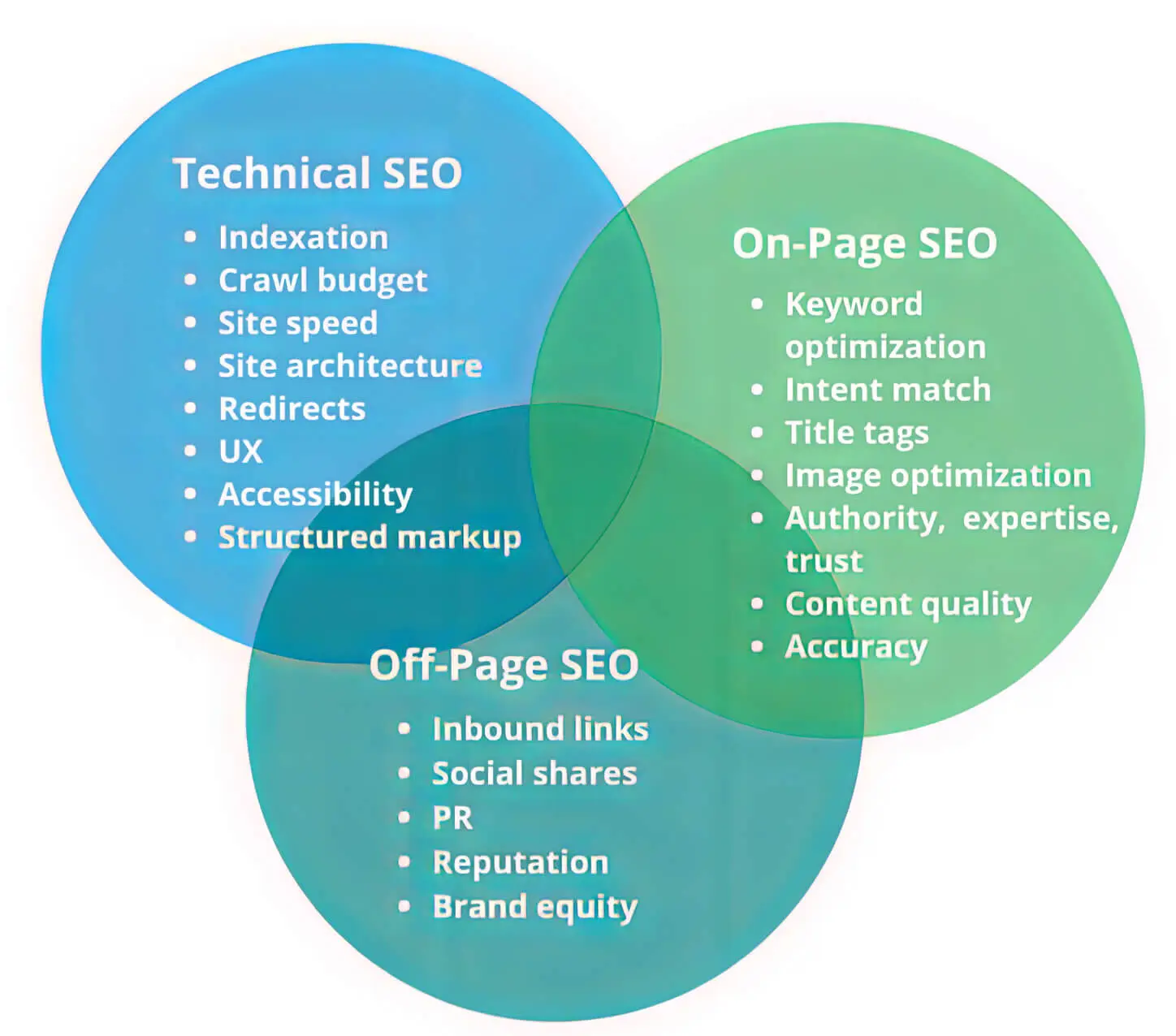
When talking about SEO, you often hear two terms: on-page and off-page. However, technical SEO is also part of the mix, and here we’ll take a quick look at how they’re related.
1. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is exactly what it sounds like: SEO activities that are not directly related to your website pages. This predominantly includes getting backlinks to your website from other credible sites. As per Google’s PageRank algorithm, more backlinks from credible sources will significantly boost your page’s rankings.
Remember that the number of backlinks is not the issue here, although that does matter. The quality of the links is more important, as are the methods by which you garner them. Resorting to black-hat techniques such as link farming can harm your website as much as links from shady online sources.
2. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is the opposite of off-page SEO as it deals with all the SEO factors related to the pages of your website. On-page optimisations involve techniques such as keyword incorporation, meta optimisation, tag optimisation, and internal linking that help search engines understand your content.

3. Technical SEO
Finally, here is the stuff we’re dealing with in this guide! Technical SEO is everything related to organic SEO involving the actual website technology and structure. This is also called the invisible part of search engine optimisation, as these factors don’t visibly show up on web pages as external and internal links or keywords and headings in the content do.
Technical SEO involves behind-the-scenes elements such as fixing broken links, improving crawlability, and helping search engine algorithms find and rank your site faster. It even involves server-side optimisations that can help load your website faster across multiple devices.
If you think about it closely, technical SEO can be classified as a part of on-page SEO as it’s related to website page elements. However, experts prefer to separate it from regular on-page/off-page optimisations as it does not deal with content optimisation or link building. Instead, it’s an entirely technical aspect that involves optimising JavaScript files, and a detailed understanding of SEO and website operations is needed.
The Importance Of Technical SEO
After reading up to this point, you may wonder why we’re worried and why technical SEO is essentially worried (and why you should also be) about getting technical SEO right. After all, if you want to make your website more visible, it ensures the website pages are visible to Google.
Well…yes, in a way, and no.
While technical SEO is about sending out the proper ranking signals to search engines, it’s much more than that. Sending the right ranking signals to search engines is part of the technical SEO checklist, which can also be achieved with proper backlinking and quality content.
However, no matter how good your content and high-quality backlinks you can garner, all that will only be worthwhile if a search engine can crawl your pages. At the most fundamental level of SEO, a search engine bot needs to be able to find, crawl and index your website. You can start thinking about Google ranking signals when these things are achieved.

Just The Tip Of The Proverbial Iceberg
But wait! Don’t get too comfortable, because as with everything related to the internet, that’s only scratching the surface. Even after the search engine crawlers have found their way into your website, the task is far from done.
To reach the top (or at least the first page) of Google rankings, you must go through a thousand (maybe not that many) other things. These include making your website more secure, fast-loading, optimised for mobile, and eliminating duplicate content…the list is rather long. But we’ll get into it in a bit.
When done correctly, Technical SEO can help cut down redirect chains and support other on-page and off-page SEO tactics to ensure that your search rankings are spot on, or at least better than your closest competition. By improving your website’s technical aspects, such as structured data and broken links, you can get your website indexed and ranked faster.
And naturally, the reverse is true as well. If you’re making severe technical mistakes on your website, it can cost you SERP rankings. A stray slash in just the wrong place in your robots.txt file can stop search engines from crawling your website.
Technical SEO For Humans
Until now, we’ve mostly talked about how improving technical SEO can help your important pages rank higher on searches. This might have led you to believe that technical SEO focuses solely on search engines and how they perceive your website.
Well, if you think that, then you’d be wrong.
Improving technical SEO, including the load time of your web pages, indeed helps your search ranking by making your website more accessible to search engines. But that’s not the only aspect it helps; technical SEO is also targeted towards human users. Improving aspects of technical SEO ensures that your website works flawlessly and offers a great user experience to visitors.
Improving technical factors such as site speed and responsiveness helps reduce bounce rates and keeps visitors on your site for longer. Again, this sends positive signals to search engines, leading to better SERP rankings.
So, technical SEO, which includes things like installing an SSL certificate, is one aspect of optimisation you can’t deny, whether for search engines or humans. But as we’ve already said, even the technical SEO basics checklist is long, and not all factors are as important as others, and it’s crucial to follow the best practices as the others. The next section will discuss some crucial technical SEO factors to consider while optimising your website.
Technical SEO Factors To Keep In Mind

At the risk of sounding repetitive, technical SEO is not just a function of crawling and indexing your website pages. It’s a much more nuanced task that involves multiple technical factors of your website. With that in mind, let’s jump into our technical SEO checklist.
1. Navigation And Site Structure
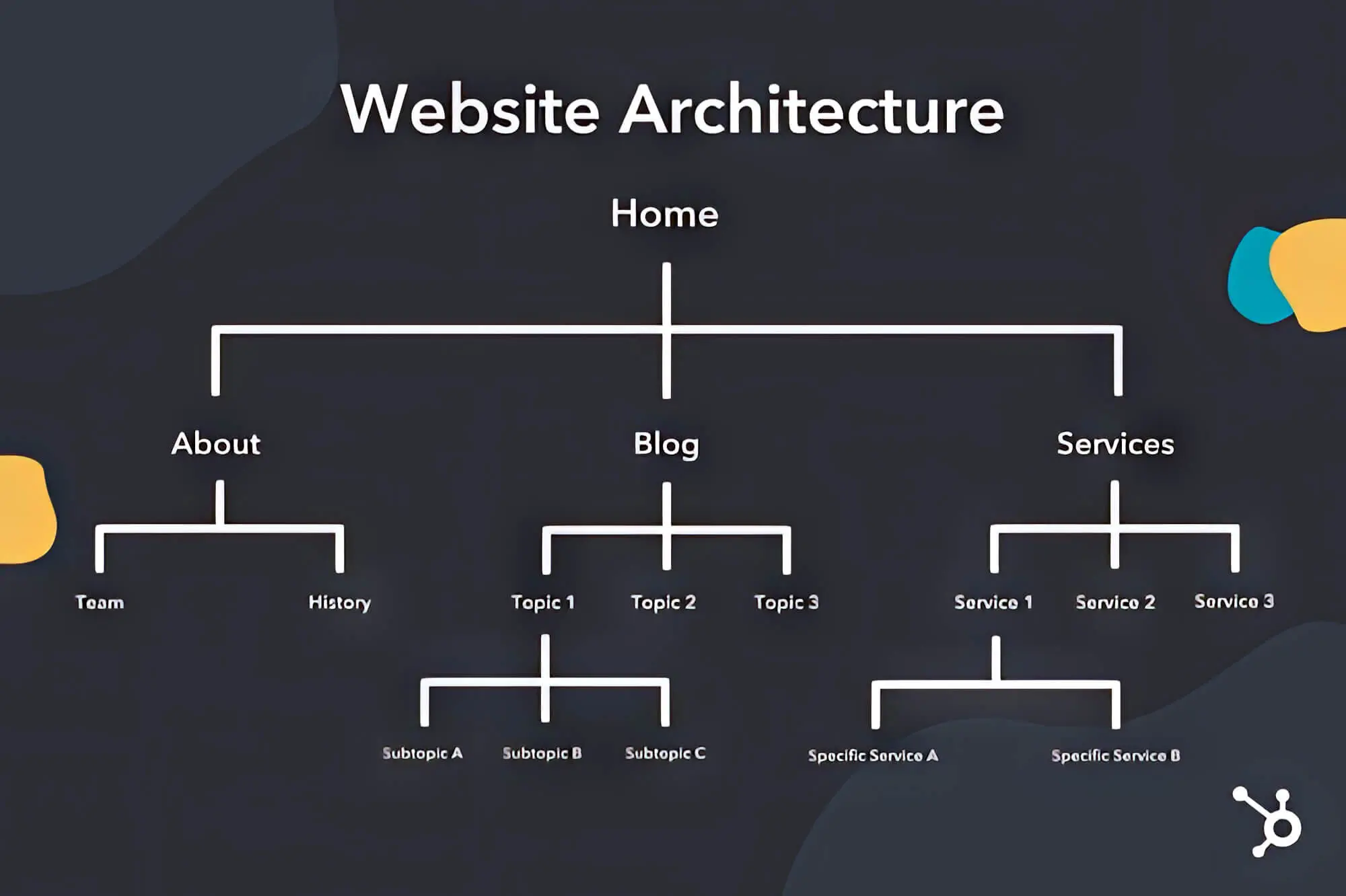
Return to our store/office analogy and consider mobile-friendliness as an important aspect: your website is your business’s online property, and ideally, pages should load within 3 seconds property, and you should treat it like you would a physical location property. And just as a store/office has multiple departments, your website also has various pages and sections.
Now, if your online property, especially your home page, is messy and disorganised with stuff strewn all over the place, neither visitors nor employees can find the right things when needed. Similarly, a website with a messy structure and poor navigability hurt your SEO efforts in multiple ways.
We’ve observed that in many cases, webmasters trying to optimise a website for conversions end up tinkering with the site structure, which usually does more harm than good. A poorly designed site structure can lead to long-term crawling and indexing problems.
In addition, the site’s structure influences every other step you take to optimise it. Whether fine-tuning page URLs, using SEO tools like Screaming Frog, submitting the sitemap file, or using the robots.txt file to prevent search engines from indexing certain pages, it all flows from the site structure.
So, what steps can you take to optimise your site structure for the better? Let’s take a closer look.
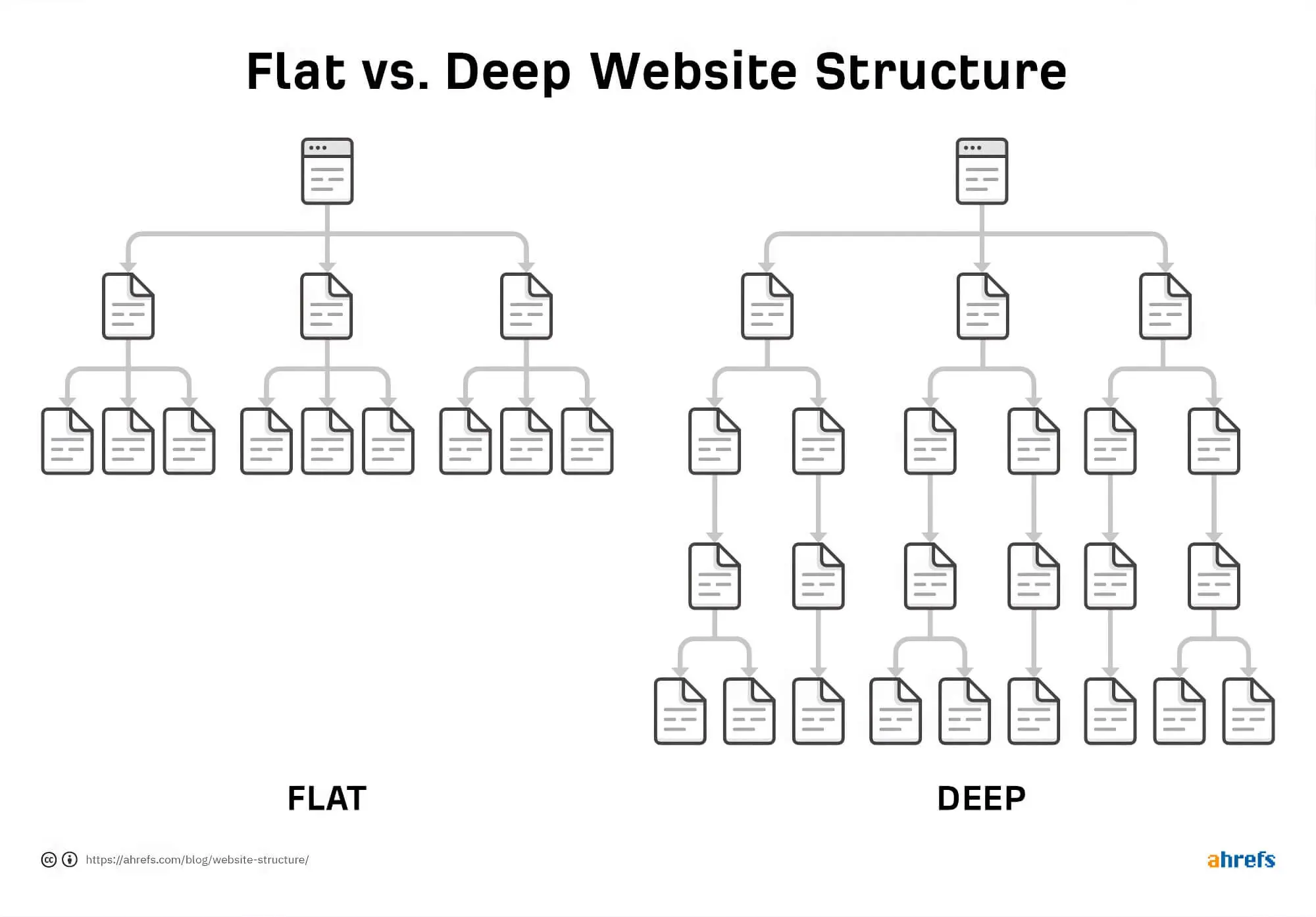
A. Stick To A Flat Site Organisation
In a nutshell, your site structure refers to the organisation of all your website pages. For best results, you’d want this to be a “flat” structure, saying every page should have only a few links separated from every other page.
This is vital because a flat site structure is more effective if your website is mobile-friendly, making it simpler for major search engines to crawl all your website pages. And while how search engines crawl your website is not a significant deal for small, single-page sites, for a massive website (think Amazon), it can make a massive difference.
Apart from “flatness,” another aspect to consider is page organisation, which should be neat and orderly. Messy structures can lead to “ orphan pages,” which are pages without any internal links; these can affect various ranking factors and internal links to them, making indexing challenging.
B. Make Sure The URL Structure Is Consistent
We get it: URL structures for large sites tend to get complicated; however, URL structure consistency is vital for larger websites with multiple URLs. For smaller websites, there’s no need to overthink URL structures.
Whatever the case, a clear and consistent URL structure, even if you have two versions of your site, helps visitors navigate. A consistent URL structure also helps visitors find their way around the site. Also, putting different pages under related categories helps search engines get additional context about every page under each category. For instance, even though Google SERPs show page-level results, the algorithm needs to derive a better context of how the page fits into the larger scheme of the site.
C. Include Breadcrumbs Navigation
Almost every SEO professional worth their salt knows that breadcrumbs navigation goes a long way to support SEO by automatically adding internal links to subpages and category pages. This way, they help improve your site architecture and support that Google turns URLs into breadcrumb-style navigation in the search results.
D. Use Structured Data Markup
Structured data markup is another vital aspect of technical SEO you should pay attention to. Structured data helps search engines understand your site’s content and its purpose. Additionally, structured data can provide Google and other search engines with a better understanding of your business.
For instance, if you’re an eCommerce store, structured data will help Google understand what kind of goods you’re selling. This way, search engines can quickly interpret the context of your content and serve it to searchers as and when needed.
Using structured data will help search engines better interpret your website but will also help you get into the featured snippets on Google. And as we all know, everyone is vying for featured snippets nowadays. So, remember to add structured data to your technical SEO efforts.
2. Register With GSC And BWT
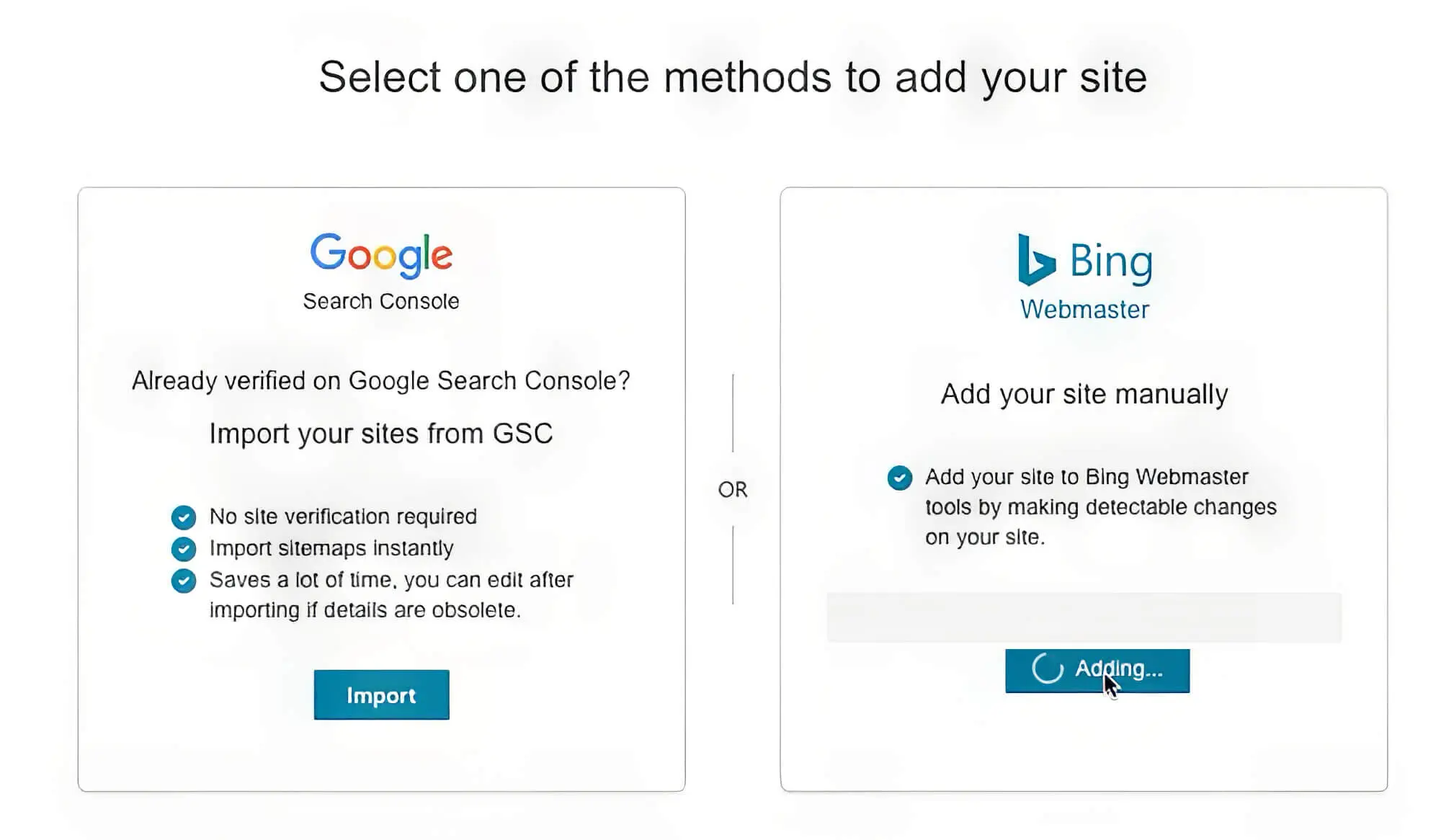
Sounds cryptic? Not when you know that GSC is Google Search Console and BWT is Bing Webmaster Tools (that last one we made up for fun!). Both Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools are free tools from the respective companies that make it easy to submit a website for indexing.
All you need to do is create and submit an XML sitemap of your website to both Bing Webmaster tools and Google Search Console so the bots can start crawling and indexing your pages. The faster you complete this process, the earlier your pages appear in the SERPs.
Apart from letting you submit XML sitemaps, both Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools allow you to monitor your website’s search engine performance. You can even use the tools to test your website’s backlink status, remove spammy links and access search analytics.
Before submitting XML sitemaps, ensure they’re clean, with all URLs enabled to return 200 status codes and suitable canonicals. This will ensure that the allocated crawl budget is not wasted on broken or duplicate pages.
3. Prepare The XML Sitemap With Care
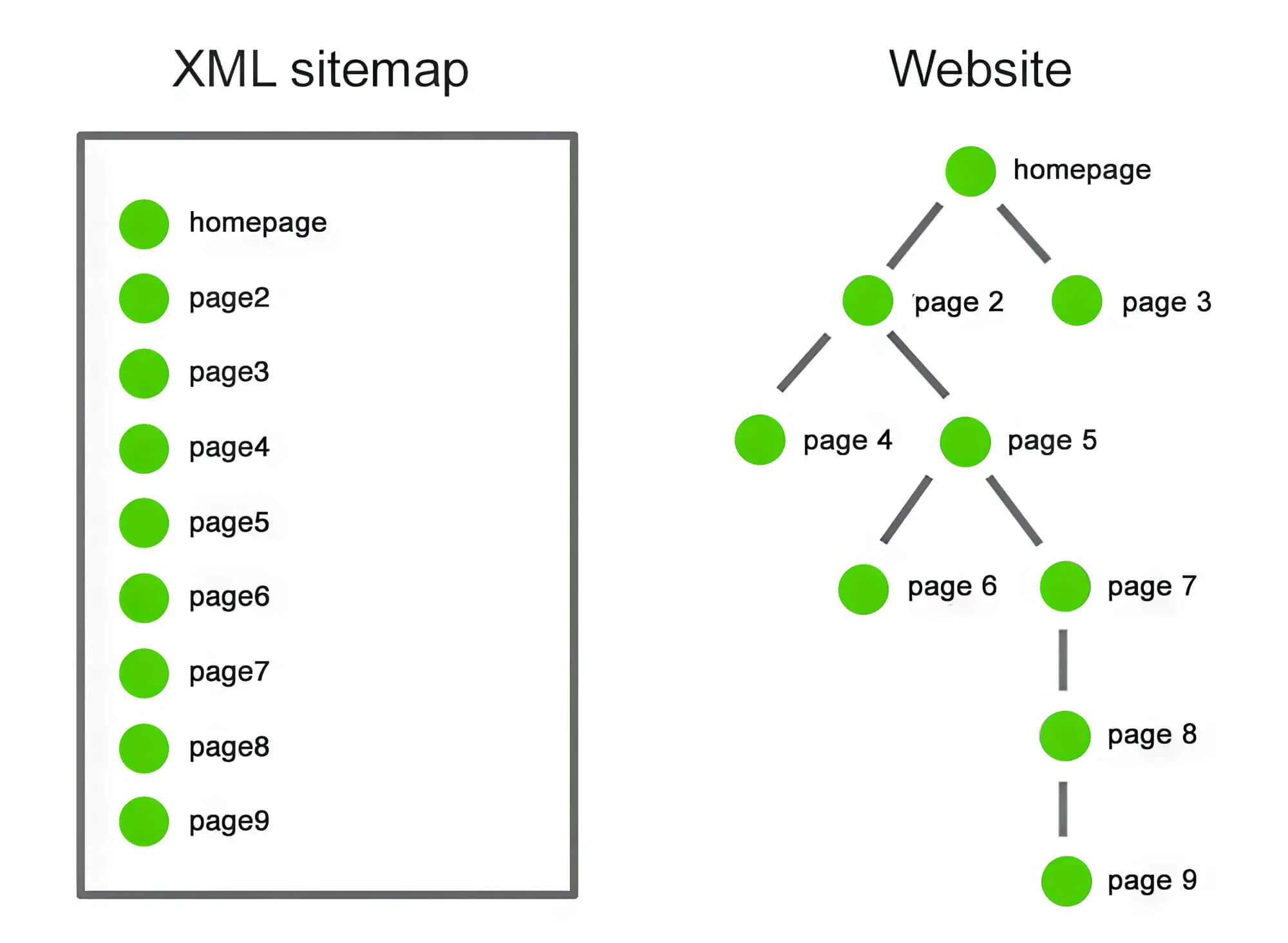
To be honest, this could have been mentioned before the above point, but we wanted to ensure that you understood why it’s needed in the first place. Now that you know the value of XML sitemaps, let’s look at why you should prepare them with care.
An XML sitemap is a simple XML file containing information on your website’s pages and relevant data about them. This sitemap file is vital because it helps search engines easily understand your site structure.
Before submitting an XML sitemap, please ensure you only include those pages that are vital to your website. Things not to include in an XML sitemap are author pages, tag pages, and pages with little or no content.
4. Focus On The Robots.txt File
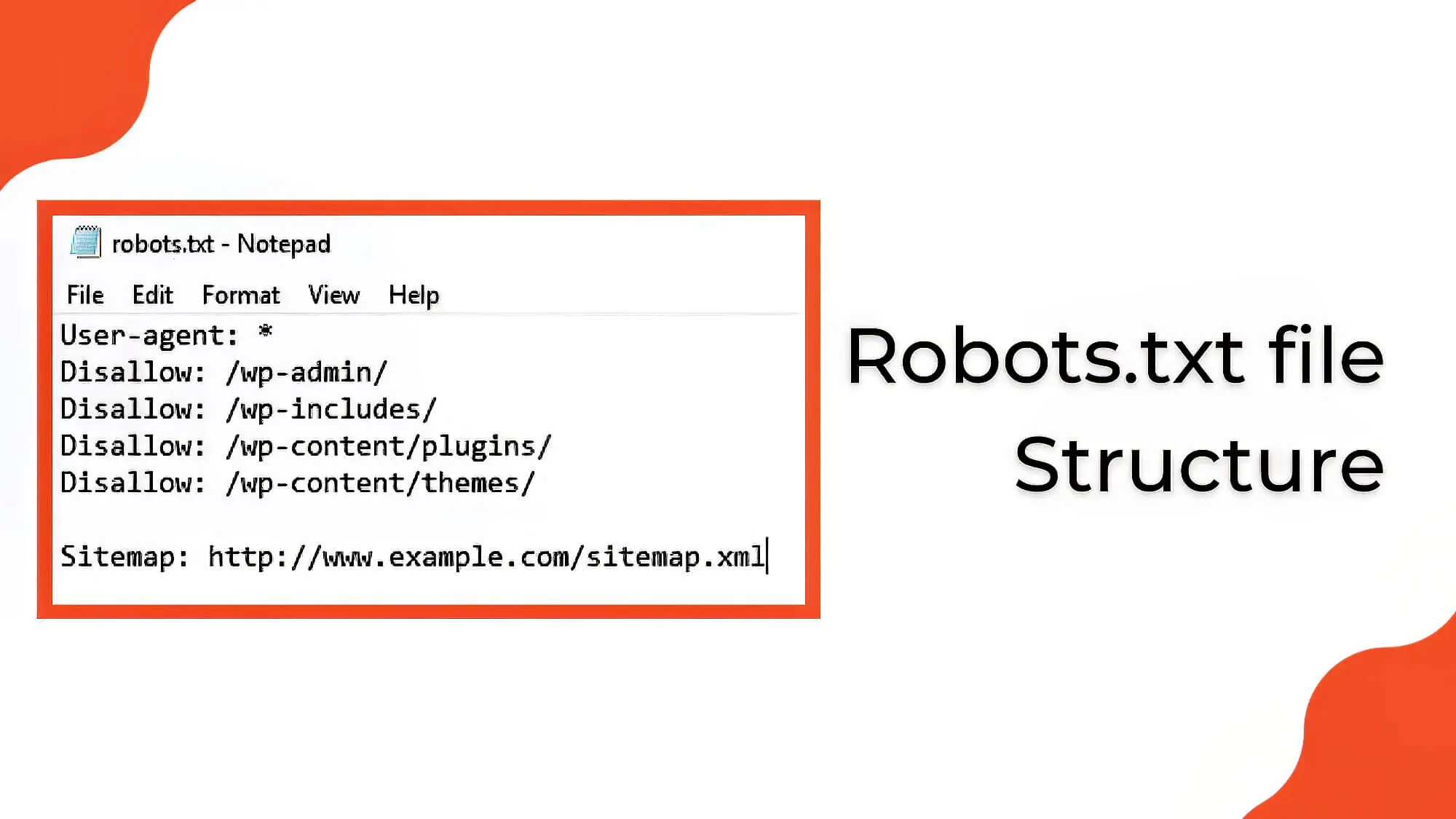
Even after submitting your website to the appropriate search engine, you might see that some pages aren’t indexed. This can be due to problems in your robots.txt file. This simple text file allows you to control page visibility concerning search engines.
As a web bot begins to crawl your website, it first goes to the robots.txt file to understand which parts of your website it can access. This is per the Robots Exclusion Protocol, which controls which parts of your website the crawlers can reach. Using the robots.txt file, you can block pages from getting indexed with the noindex meta robots tags.
But why would you want bots not to crawl your website? We mean, that’s what we want, right? Yes, that is true for usual search engine bots, but there are bots out there with malicious intent that can harm your website.
These bots can scrape your website content or even send spam on your forum discussions. The meta robots tags in the robots.txt file can be used to prevent them from doing damage. In this case, the robots.txt file is a barrier against bad bots.
As for good bots (read “search engine bots”), you want them to crawl and index your site. But as we mentioned before, the crawl budget is limited and needs to be utilised judiciously. So, you should exclude certain pages you know won’t help the bot index your site.
Whatever you choose to achieve with your robots.txt file, ensure no unintended blockings can harm your SERP rankings.
5. Stick To HTTPS

We no longer live in the HTTP age; instead, Google has clarified that HTTPS sites will have greater preference over non-HTTPS sites. Switching over to the HTTPS protocol is essential, as HTTP sites risk being entirely overlooked by search engines.
Most web browsers, such as Chrome, warn users explicitly against visiting HTTP sites as they might compromise data safety. So, if you’re still using HTTP, it’s time to contact your hosting provider and switch over to the HTTPS protocol.
6. Improve Site Speed
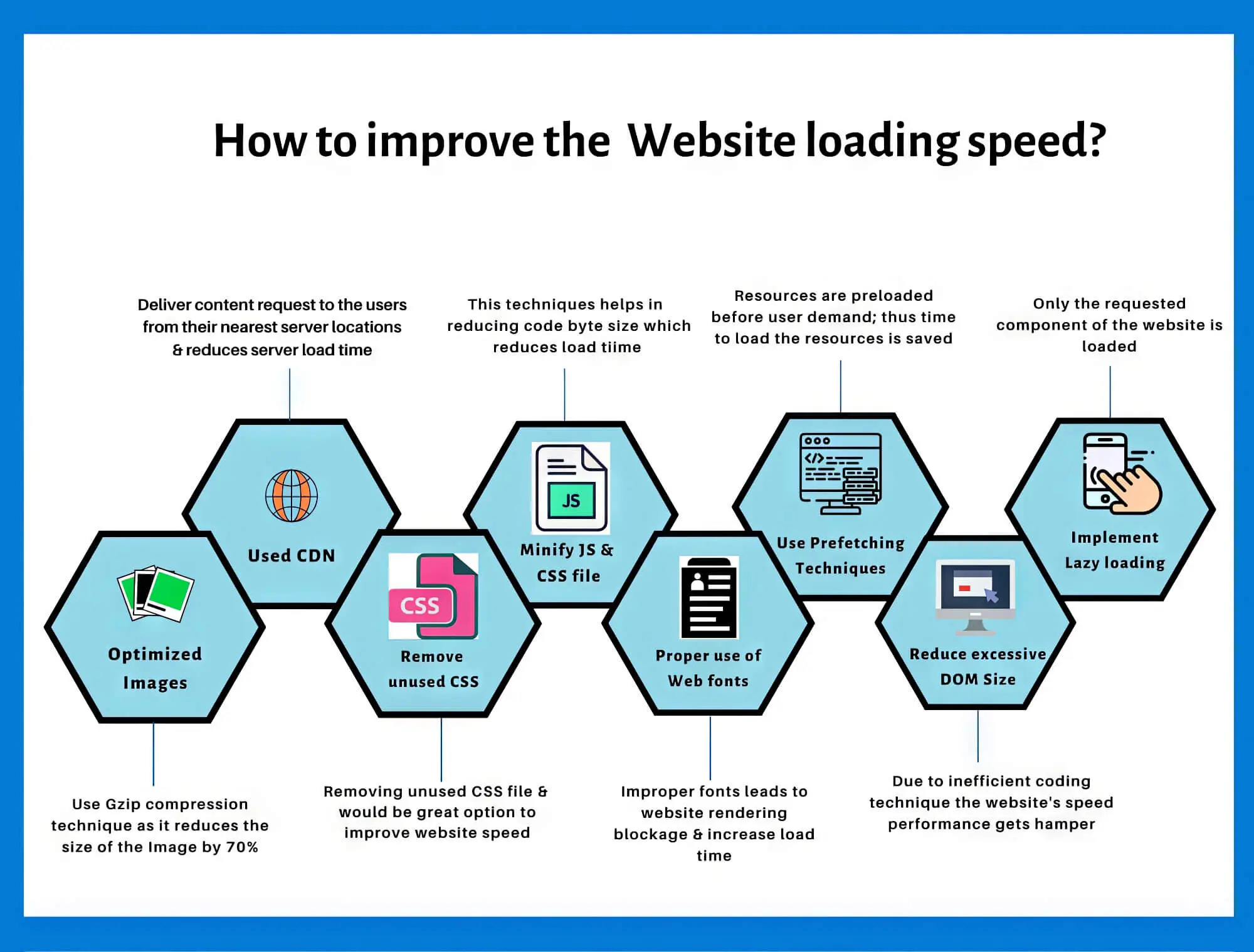
Let’s face it: we all love things that go fast, and websites are no exception. People in the 21st century won’t wait more than six seconds for a webpage to load. You’ll need to improve your website speed drastically to catch more traffic.
As website traffic is directly related to your SERP ranking, we can safely say that site speed is an essential technical SEO ranking factor. Even Google openly states that since 2021, page experience has been an official ranking factor.
Increasing website speed is an entirely technical issue and involves changing your website and hosting infrastructure. Here are some techniques to improve your website page loading speeds significantly.
A. Minimise Web Page Size
While multiple approaches can be adopted to reduce web page size (read: caching, CDNs, lazy loading and CSS minification), reducing the actual web page size is the most important. In fact, according to Backlinko Page Speed Stats, the page size is more directly correlated with load times than other factors.
Long story short: You can compress images and cache your site to oblivion, but if your web pages are too large, they will take longer to load. This means you’ll need to ensure that your website pages have only as much content as is essential and cut out the vanilla stuff.
B. Minimise Scripts
Apart from the content on a page, the associated scripts affect page speeds. So, make sure you use minification on JS and CSS files, which can help improve load speeds. Another aspect to look into is using rel canonical tags in your site’s code, which is the presence of 3rd party scripts on a page and removing the unnecessary ones.
C. Test Load Times Via CDNs
It’s common knowledge that CDNs help speed up the delivery of web pages… but as is the case with common knowledge, usually, it’s wrong. Well, not entirely, but definitely to some extent. While a well-configured CDN can boost page speeds, a misconfigured one can slow your website drastically.
That’s why, before relying on a CDN, you must test your load times with and without it. If you notice that the CDN is causing the website to slow down, think again about using it.

D. Compressing Videos And Images
Compressing images and videos on web pages isn’t the be-all and end-all, but it can work wonders in some cases. So, carefully identify heavy visual content and compress it to ensure your site loads faster.
E. Cleaning Up Codes And Plugins
The way your website is coded also affects its page speed. Unless website code is written to efficiently handle memory allocation and filesystem operations, it can build up over time, leading to a slow page speed. Hence, code refactoring is often essential to ensure a faster website.
For instance, no matter how carefully you code your website, it can become cluttered with unnecessary tags and markups. Even copying code from online sources or from one editor to another can introduce unnecessary code snippets.
Such extra code can go unnoticed during development, so ensure it’s cleaned up before the site goes live. Another aspect to consider is heavy plugins and themes, especially for WordPress sites. Try to avoid using graphics-heavy themes that can impact site performance.
The best way to assess your site’s current speed is by using the Google PageSpeed Insights tool. All you need to do is enter your website speed, and the tool will generate a detailed report. You even get insights into how your website does on mobile devices…which brings us to our next point.
7. Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
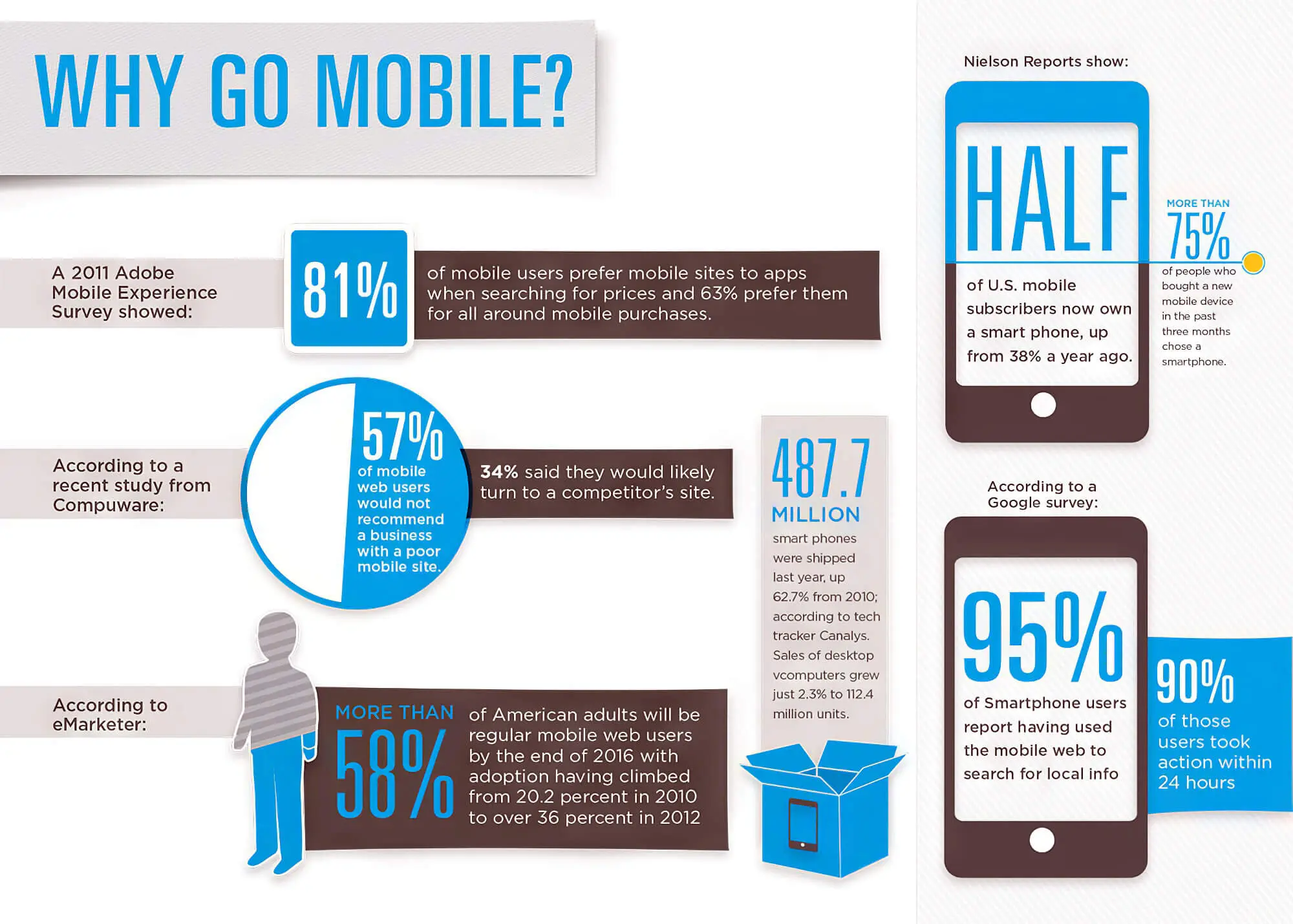
Today, with AI-driven search engines, ensuring your website looks great on any device isn’t just a suggestion—it’s a necessity. Since most people browse on mobiles, Google rolled out “mobile first” indexing. Mobile-friendly sites are set to stay ahead of the game.
Testing whether your website is mobile-friendly is a cinch; go to the Google mobile-friendly test tool from Google Search Console and paste your site’s URL. The tool does the rest and provides valuable insights into the page’s mobile state.
When assessing the mobile-friendliness of a website, the following are some of the things you’ll need to keep in mind:
- Whether on-page videos render correctly on all devices
- If scrollability is being affected
- Avoid using pop-ups on mobile
Once you’ve decided whether your site is mobile-friendly, you can use multiple routes to ensure users get a good experience on mobile devices. These include using responsive themes, eliminating pop-ups, and accelerating mobile pages.
8. Pay Attention To Rankability
We’ve been primarily discussing points related to improving website performance and indexing. Let’s now devote some time to technical SEO factors that improve rankability. Getting your web pages to rank includes aspects of on-page and off-page SEO but from a technical viewpoint. Let’s take a look at what they are:
A. Internal And External Links
Proper external and internal links help improve a site’s ranking. Links in a website give crawlers context for how to fetch and rank the pages on that site. Just like links guide human users from one part of the website to another, they also guide search bots to related content and pages.
In this regard, we must mention the problem of “Deep Pages,” which are pages that are several links deep from the homepage. While the homepage of a website is easily indexed, these deep pages sometimes face problems.
Although the problem can be eliminated with a flat architecture, it’s best to provide direct internal links to pages you want to ensure are indexed. After all, it’s better to stick with tried and tested internal links when in doubt.
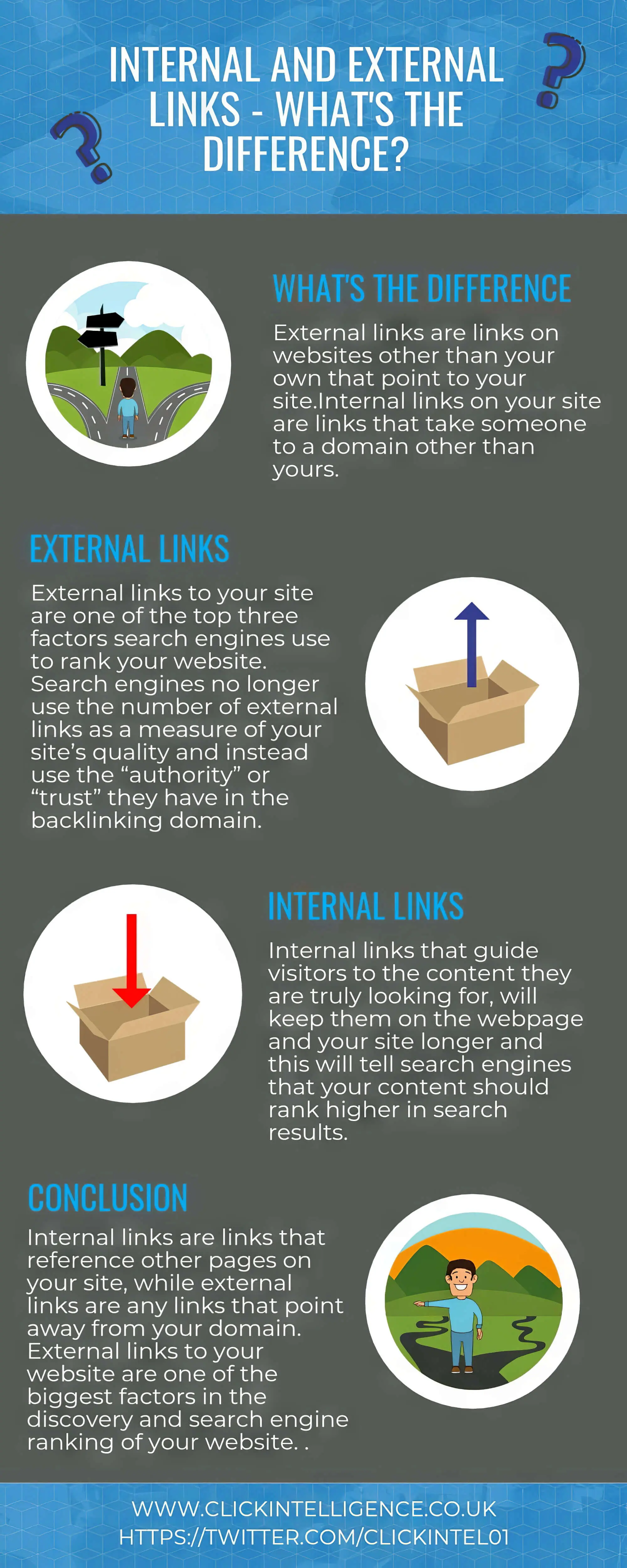
B. Quality of Backlinks
Backlinks (as we’re sure you already know) help improve your site’s reputation in Google Search Console’s eyes and that of bots. Backlinks tell the search engines that the external websites believe your pages are high-quality and worth ranking.
Naturally, this might lead you to believe that the more backlinks you get, the better your ranking. However, it’s not that straightforward a correlation. True, the number of backlinks matters, but so does the quality of those links.
As we’ve already said once before, low-quality backlinks can hurt your website. So, be careful about the backlinks you include on your website.
C. Broken Links
When doing technical SEO, checking for broken links is the final linking factor you need to consider. Any broken link can be detrimental to your SEO efforts in multiple ways: it can waste your crawl budget, negatively impact the site’s UX, and lower SERP ranking.
The best way to find where your website’s broken links are hiding is to check the Google Search Console crawl reports. And since this information is auto-updated each time Google bots crawl your website, you’ll get a dynamic view.
9. Remove Duplicate And Thin Content

Duplicate content is the bane of any website and is hard to avoid, even if you are creating unique, original content for every page on your site. This is especially possible if your content management system has created many versions of the same content on different target URL(s).
And the same goes for thin content; it’s not avoidable entirely and can hurt your site’s rankings. That’s why both these problems are worth looking into and eliminating and should be a part of your content checklist. The following are some methods of checking for duplicate and thin content.
A. Batch Search On Copyscape
One of the best ways of checking duplicate content on your website is to use the Copyscape Batch Search feature. You can upload the list of URLs you need to check in this tool and see where they are being duplicated on the web. This includes your site as well as other websites.
One thing to remember here is that if Google displays your page as the first page on the results, it considers your website the original content source. If other people copy and put the same content on their website, it’s their duplicate content problem. They need to tackle these duplicate content issues at their end.
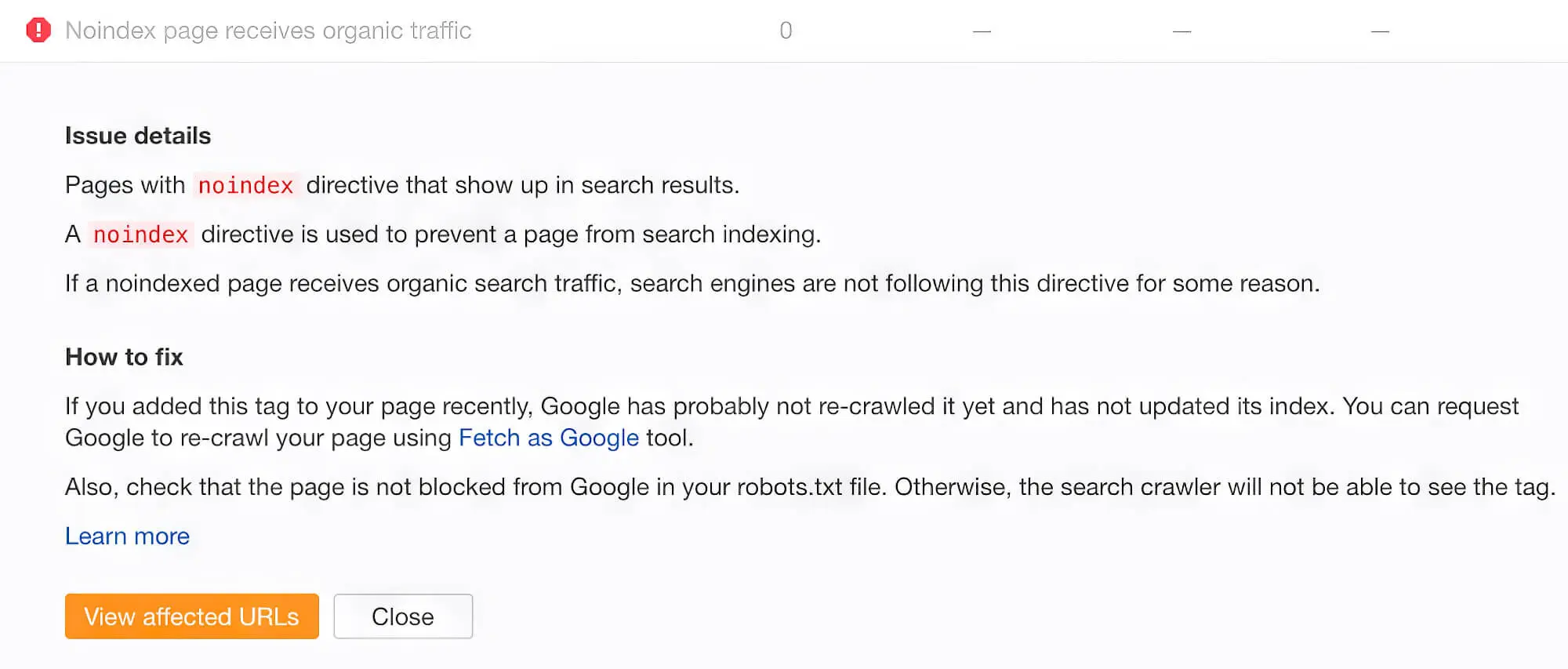
B. Use Noindex On Pages With Non-unique Content
As we’ve said before, every site will have some duplicate content, which is fine as long as the duplicate pages are not being indexed. So, how can you stop these pages from being indexed?
The solution is to add a noindex tag to these duplicate pages. This explicitly tells search engines not to index them. Once done, you can double-check that the noindex is set up correctly using the Google Search Console Inspect URL feature.
Based on your crawl budget, it might take days or weeks for Google to re-crawl and un-index pages you don’t want to be indexed.
C. Use Canonical URLs
Besides creating unique content for every page and using noindex, the third option is canonical URLs. Canonical tags are suitable for pages where the content differs by a very slim margin, for instance, multiple versions or colour themes of the same product on eCommerce websites.
Based on your site’s URL structure, every version can result in different URLs. This is not good for SEO; thankfully, you can use a canonical tag and let search engines know which page is the main page and which are variations. That’s the use of the canonical tag in a nutshell.
10. Use Hreflang
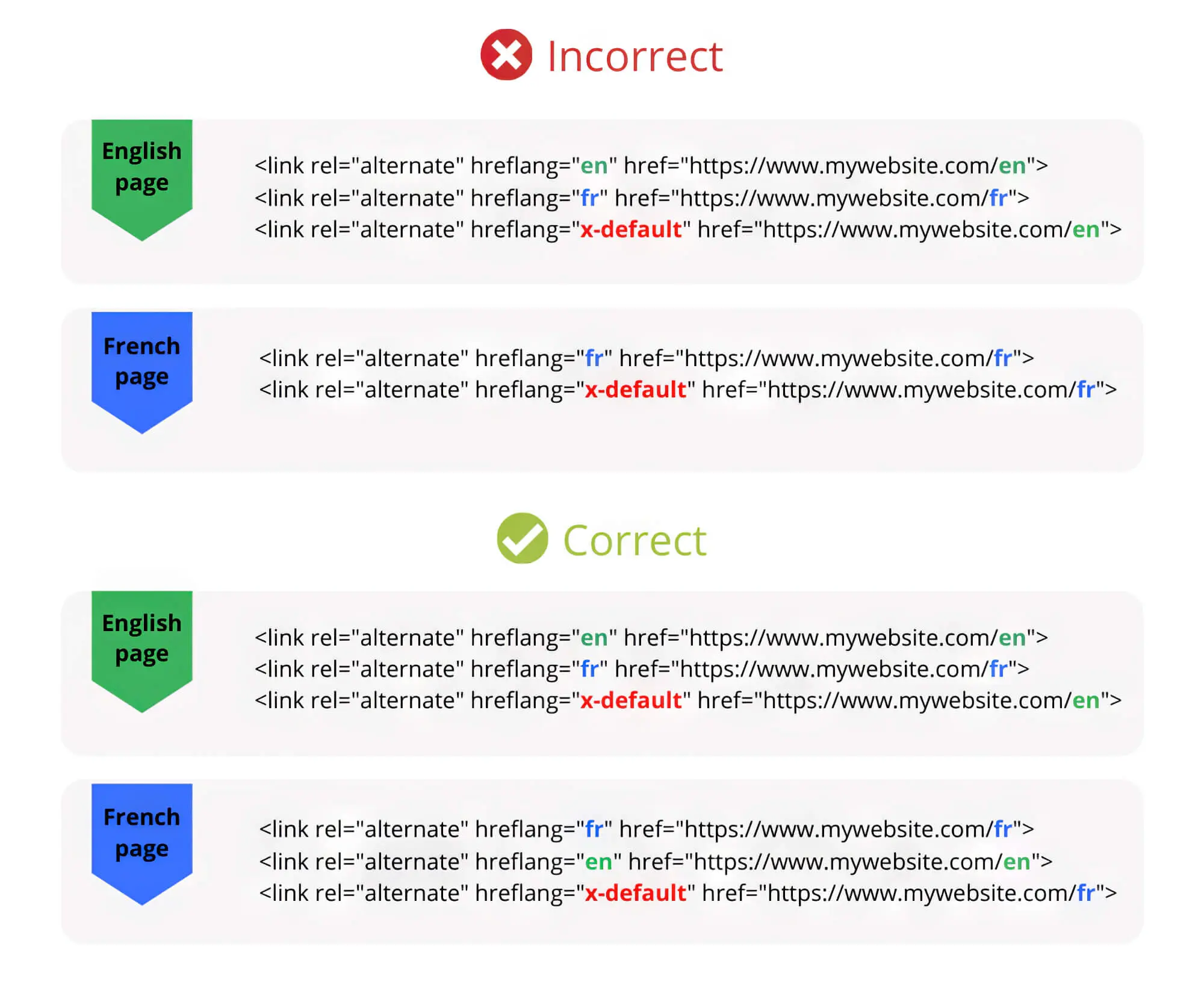
For international websites, it’s common to have multiple versions of pages in different languages. Often, pages have different content optimised for specific regions and locales. If yours is such a site, then using hreflang can greatly help.
The hreflang tag helps you specify geographic restrictions and languages for website pages. You can use this to inform search engines about your website’s geographical specifications and preferences.
Hreflang tags are helpful because they help search engines present the correct version of a webpage to users based on their region. However, they’re tough to set up, and even Google’s documentation is unclear on this tag.
11. Select The Preferred Domain

Everyone knows what a domain is, but in the doubtful case that you didn’t, it’s the URL you type to arrive at any website, like www.google.com. The domain name is the way people remember and reach your website.
When putting up a website, you’ll need to select a preferred domain to inform the search engines about which version of the domain you want to use. This can be of two types: the www version or the non-www version. For instance, you can prioritise www.mysite.com over just mysite.com. This will ensure that anyone who types just mysite.com will be redirected to the www version.
Unless you do this, search engines will treat each version as a separate site, and your SEO value will get dispersed accordingly
12. Browse Through Your Site Log
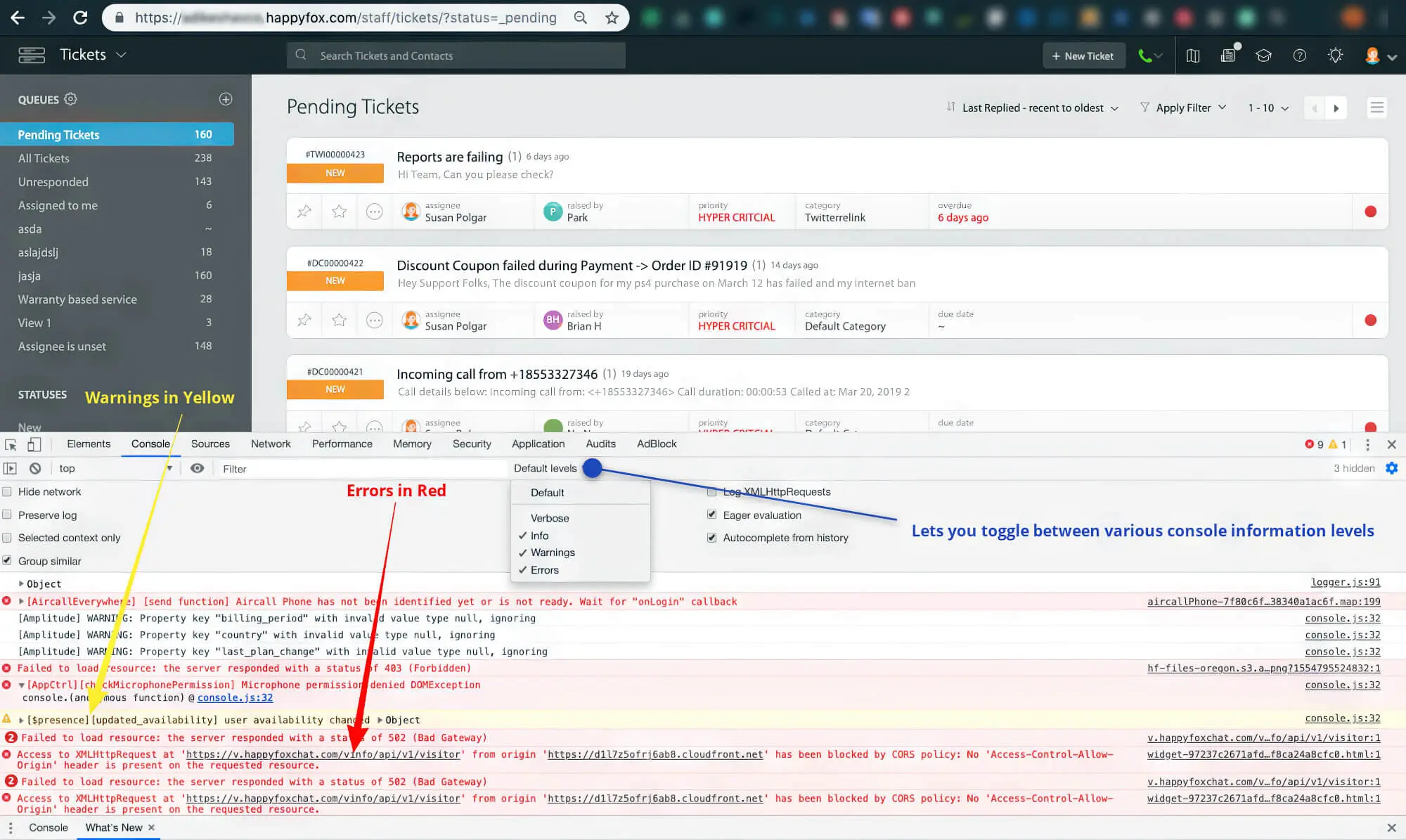
Browsing through log files can be a harrowing task, but sometimes, it’s essential to understand how crawlers treat your site. Log files are essential entries of all site activity and are automatically updated by the server whenever it takes action on your site.
Log file data lets you get details such as the user agent type (human or bot), request time, requested content, and even the requested IP. You might be wondering what all this historical data has to do with SEO…well, a lot.
Search engine bots will always leave log trails when crawling your website. This can help you clearly understand which pages are being properly crawled and which aren’t. It also enables you to determine how your crawl budget is being utilised and what prohibitions indexing the search bots face.
13. 404 Page Optimisation
A 404 error page is shown to visitors when they try to access a target URL that doesn’t exist on your website. This can happen in the case of mistyped URLs or deleted pages.
Many CMSs, such as WordPress, have optimised 404 pages built-in, but sometimes you need to do it manually. In general, an optimised 404 page should have the following characteristics:
- Similar structure and navigation to the main website
- Display a clear and friendly message to the visitor explaining what’s missing
- Suggest related alternatives
- Have straightforward design navigation to other pages on the website, such as the homepage.
What’s the simplest way to check your site’s 404 page? Just open a browser and type in the wrong URL on your site; you’ll see a 404 page.
14. Avoid Duplicate Meta
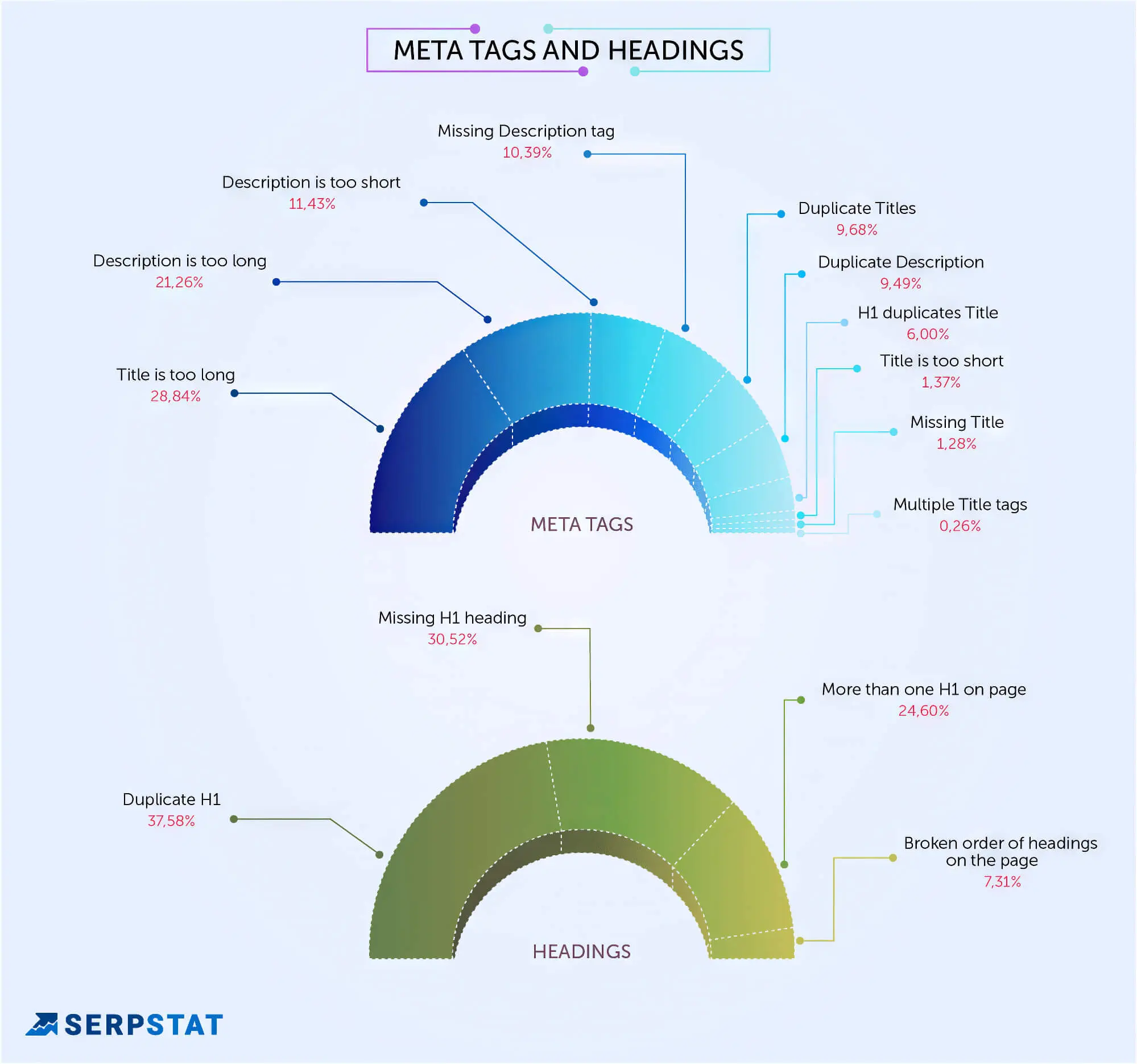
Optimised meta descriptions and metadata are known SEO factors, and the meta description can play a crucial role in whether a user clicks through to your website. Duplicate meta descriptions or metadata can harm your SEO efforts.
A redundant meta description can result from copy-pasting content onto identical pages. However, you can perform an SEO audit to detect and remove them. Identifying and replacing everything with unique content will take time, but the improvements justify the efforts.
15. Stay Away From Keyword Cannibalisation
By now, you’ve understood that Google Search Console is a boon for webmasters looking to get their site high up on the SERPs. This tool can help with almost anything you’d like to check on your website, from optimising internal links to targeting long-tail keywords.
And speaking of keyword research, no keyword research checklist is complete without warning about keyword cannibalisation. Sounds sinister? Well, it is.
Keyword cannibalisation occurs when multiple pages on your website are trying to rank for the same or similar set of keywords. This can confuse search engines and negatively impact your SERP ranking.
Keyword cannibalisation will lower your pages’ CTR, conversion rates, and authority. To avoid this, make sure your keyword research is specific to each page and that target keywords are not duplicated across related pages.
You can use the Performance Report on the Google Search Console to see which pages compete for the same target keywords.
16. Select SEO-Friendly Hosting
When doing SEO, especially the technical kind, there’s no shortage of things you need to keep in mind (and lose sleep over). There are always the golden oldies, like backlinks and sitemaps, and the newer stuff, such as featured snippets and mobile-first indexing.
However, site uptime is the one thing we tend to forget amidst all this. After all, if your website is down, then none of the other factors matter in the least. And this depends on the web hosting you’re using.
The web host you decide to use will determine visitors’ experience on your site. Bottom line: A reliable web host is essential to prevent page timeouts and server errors and reduce bounce rates.
Sadly, not all web hosting is always SEO-friendly. But to help you out, here’s a list of four factors you need to look out for when deciding if your web host will support your SEO efforts and not hinder them.
A. Uptime Guarantee
Uptime is the percentage of time your site is live online and accessible. This means you’ll need to select a hosting service with very high uptime, preferably 99.9 per cent. The higher the uptime, the better your user experience will be and the fewer chances your visitors will bounce.
But be warned: if someone guarantees 100 per cent uptime, take it with a grain of salt. Downtime is a reality of hosting, and some of it is natural. The trick is to keep it as low as possible to ensure continued server response.

B. Server Location
While uptime refers to your website’s accessibility, server location will determine the speed of such access. Hosting can be VPS, shared, dedicated (for physical data centres) or entirely cloud-based.
In the best case, your data centre should be located geographically close to your target audience. This ensures faster load times; the reverse is true, as the farther your server location, the longer your server response time.
Additionally, off-beat server locations can seem suspicious to search engines and affect your SEO. For instance, if you operate in Australia and your website is hosted in Bermuda (so to speak), you might be construed as a shady business.
The crux of the matter: server location determines your server response and credibility. So, choose wisely.
C. Scalability
Your business might be local now…but it can grow to a global scale anytime (we trust your hard work!). So, you must ensure that your hosting can scale with your business.
You should opt for web hosting companies that offer multiple tiers and add-ons. Some of the SEO-friendly options that you might look for are:
- Auto-backups
- Multi-tier hosting
- Solid security
D. Responsive Support
Finally, a support team available 24/7 to tackle issues is essential to maintaining a well-functioning website. Make sure you read multiple reviews and check out social channels to understand the service’s reputation for customer support.
Good, SEO-friendly hosting operates quietly in the background without you needing to worry about it.
Advantages Of Technical SEO
By this point, you’ve got the gist of major technical SEO challenges and the factors you should consider for a technical audit. While we’ve highlighted why technical SEO matters, it’s crucial to see how your business stands to gain from putting it into action.
Local businesses and large international websites have different requirements and business models. Still, some aspects of SEO, such as optimising the Core Web Vitals or ensuring that the site is mobile-friendly, remain the same. So, even if you’re doing the bare minimum in terms of technical SEO, it’ll still improve your site’s performance.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at some of the essential advantages of performing technical SEO:
1. Increases Reach
The primary advantage of technical SEO is that it helps improve your visibility across the internet. Since technical SEO directly affects the factors that influence search rankings, it can help push your website up the SERPs. And as your web pages rank higher, they will surely attract more clicks.
We’ve also mentioned that technical SEO helps improve the user experience. So, not only can technical optimisation bring more traffic to your website, but it can also convert visitors into paying customers.
2. Gets You Rich Snippets
Organic traffic doesn’t just go to the top-ranking pages on the search results. Organic traffic flows to websites that can occupy more digital real estate in search results. This means occupying the rich snippets and knowledge panel section, and technical optimisation can take you a long way towards that.
3. Provides Better Social Media Exposure
Technical search engine optimisation ensures that your website doesn’t suffer from incorrect images, texts or metas when being shared on social media. This helps portray a consistent image across social media and enhances social media exposure.
4. Identifies Technical Holes In Your Content And Plugs Them
Broken links, missing alt tags, and duplicate content are technical weaknesses in your content that need to be resolved. Technical SEO targets all these factors and ensures they don’t harm your ranking efforts.
5. Improves Website Security
As SSL and HTTPS are vital in technical SEO, implementing technical SEO helps enhance your website security automatically. Using SSL protects your website from being hacked and stops unwanted pop-ups from messing up your UX.
Steps To Conduct A Technical SEO Audit
We’ve covered the essential factors of technical SEO and understood how it could benefit a website and business. But how do you implement technical SEO in real life? Well, that requires conducting a thorough technical SEO audit of your website.
A technical SEO site audit is a part of website optimisation and maintenance that helps you analyse, understand and optimise technical aspects of your site. A thorough technical site audit will not only catch technical errors but will prepare your website’s relevant pages for ranking on multiple search engines.
Such preparation will ensure zero problems related to crawling and indexing, elimination of crawl errors, and suitable website structure and sitemap files, among other things. An audit of the entire site will ensure your site is not missing out on anything related to technical optimisation.
However, remember that technical audits are not straightforward unless your website is very small. However, auditing can be a tough ask for a reasonably complex website like an eCommerce store with large numbers of pages and plugins. In fact, in some cases, an SEO plugin that’s incorrectly implemented will be more harmful than useful.
Whatever the case, here’s a list of eight steps to conduct a technical site audit of your entire site. Remember that, like everything related to SEO, these steps are not set in stone and can be modified per your needs.
1. Perform A Crawl
The first step is crawling your website using a site audit tool. Such tools usually scan your site to determine its number of URLs and pages indexable and identify crawl errors.
The site audit tool will create a detailed report on issues that might be hindering your site’s Google rankings based on this information. For more advanced investigation, you can use Google’s search console or Google Analytics reports linked to your website.
2. Identify Crawlabity And Indexation Problems
By now, you know that crawling and indexing a website is the first and foremost step to Getting to the top of search engine rankings. It requires having a mobile-friendly website on Google (or any other search engine, for that matter). This means these are the two aspects you must look into most assiduously when performing your site audit and devising an SEO strategy. Here’s a list of sub-steps you can follow to get this done.
A. Spot Indexation Problems
Ensuring all your website pages appear on Google’s index is imperative. You can quickly check the status of your webpage indexation from the Google Search Console Coverage report. This report lets you see which pages are indexed, which aren’t and which have warnings. Once you’ve spotted the problem pages, prepare to tackle them one by one.
B. Inspect The Robots.txt File
We’ve seen the purpose of the robots.txt file and how easy it is to work with, but that makes for its greatest flaw: it’s straightforward to get it wrong. For instance, the following text will tell search engines not to crawl any website pages:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
While this might come in handy during testing, you don’t want it to remain in the robots.txt file after your site goes live. So, ensure you have scrutinised the robots.txt file to ensure everything is on point.

C. Check The Robots Meta Tags
A robot’s meta tag tells a search engine exactly how it should crawl and index a particular page. It’s usually placed in the header section of the HTML file and reads like this:
This bit of HTML tells the search engines not to index this page. While you might wonder why you wouldn’t want a page to be indexed, there can be multiple situations when that’s precisely needed. Some of these are:
- Pages with low-value or thin content
- Pages still in staging
- Admin pages
- Internal search pages
- Landing pages for PPC campaigns
- Promotional pages that shouldn’t be live yet
- Duplicate pages
SEO plugins (such as Yoast for WordPress) often don’t include noindex by default. In that case, you’ll have to add it manually.
D. Go Through The XML Sitemap
Before submitting your sitemap, make sure you go through it thoroughly one more time. The sitemap helps search engines find their way into your website’s essential pages. It’s essentially a set of directions for the crawlers to explore a website.
Unless you’ve included all essential pages in the sitemap, pages can get left out. Also, ensure you don’t have dead pages on the sitemap, which can confuse the bots and affect your crawl budget.
E. Analyse The Crawl Budget
Speaking of the crawl budget, we’ve mentioned this term a few times before but not entirely explained it.
The crawl budget refers to the rate at which Google and other search engines crawl pages on your website. Depending on several factors, such as the size of the site, your website value, etc., a search engine can crawl anything from a few to a few hundred pages on any given day.
However, having a large crawl budget doesn’t mean your site will shoot to the top of the SERPs. It’s not that simple, and search engines aren’t making it easy anytime soon. But if you have a proper SEO strategy in place, the crawl budget can be optimised.
How can you tell if you have an excellent crawl budget? Well, if your pages are popular on the SERPs and receive a lot of organic traffic and backlinks, you’re in good shape. Also, internal links play an important role in increasing the crawl budget.
Remember that new pages or ones that aren’t linked well might not be crawled properly. And for massive sites with millions of pages, the crawl budget can slow to a crawl. So, we recommend you use the Crawl Stats report on Google’s Search Console to understand your site’s current crawling scenario and address any issues you detect.
3. Optimising On-Page Technical Factors
On-page issues can harm your technical SEO, so keeping a close eye on these is essential. Factors such as meta descriptions and header tags must be considered and optimised for ranking near the top of search results.
Of course, not all on-page factors are of the same importance. For instance, some medium and low-priority on-page factors that you can tackle easily are touched upon below:
- Make sure title tags are of the correct length (less than 60 characters, ideally).
- Optimising the meta descriptions
- Properly configuring SEO plugin settings for individual pages
Similarly, some of the higher priority factors are:
- Using canonical tags
- Using hreflang for international websites
- Including a structured schema markup
Of these, ensuring suitably structured schema markup is particularly important as it helps Google understand your website and also helps with semantic search and E-A-T.
4. Tackling Image Problems
As mentioned before, image optimisation can help to improve the site and page loading speeds. Also, optimised images help to bring in more traffic through image search, provide a better UX and enhance accessibility. Common image problems are as follows:
A. Broken Images
This is a high-priority problem and should be treated as such. Broken images that don’t display on your site lead to a poor user experience and make it look spammy. Users usually leave the impression that the site is not professional and poorly maintained.
B. Massive Images
Massive, high-res images can cause problems for your website, slowing loading speeds to a trickle. It is better to optimise and shrink the images before uploading them to your website. You want the smallest possible image size for the best results.
However, many plugins can get the job done if you want to optimise existing images. Remember that image optimisation is a high-priority factor and should be getting due attention on your SEO checklist.
C. HTTPS Links To HTTP Image
Though this is not as important as the above two requirements, it’s certainly something you shouldn’t overlook. A mixed content problem is when an HTTPS page contains visual content (images or videos) on insecure HTTP.
This can lead to security issues, especially for those trying to monetise websites with display ads. Moreover, such mixed content can cause browsers to ban your page resources, leading to a poor user experience on your website.
D. Alt Text Missing
Alt text is a textual description of an image on a web page. This is vital in image optimisation as it improves your website’s accessibility to visually impaired visitors.
Visually impaired customers might use screen readers that render images into audio descriptions, which is where alt-text comes in handy. It can improve topical relevance and improve your image (and page) rankings.
5. Internal Link Analysis
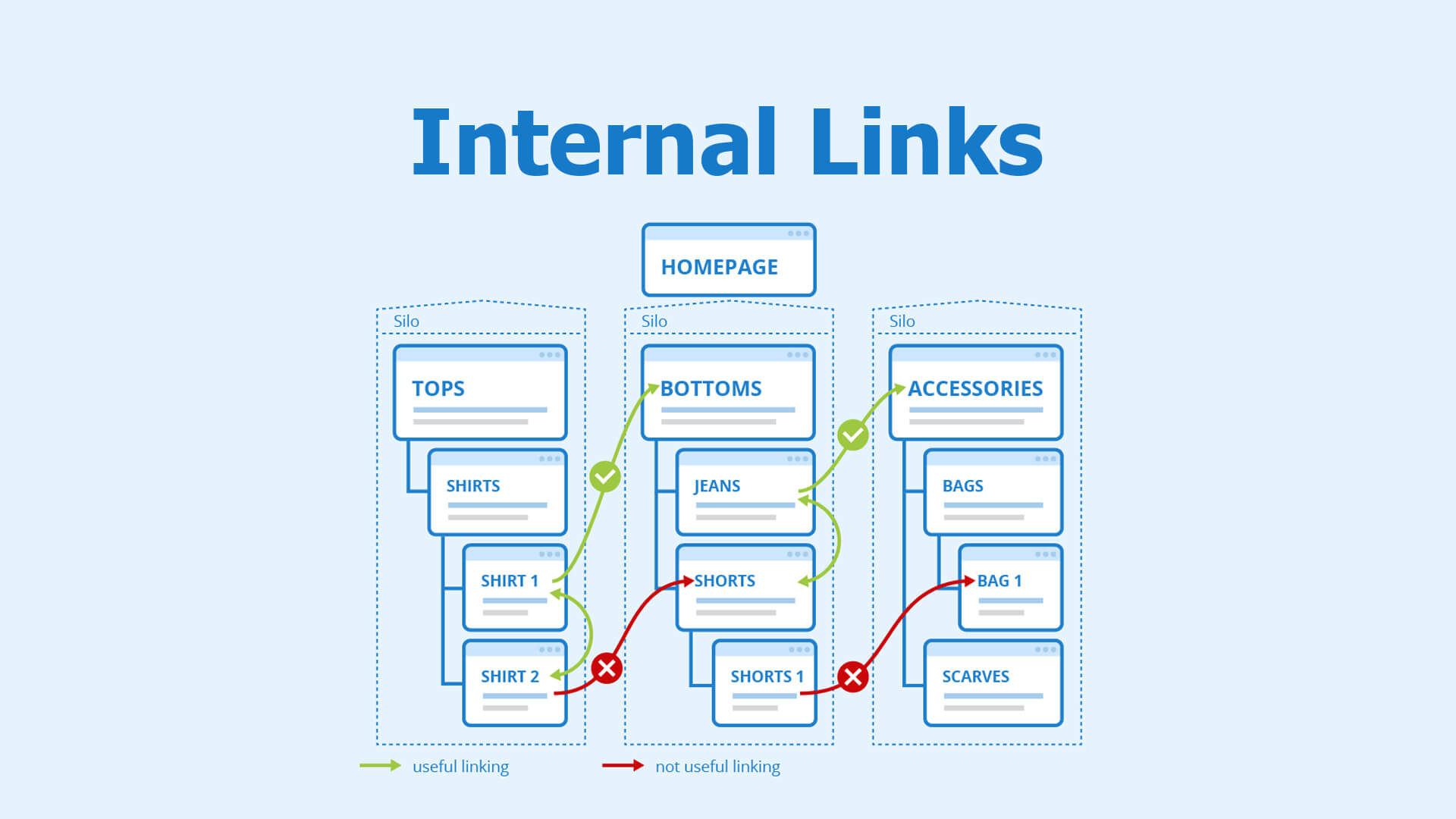
When SEOs talk about link analysis, most people’s minds jump immediately to backlinks. True, backlinks are crucial in SEO, but internal linking is as important as backlinks. Some experts even claim internal linking to be more critical…but that’s a matter of debate and best settled over cups of steaming latte, so let’s leave that for now.
Getting back on track, internal linking helps search engines and humans explore your site better. When you properly silo related topics using internal links, it creates a topical roadmap for your site. This has multiple benefits, such as:
- Helps provide relevance for keywords
- Ensures proper crawling of content
- Provides navigation fluid
When analysing internal links as part of link building, make sure you pay special attention to the following:
- 4xx status codes
- Orphaned pages
6. External Link Analysis
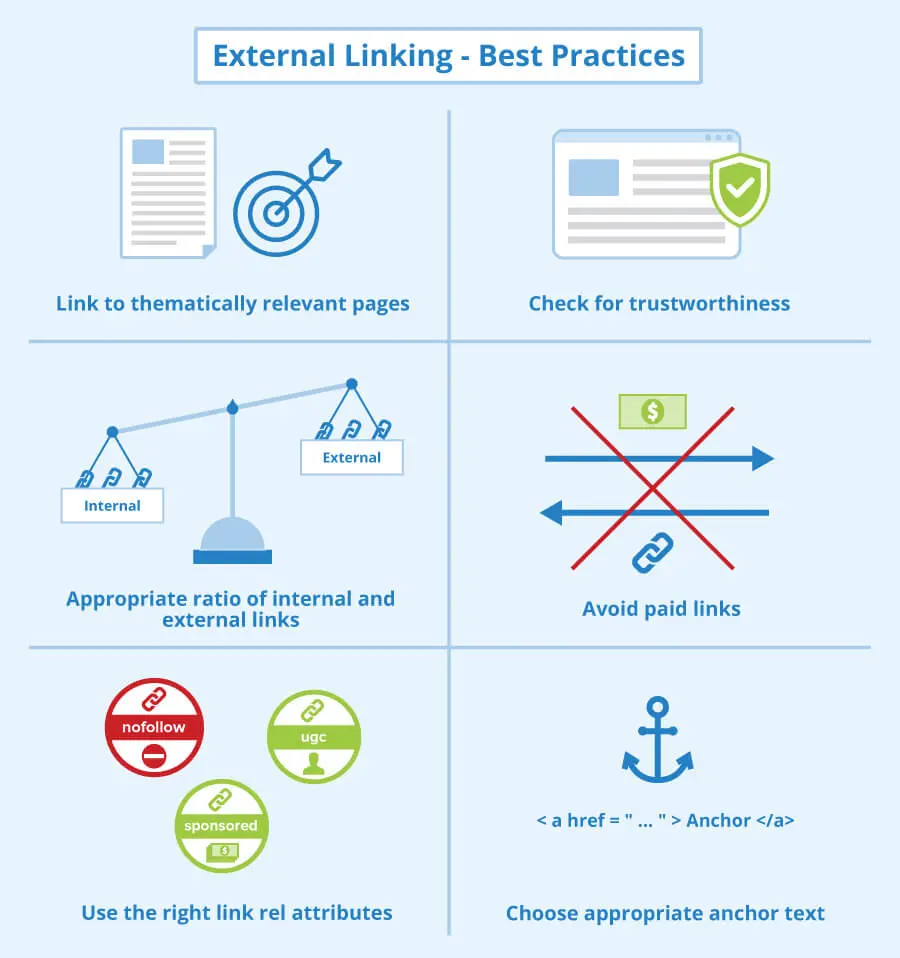
The next logical step in your technical SEO site audit will be to analyse external links. Just as you add internal links for SEO benefits, external links also boost rankings by increasing the trust factor of your website. It also shows that your content is vetted, well researched and supported by expert information.
However, even external linking comes with its own set of troubles, such as:
- Links to broken pages
- Dead-end pages, i.e. pages with no outgoing links
7. Overall Site Performance
Finally, overall site performance must be tested before exiting the technical site audit phase. Here, it’s important to check factors such as mobile-friendliness and site speed. Of these, site speed is vital (as we’ve said, who knows how many times earlier!) since Google already lists it as an official ranking factor.
When analysing site speed, you need to pay attention to Google Core Web Vitals, a speed metric used by Google to rank websites. The Core Web Vitals include the following three parameters:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): assesses visual load
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): tests visual stability
- First Input Delay (FID): measures interactivity
The purpose of these factors is to enhance user experience and allow visitors to get the right results faster and easier. You can use Google PageSpeed Insights to assess your site’s speed for free. And for mobile-friendliness, you can use the Google Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
Follow these basic steps to create a suitable site audit report. Keep in mind, however, that this report is a dynamic document that needs to change along with your website and advances in Google search technology.
And as we all know, Google is notorious for continuously changing its search algorithms. So, you shouldn’t rest on your laurels and keep auditing your website for technical SEO factors. Like link building, continuous SEO sends a positive ranking signal, which helps rank your website better.
Performing Technical SEO
And that’s the list of technical SEO factors we needed to share with you. It’s not a complete SEO checklist (if there ever was such a thing!), but it’ll help you know about any essential ranking factor you need to remember.
Remember one thing before embarking on your technical SEO journey: the search engine result pages are tough to navigate. So, be patient and keep a close eye on Google Analytics and search console. It takes time to reach the top of search results, so stick to the vitals, and you’ll get there in no time.
And while you’re at it, make sure you’re keeping the details of this guide in mind. And if you feel it’s a lot to take in at once and implement, you can hire a professional SEO agency to help you optimise your site’s technical nuances.





