In today’s world of ever-evolving web applications, making your website’s design user-friendly is essential. This not only helps in drawing visitors but also ensures they stick around, enhancing the overall experience.
Consistent application of website usability tips, including addressing slow page speed, can ensure users have a mobile-friendly and great website user experience when visiting any system or website. On the other hand, complex web designs are often considered cumbersome since they make the users feel lost while navigating.

The significance of User experience and interface design lies in its ability to make a website layout user-friendly and effortless to navigate. This guide has been created to recognise the importance of UX design for websites to help you comprehend how a well-executed UX design for web pages can improve your user experience website and, by extension, your business success.
So, let’s get started!
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
What Is User Experience?
Before discussing UX design and how it can improve a website, we must understand user experience. In essence, user experience translates into the user experience UX design that evokes emotions after their interaction with a specific user interface design, ideally aiming to improve your website’s user experience in a meaningful and impactful way.
The system, whether desktop software, a mobile app, or accommodating website users or human-computer interaction (HCI). Enhancing user interaction with a system and eliminating technical obstacles can promote frequent usage and foster customer satisfaction.
Interestingly, Don Norman coined the term “user experience” During the 90s, underscoring why UX is important. Here are a few key aspects people look for while using a digital product such as a website or web application:
- How intuitive the navigation is whenever the users interact with the system
- The visibility of the key features of the task
- Proper cues to help them reach the goal.
As such, people who work on UX (user experience) evaluate and observe how users interact with the system and its utility. UX designers work towards creating better and more responsive design solutions that cater to the user needs of both existing and potential users.
The Difference Between UX And UI Design
Most people these days often misunderstand UI And UX as interchangeable terms. However, these two terms are fundamentally different and serve different purposes.
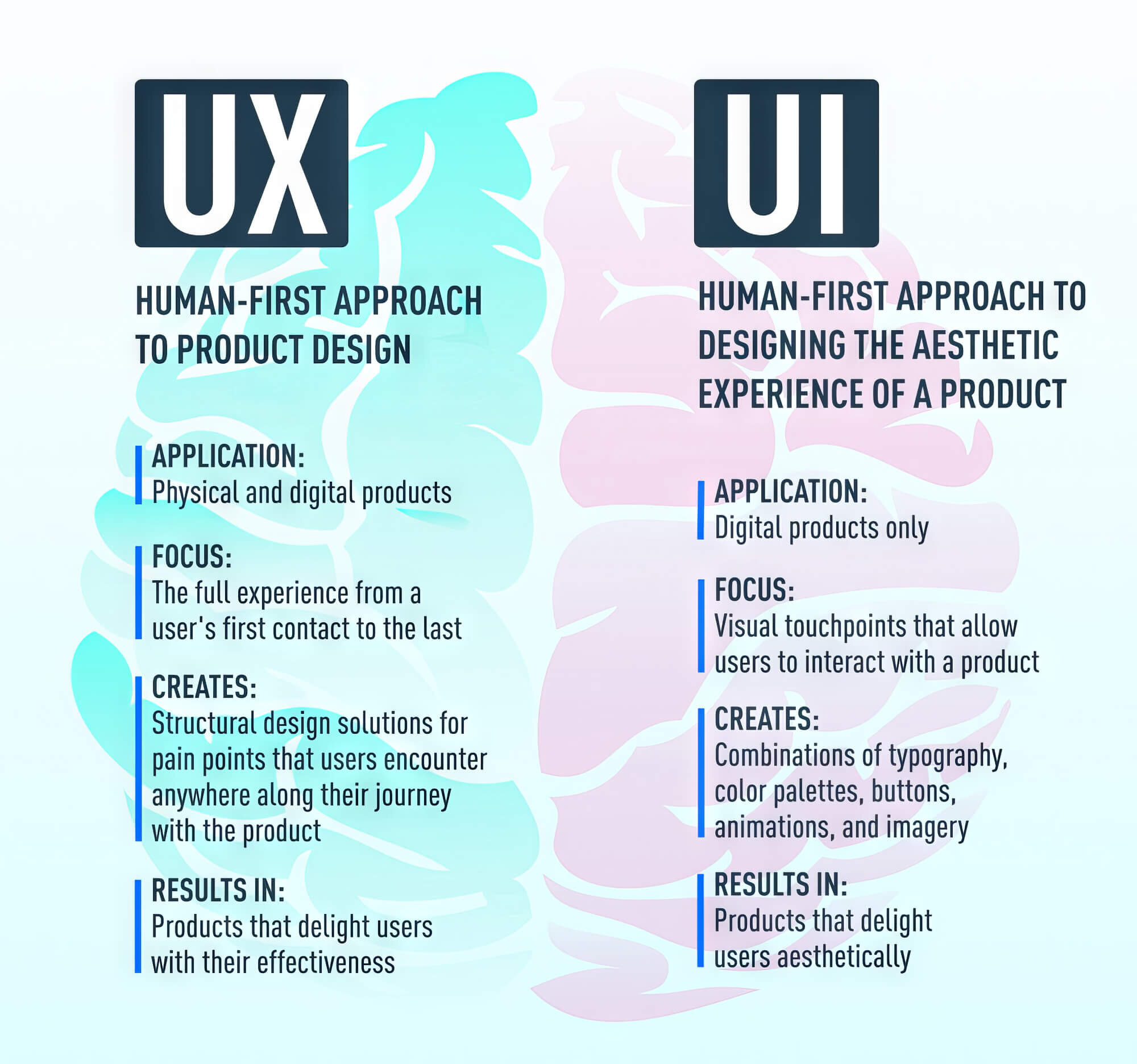
User Interface (UI) design refers to the actual interface that users interact with on the screen, encompassing the visual design and navigation options, aiming to be visually appealing and user-friendly. For instance, a website with a button to click a certain option is considered a UI design.
In short, the user interface UI design primarily focuses on the visual and interactive elements of the product and system. Conversely, UX focuses on defining customer journeys to understand how a user navigates through a problem-solving process.
That said, we have focused this guide on explaining the different components of user experience design and how you can use it to improve the user experience of a website. Since UX and UI go hand-in-hand, you will notice these terms used throughout the article, but you should avoid misunderstanding them.
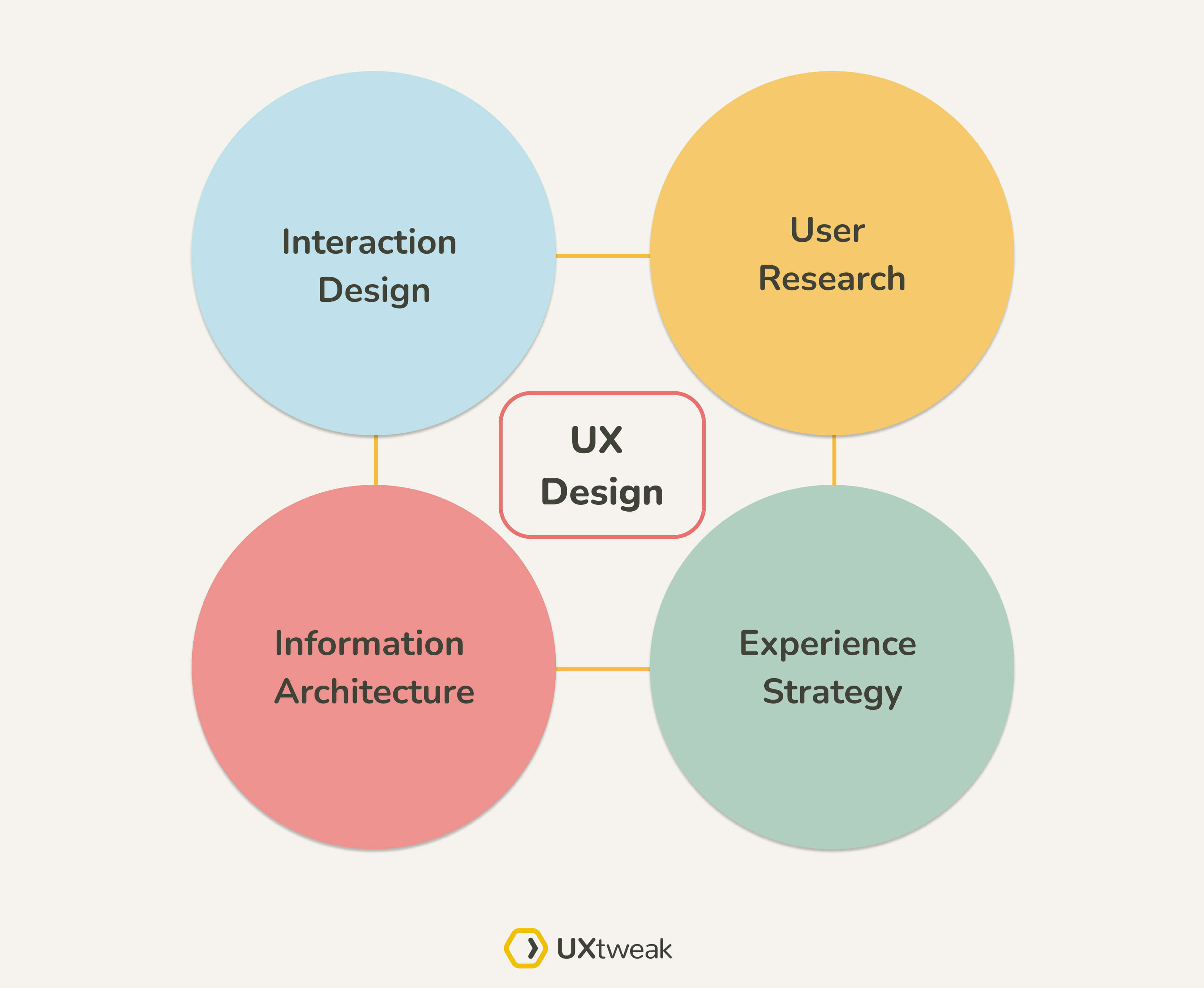
UX Design Disciplines: The Quadrant Model
When it comes to UX design can be divided into four main disciplines, which are as follows:
- Information Architecture (IA)
- User Research (UR)
- Interaction Design (IxD)
- Experience Strategy (ExS)
This section will discuss these disciplines and how they have a major role in adding interactive elements to the system.
1. Informative Architecture (IA)
Informative Architecture is a UX discipline in which content and information are organised in an accessible and meaningful way. This helps the users navigate the product easily without wasting too much time. To design an IA for a particular product, the architect must first connect the different content and form a relationship between them.
Besides this, they pay attention to details such as the language used and its consistency throughout.
2. User Research (UR)
Another critical domain of UX design is User Research (UR), where designers conduct user research to identify system issues and formulate efficient solutions. For this discipline, a lot of extensive research and user feedback is required to be collected from potential and existing customers. For this step, user testing is essential.
As such, UX designers launch several surveys and use Google Webmaster Tools to gather valuable customer insights. In addition, they perform usability tests and create user personas as a part of the user research since it helps to understand the user’s needs.
The information can be collected using a quantitative and qualitative approach, which helps make precise decisions while designing the website.
3. Interaction Design (IxD)
Regarding interaction design, the designer studies the system and observes how the user interacts with the system. This information is collected while performing a survey during the user research phase of the project.
The interaction design includes different interactive elements, such as page transitions, animations, and buttons. Besides this, interaction designers incorporate calls to action within intuitive designs, which enable users to complete different actions and tasks effortlessly.
4. Experience Strategy (ExS)
Besides helping users interact with the system effortlessly, UX design can help businesses improve their revenue through experience strategy. The designers create holistic business strategies that help businesses boost their sales by catching a larger target audience.
Most marketing strategies are designed to keep the customer’s needs in mind while improving user experience and enhancing the company’s revenue. Hence, UX design can be considered a double-edged sword since it caters to the needs of potential customers and business objectives simultaneously.
That said, the discipline of UX design doesn’t end with just these four categories. It can be further broken down into various sub-disciplines. User experience encompasses computer science, psychology, cognitive science, communication design, usability, etc.
What Does A UX Designer Do?
Technically speaking, a UX designer specialises in enhancing the website’s user experience by making technology and products more accessible and enjoyable. To achieve these goals, they use a design thinking process to understand the user’s desire while incorporating a business strategy to improve sales.

The Design Thinking Process
The first stage of the design thinking process begins with “inspiration.” The UX professional aims to better understand the problem by performing UX research at this stage. Besides this, they also perform competitor analysis, which provides the insights they need to know about potential challenges they might face while solving the problem.
User interviews are one of the most effective ways of collecting data from users directly involved with the system. All the information collected is used to form user personas, which act as a foundation for the next stage.
From here on, the UX designers spend considerable time understanding what the personas are trying to accomplish with the service or product. In addition, they also study the journey each persona experiences with your product or service as they try to achieve their goals.
Using this information, UX professionals design information architecture and use different techniques to map out the user flow.
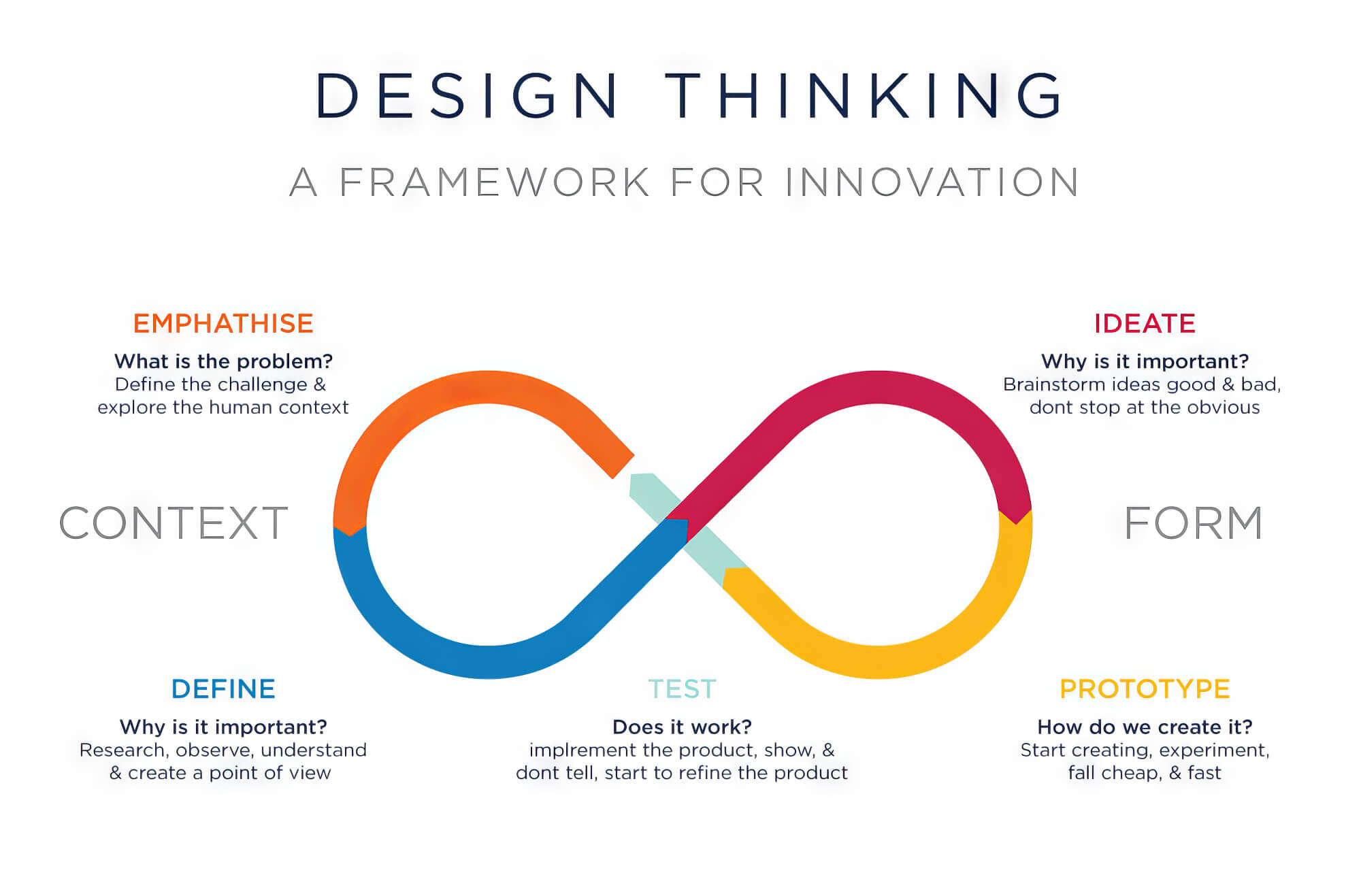
Once the user flows are established, designers employ them to predict and plan every action a user might make in their journey towards a solution, thereby contributing to the creation of a website with better user engagement. In addition, they create wireframes and prototypes for the final product, which will go through a series of tests before it reaches the end user.
The end user’s interaction is noted during the usability test, and further improvements are made to the product to give it a stable and accessible design.
Additionally, UX professionals play a major role in keeping the interest of stakeholders. For this purpose, they provide timely updates on the changes made during the different stages, including digital marketing efforts, while finding a solution.
Does Company Scope Determine What A UX Designer Does?
The company scope is often misunderstood as an unnecessary factor in the UX design process, but it still plays an important role. Usually, a UX designer’s task depends on the firm’s specific needs and the company’s size.
When it comes to larger companies, a team of UX designers is recruited, and each designer is given a specific task to complete while they try to solve the problem. For instance, one designer can focus on UX research while the other can develop a visual design.
On the other hand, smaller companies and startups prefer to recruit a single UX designer for all types of tasks. As such, they might have to recruit someone specialising in different UX design fields.
Critical Questions Asked By Most UX Designers
Before designing any services, web design, or products, UX designers will ask themselves specific questions that help them in the design. These questions also help fine-tune the user interface and eliminate hurdles while developing a solution.
Here are a few questions UX designers often ask themselves when they take on a project:
- How usable and practical is the product?
- Is the product easy to use and self-explanatory?
- Can different categories of users access the product without any difficulty?
- Does the product leave a positive impression on the user?
- Should surveys and interviews be used to collect feedback after user testing?
- Are the design elements intuitive?
- Does the entire process have any technical feasibility?
- How can we troubleshoot the end users if they encounter a problem while reaching their goals?
- Does the business strategy provide high-quality competitive advantages for the company?
- How long will it take the users to adapt to the web design?
What Type Of Projects Do UX Designers Undertake?
Over the years, the tech industry has grown exponentially; UX design has become more complex and varied. On that note, UX designers often work on different types of products, which may vary based on the context. Here is a list of a few projects that UX professionals work on these days:
1. Software Designs, Websites, And Apps
Nowadays, most people are well accustomed to internet connections and smart devices. Most of the time, UX designers try to improve the products and services, focusing on factors like page load times so that people face fewer challenges while using them. UX designers merge UI design with UX design to ensure that the apps on mobile devices run smoothly and effortlessly.
They also work on other projects such as dating and shopping apps, CRM software for web-based email clients, and many more.
2. Voice Design
Are you aware of the possibility of someone voice-searching your business? Voice user interfaces such as Amazon Alexa, Echo, and many more have become a part of our daily lifestyle since they help make our houses smarter and more efficient. UX designers are responsible for designing the voice for such interfaces and ensuring they are user-friendly and easily accessible to the end users.
The navigation option on Google Maps is a prime example of the voice user interface. This app provides the users with vocal assistance that helps them reach places faster while driving or walking.
3. Augmented Reality (AR) And Virtual Reality (VR)
With the rapid increase in augmented reality and virtual reality gaming, many UX designers have started working on projects where they develop an immersive experience for the users. One example of augmented reality is Pokemon Go, a popular game that kids and adults can enjoy.
However, AR and VR are relatively new; therefore, a lot of market research is required to make these types of projects successful. Besides, the UX designers must ensure that the latest technologies are compatible with the current user interface. If a device cannot support the immersive UI elements, the users might not feel satisfied with the product.
4. Service Design
Besides designing and developing tangible products, UX designers work on service designs that you can not measure physically.
A service design is an activity in which the UX designer organises and plans out the materials, infrastructure, and necessary logistics for a certain service. This design helps improve the customer’s overall interaction with the service provider.
For example, whenever first-class ticket holders visit an airport, they are given complete access to the lounge and first-class service provided by the staff.
Some people are even offered free food and beverages while they travel on the plane. These experiences are a part of the service design, carefully designed by a UX professional.
When Should You Use UX Design?
As mentioned earlier, UX design is complex and intricate, so you cannot use it in every situation. In this section, we have listed a few areas that help UX designs stand out the best.
1. Complex Systems
UX design is one of the best ways a company can simplify a complex system and provide a great website user experience to a large target audience. On that note, a complex system or website will require more UX research and planning before finalising the architecture.
Using a multi-user UX study to create a great user experience for a simple website will be unnecessarily resource-intensive. On the contrary, a UX design can greatly benefit eCommerce, advanced websites, and interactive web applications.
In addition, some systems incorporate many different user tasks, which might require excessive UX design to make the interaction easy.
2. Projects With Longer Time Frames
Projects with longer timelines tend to suffer a loss in the long run since they require more resources and money to complete them. However, hiring a UX designer can help to shorten the time frame.
This potentially saves money, resources, and time; therefore, the business can focus on more critical tasks.
Criticisms Of UX Design
Now that we have discussed the benefits of using UX design, we would like to point out a few drawbacks you should keep in mind.
1. Adds Complications And Financial Burden
Small agencies and startups require few resources to operate their traditional websites. As such, hiring a separate UX designer for each task can increase the overall financial burden.
Typically, a small firm hires one web designer to develop the user experience and other tasks, such as creating wireframes and a functional prototype. However, hiring multiple UX designers for a simple website will complicate the entire process and cause the company to lose more money.
2. Results Are Not Directly Measurable
When evaluating the effectiveness of a user experience UX designer, you might face many challenges since you can not measure it in quantitative terms. UX design is a subjective field. So, the user’s emotions cannot be measured in numbers.
You might need to use a few unconventional means if you want to measure the effectiveness of the design on your online presence. For instance, you can analyse the website’s performance in search engines or perform monthly surveys. Nevertheless, these add to the overall expenses, and much time gets wasted.
The Value Of UX Design
One of the most common misconceptions of UX design is that people assume it is “just a fad” or “a gimmick to attract an audience.” However, this isn’t the full truth since the true value of UX design on your bottom line is the immersive experience it gives the users. Apart from this, it is a tool that helps boost a business or brand.
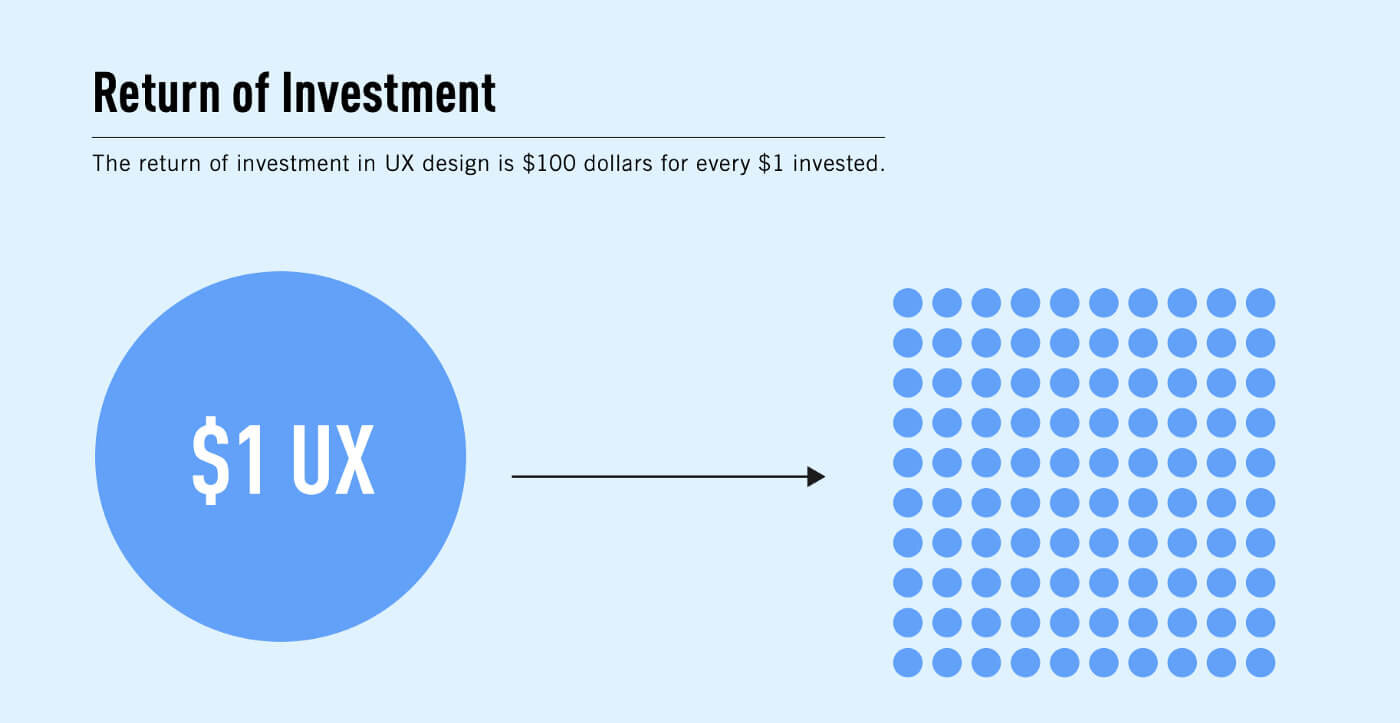
From the end user’s perspective, a reliable UX design will allow them to reach their daily goals with a good website user experience, saving them a lot of time. For instance, the alarm app on a mobile device lets the users set the alarm so they never miss out on important meetings and appointments.
In the same way, Facebook is another example that allows different users to connect with their friends all across the globe. UX designers use inclusive design, also known as universal design (UD), to bring out the best value for all kinds of users.
Universal Design (UD)
In simple terms, a universal design is a type of design that can be enjoyed by every single user, irrespective of their background. Additionally, the system or the interface isn’t limited to a specific ability, age, size or person. Therefore, anyone can use them and reap the system’s full benefits.

Nevertheless, universal design is a bit challenging since UX professionals need to follow a set of core UX principles. If the system lacks even one of these principles, it can not be considered a universal design. In total, seven key principles form the foundation of universal design, and they are as follows:
1. Equitable Use
According to this principle, a universal design must be useful and marketable to all types of consumers regardless of their abilities. Thus, the website should be designed so that even blind or deaf people can enjoy the interface.
At first glance, this might seem impossible, but there are ways of making an interface easily accessible for everyone. For instance, someone with a visual impairment uses a website to shop for certain grocery items. The designer can add voice navigation and AI assistance to help them navigate the website easily.
Similarly, deaf people can benefit from a design that provides plenty of visual illustrations while they use the website.
Guidelines:
- Offer all the end users a similar and identical interface whenever possible.
- Try to make the design appealing and interesting for every user
- Provide various essential features to the users, such as safety, privacy and security, so that they feel secure while accessing the interface
- Don’t stigmatise or segregate any user
- Give complete freedom to the users to access all the features and options in the system while ensuring adequate white space for readability
2. Flexibility In Use
Another important factor a designer should keep in mind is that it should accommodate different types of preferences and abilities of the consumers. Hence, no consumer should feel left out while trying a specific interface for the first time.
For instance, some food delivery apps allow users to choose between vegetarian and non-vegetarian dishes. By doing so, they can gather a larger audience for their app since everyone can enjoy their meal according to their preference.
The same logic applies to streaming apps that provide users with different types of movies and series content. People who prefer documentaries can simply access the documentary category of the app.
Guidelines:
- Offer the users different types of choices and methods to achieve their goals.
- Let the interface adapt to the user’s pace so that they feel less stressed while using it.
- The design should facilitate the user’s precision and accuracy
- It should be accessible to both right and left-handed users.
3. Simple And Intuitive
A universal design should be easy to understand regardless of the user’s abilities or prior experience. Therefore, they shouldn’t struggle while using the interface or system for the first time.
Other factors, such as language barrier and focus, should be considered while developing the main design.
For instance, some interfaces allow the users to pick a specific language option that allows them to feel comfortable using it. This doesn’t restrict them from using the different features since the options are available in their preferred language.
Guidelines:
- Provide the users with prompting and feedback options after they have completed the task.
- Arranging the information in a systematic and consistent order makes it easily accessible.
- Incorporate a wide range of languages and levels of literacy so no one feels left out.
- Avoid unwanted complexity procedures.
- The interface should be consistent with the user’s expectations.
4. Perceptible Information
UX designers must also ensure that the design communicates the necessary information to the users so that they can complete the task effortlessly. Besides, they should ensure that the users’ environment and sensory abilities don’t restrict them from enjoying the full experience.
For example, if a website tries to explain the various benefits and demerits of using a particular product, the designer can use different modes to communicate the information. Graphs or infographics are among the most efficient ways of presenting statistical data to end users. Similarly, pictorial messages can be used to communicate information to all types of age groups.
Guidelines:
- Make sure that the information is authentic and legitimate
- Provide adequate contrast between the surroundings and essential information
- Use different modes of communication such as verbal, graphs, pictorial and more
- Each element should be different from the others and easily recognisable.
5. Tolerance For Error
While designing an interface or a system, the designer must ensure that it minimises the scope of an accident or hazards that can cause end users discomfort. By doing so, the users feel safe, and they would feel like using the system regularly since it keeps them away from danger.
One prime example of this principle is educational software that prompts users whenever they choose the wrong step or option. This helps the user to choose the correct path and avoid the same mistake in the future.
Guidelines:
- Provides sufficient warning for errors and hazards while completing a task or goal
- Discourages the wrong and unconscious actions of the users to prevent them from repeating them
- Offers the user a fail-safe feature
- The UI elements are arranged with elements like visual cues that minimise errors and hazards during the process
6. Low Physical Effort
Nowadays, everyone looks for a simple and easy lifestyle since they want to avoid physical assertion on the body. A designer must ensure that the interface is extremely efficient and user-friendly. This allows the users to feel comfortable using the system and not feel tired while completing the process.
The automatic smart doors in malls exemplify this principle since the users don’t need the energy to open the doors. Additionally, smart LED bulbs and home appliances can be considered suitable candidates for this principle since consumers can operate them through voice commands and gestures.
Guidelines:
- The design should minimise sustained physical effort while completing the process.
- It shouldn’t repeat actions to the user as it can waste time and energy.
- Make sure to use reasonable operating forces.
- The interface should allow the users to maintain a neutral body position
7. Size And Shape For Approach And Use
Lastly, the design should offer the user appropriate shapes and sizes, which allows users to accomplish their tasks efficiently. Giving the users more options makes them feel empowered since they can adjust the path according to their preferences. For instance, an adjustable table is extremely convenient since you can adjust the title according to your preference.
Guidelines:
- The essential elements should have a clear line of sight, allowing users to find them easily.
- Offer variations in grip size.
- Adequate spacing must be provided for specific devices used for personal assistance.
- All the components should be comfortable and easy to use
UX Implementation For Your Website
With that, we have reached the end of this informative guide on UX design and how it can improve your business. Before signing off, we would like to share key points to help you decide when to use UX design for the website.
Firstly, UX design is one of the best ways to simplify a complex system or a complicated website. Business depends on the user’s interaction with the website, and UX design helps to make your website navigation easy and intuitive, thereby improving the user’s experience.
Secondly, we recommend not getting a UX designer if you have a small website design team, as they can complicate the whole process. UX designers are best suited for a larger team with multiple departments for different fields. In this way, they can contribute to a well-designed product without hampering the work of other teammates.
Are you looking for a user experience designer? Let the team at sitecentre® assist with your UX design process. We can help you build websites using user-centred design, implement human-centred design principles, perform usability testing, and interpret user testing data! Reach us at our email address today for more information.
We hope you enjoyed our guide on the user-centred design process. See you next time!